Published July 2020
Thermoplastic copolyester elastomers (TPC) are a class of thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) that combine many of the properties of both thermoplastics and rubbers. TPCs are high-performance engineering materials with thermoplastic behavior and structural strength, but also exhibit elasticity and resistance to impact and flex fatigue. At low strains, they have a low hysteresis and behave like a perfect spring with ideal elasticity. In addition, these materials possess excellent resistance to oils and chemicals and have high service temperatures. TPCs have replaced other materials, such as metal and general rubbers, and will continue to do so, as well as replacing composites of rubber with metal, glass, and fabrics without reinforcement.
TPCs are used predominantly in automotive parts, hose and tubing, medical uses, and wire and cable.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of thermoplastic copolyester elastomers:
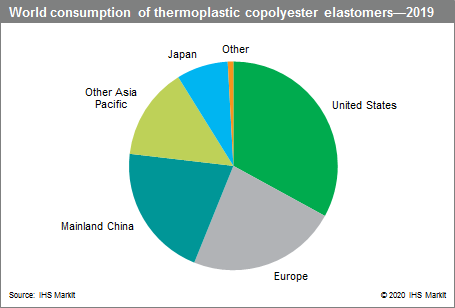
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Thermoplastic Copolyester Elastomers is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Thermoplastic Copolyester Elastomers has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade, and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations, and other factors on chemical profitability


















