Published July 2023
Ethylene is primarily a petrochemically derived monomer used as a feedstock in the manufacture of plastics, fibers and other organic chemicals that are ultimately consumed in the packaging, transportation and construction industries, as well as many other industrial and consumer markets. Nondurable or consumable end uses—in particular, packaging— account for more than half of all ethylene derivative consumption worldwide. One particular plastic resin, polyethylene, accounts for most of the total ethylene consumption. Because ethylene is one of the largest-volume petrochemicals worldwide, with a diverse derivative portfolio (including nondurable and durable end uses), ethylene consumption is sensitive to both economic and energy cycles. Moreover, because of its size and broad usage, ethylene is often used as a benchmark for the performance of the entire petrochemical industry.
The following chart shows world consumption of ethylene:
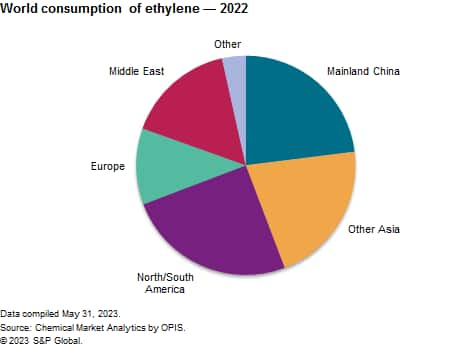
Most of the increased consumption over the last five years is from Northeast Asia, North America and the Middle East; within these three regions, ethylene derivative capacity has been developed to capitalize on superior ethylene costcompetitiveness (Middle East and North America) or to serve booming markets (Northeast Asia). Overall demand for ethylene derivatives is now fueled primarily by emerging economies and is projected to further grow in the near future. Since early 2020, markets have been consecutively hit by the COVID-19 pandemic and the fallouts of the Russian invasion of Ukraine. In 2021, despite the persistence of some shipping bottlenecks, markets benefited from a broad recovery across all major manufacturing sectors. The Russian invasion of Ukraine in early 2022 has nevertheless sent world energy markets into great turmoil, adding significant volatility to the world economy and a feedstock price uncertainty for the chemical industry
Polyethylene (HDPE, LDPE and LLDPE) is the major outlet for ethylene. The next-largest market is ethylene oxide (EO), used primarily to produce ethylene glycol (EG), which is used primarily in the production of PET (for polyester fibers, PET bottles and polyester film). The third-largest outlet is ethylene dichloride (EDC), which is used for the production of PVC. Other major ethylene uses include ethylbenzene, alpha-olefins and vinyl acetate. Overall, ethylene demand is exposed to the broader economy, underpinning diverse sectors. Some derivatives tend to be more cyclical as they are ultimately used to produce durables (EDC, EB, alpha-olefins and acetyls), while others (HDPE, LDPE, LLDPE, EO or linear alcohols) tend to be more resilient as they are used primarily in consumable products.
During 2022–27, global consumption of ethylene is forecast to further expand, driven primarily by growing needs of emerging markets. Polyethylene production will account for the largest share of new ethylene consumption, followed distantly by ethylene oxide and ethylene dichloride. Ultimately, ethylene demand will be driven primarily by the growth of polyethylene-based consumables; increasing PET fiber, bottle and packaging demand; and increasing requirements for PVC used in construction and pipe applications. Mainland China is projected to account for a large percentage of new ethylene demand expected through 2027; a growing middle class, improving living standards and fast-developing infrastructure is driving significant ethylene demand growth.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook - Ethylene is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key Benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Ethylene has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers, organizations and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence, expert insights into industry dynamics, trade and economics.
This report can help you:
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations and other factors on chemical profitability


















