Published June 2021
Chlorinated methanes include methyl chloride (CH3Cl), methylene chloride (CH2Cl2), chloroform (CHCl3), and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). Total global consumption of chlorinated methanes in 2020 is estimated at nearly 7.6 million metric tons. Consumption is forecast to grow at an average annual rate of 2.9% during 2020–25.
Chlorinated methanes find applications both as chemical feedstocks and are also used extensively for their excellent solvent properties in industrial and pharmaceutical processes.
The following table presents world consumption of chlorinated methanes by region:
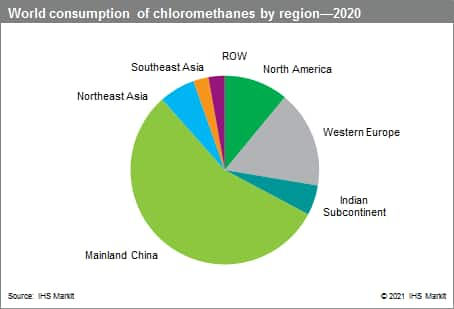
Growth in consumption will be driven primarily by mainland China, which accounts for 56% of global consumption of all chlorinated methanes. Demand for methyl chloride, chloroform, and carbon tetrachloride is primarily driven by demand for downstream chemical derivatives such as silicones, methyl cellulose ethers, and fluorocarbons. Methylene chloride is similarly seeing growth in demand for the manufacture of R-32, an effective low-cost fluorocarbon with relatively low global warming potential, but also has extensive uses as a solvent in pharmaceutical and chemical processing.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook –Chlorinated Methanes is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including

Key Benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook –Chlorinated Methanes has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers, organizations and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence, expert insights into industry dynamics, trade and economics.
This report can help you:
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations, and other factors on chemical profitability


















