Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Jan 31, 2022
Daily Global Market Summary - 31 January 2022
All major US and most APAC equity indices closed higher, while European markets were mixed. US and benchmark European government bonds closed lower. CDX-NA closed tighter across IG and high yield, iTraxx-Europe was flat, and iTraxx-Xover was slightly wider on the day. The US dollar closed lower, while natural gas, oil, gold, silver, and copper were higher on the day.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
- All major US equity indices closed sharply higher; Nasdaq +3.4%, Russell 2000 +3.1%, S&P 500 +1.9%, and DJIA +1.2%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +1bp/1.78% yield and 30yr bonds +4bps/2.11% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed -1bp/60bps and CDX-NAHY -5bps/339bps.
- DXY US dollar index closed -0.8%/96.54.
- Gold closed +0.5%/$1,796 per troy oz, silver +0.4%/$22.39 per troy oz, and copper +0.3%/$4.33 per pound.
- Crude oil closed +1.5%/$88.15 per barrel and natural gas closed +5.1%/$4.87 per mmbtu.
- Escalating tensions in Ukraine hit oil markets at a critical
juncture, after essentially a year and a half of stock draws that
have left storage thin, with recovery-born demand growth expected
by spring and the streaming of incremental OPEC and non-OPEC oil
yet to prove itself. Without firing a shot, armament along the
Ukrainian border raises risk of potential disruptions and along
with it, the price of oil. There is a rare $2/bbl premium at the
front of the Brent strip (expiring today), along with supersized
premiums over the next four months. While the range of possible
outcomes is wide, market risks can broadly be bracketed within
three distinct pathways in our view (IHS Markit Financial
Advisory's Roger
Diwan, Karim
Fawaz, Ian Stewart, and Sean Karst):
- Simmering tensions (Current base case price outlook). Tensions are contained but not resolved. There is no large-scale invasion of Ukraine. Yet modest progress on addressing core issues is limited, and relations between Russia and the West are frozen. An extended stand-off, even if unresolved, progressively allows market anxiety to eventually fade and prices to ease back into the sub-$85/bbl price range.
- Rupture - escalation. A Russian invasion of Ukraine triggers US sanctions on banking and energy sectors, and disruption of some trade flows pushes oil prices higher, though actual volumes lost on a sustained basis are relatively modest. Market anxieties are stoked, leading to a price spike above $100/bbl.
- Respite - de-escalation. Diplomatic efforts prove sufficient to push both sides to deescalate military presence along the Ukrainian border, even if falling short of resolving long-standing issues, easing oil's geopolitical risk premium and pushing prices swiftly back lower.
- Markets now currently find themselves straddled in no man's land somewhere between pathways simmering tensions and rupture - escalation, with escalating tensions showing little sign of reversal, although still falling short of material direct market impact.
- Private oil and gas explorer Maverick Natural Resources
announced January 28 it will acquire Permian producing properties
from ConocoPhillips for $440 million cash. The Houston-based
company said the assets span 144,500 net acres in the Permian in
the Texas counties of Andrews and Ector and the New Mexico counties
of Eddy and Lea. The assets produced more than 11,000 Boepd, of
which half was oil as of September 1 of last year and are largely
operated and held by production. (IHS Markit PointLogic's Annalisa
Kraft)
- The acquisition of the Central Basin Platform and Northwest Shelf assets has been approved by Maverick's Board of Directors and EIG Global Partners, its majority equity owner. The purchase will be paid for by a $500 million reserve-based loan funded by several banks including JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A.; Royal Bank of Canada; Citizens Bank, N.A.; KeyBank National Association; and KeyBanc Capital Markets Inc.
- The deal is expected to close in the second quarter of 2022 and has an effective date of September 1, 2021.
- Maverick CEO Chris Heinson remarked: "This Permian acquisition expands the scale of Maverick's operations and provides high quality, oil-weighted drilling inventory. The transaction highlights our portfolio focus in Texas and Oklahoma, which follows our recent divestitures of assets in California and Michigan.
- "Pro forma for the acquisition, Maverick's production exceeded 78,000 boepd in September 2021. We are conservatively financed with pro forma leverage of approximately 0.5x at closing and expected pro forma 2022 EBITDA of approximately $450 million. We expect to utilize our enhanced scale, operational track record, and conservative balance sheet to access capital markets for funding future acquisitions, Heinson continued.
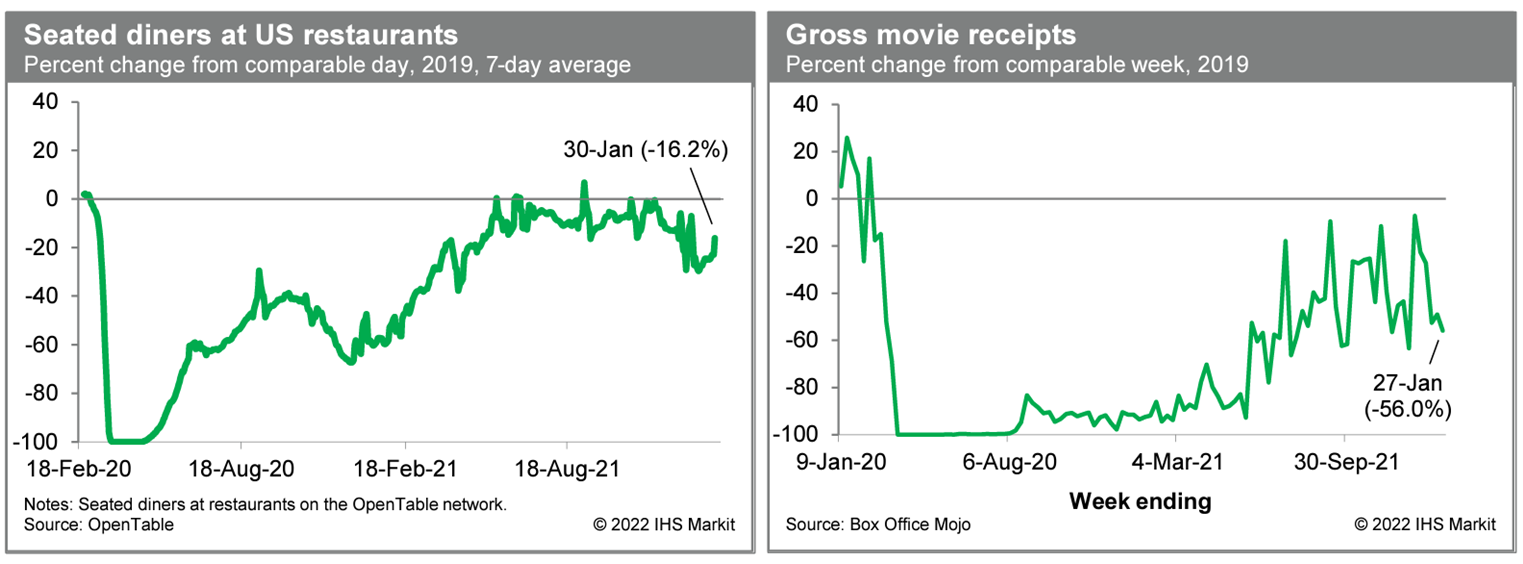
- Averaged over the last seven days, the count of US seated
diners on the OpenTable platform was 16.2% below the comparable
period in 2019. This was down materially from readings late last
year but up from lows reached a week or so ago. The rate of new
COVID-19 infections remains elevated but appears to have peaked. It
is possible that restaurant activity is mirroring this pattern.
Meanwhile, box-office revenues last week were 56.0% below the
comparable week in 2019, according to Box Office Mojo. This was
close to prior January readings and suggestive of ongoing weakness
in movie-theater activity. (IHS Markit Economists Ben
Herzon and Lawrence Nelson)
- As municipal bond investors evaluate modified behavior in the primary market, last week's calendar supplied $7.6 billion of new issue paper, with subdued investor activity noted over the course of the week given the heightened volatility across the market, resulting in wider spreads and higher costs of issuance for select issuers. The Brightline West Passenger Rail Project (Aaa/-/-) led last week's negotiated calendar, offering $894 million of economic development bank revenue bonds spanning across two series with a single 1/2023 maturity pricing at 0.85% or +30bps spread to the interpolated MAC. The Airport Commission of the City and County of San Francisco (A1/-/A+) also tapped into the negotiated arena to sell $538 million of revenue bonds spanning across two series with maturities ranging from 5/2024-05/2052, and cuts of 1-5bps noted across the scale. This week's calendar is slated to supply $9 billion of new issue deals spanning across 159 new issues with the Triborough Bridge and Tunnel Authority, NY (-/AA+/AA+/AA+) leading the negotiated calendar to provide $651 million payroll mobility tax bonds across 05/2034-05/2057; senior managed by Ramirez and selling on Thursday, 2 February. The Virginia Small Business Financing Authority (-/BBB-/BBB/-) will also tap into the negotiated market to offer $628 million of senior lien revenue refunding bonds with maturities spanning 1/2032-1/2048; senior managed by JP Morgan. This week's competitive calendar will span across 81 new issues for a total of $2 billion, led by The Commonwealth of Massachusetts (Aa1/AA/AA+) auctioning a combined total of $600 million general obligation bonds across 2/2028-2/2048, selling on Tuesday, 1 February. (IHS Markit Global Market Group's Matthew Gerstenfeld)
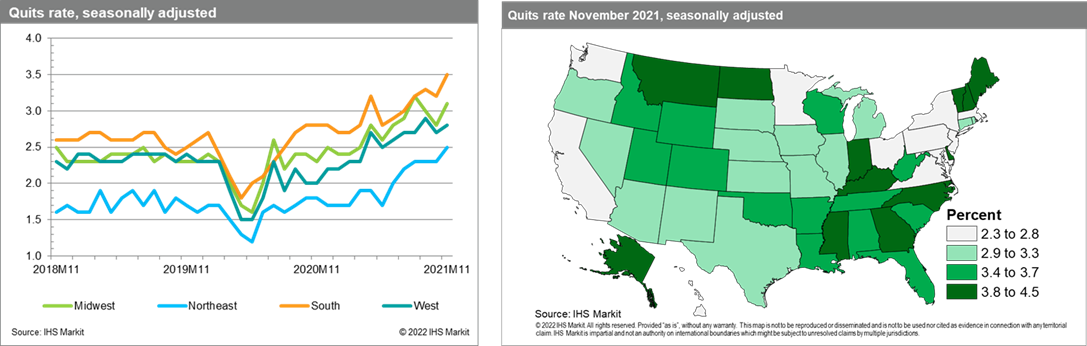
- The November data from the State Job Openings and Labor
Turnover Survey (JOLTS) revealed that the number of quits increased
in 22 states, with 19 states reaching a new series high, mostly in
the South and Northeast. The quits rate grew the most in the South
and Midwest, each adding 0.3 percentage point, to reach 3.5% and
3.1%, respectively. Except for Texas and South Carolina, every
state in the South faced a rise in quits, causing the region to
surpass its prior series peak from September. Georgia, Florida, and
North Carolina led the region in quits during November. The rise in
Florida's quits likely came from leisure and hospitality services,
which accounts for a significant share of the state's employment.
This sector was responsible for most of the month's total quits at
the US level (sector detail is not available for states). (IHS
Markit Economist Alexander Minelli)
- Ultium Cells LLC, the joint venture (JV) between General Motors (GM) and LG Energy Solutions, has expanded its agreement with Li-Cycle on recycling battery-material scrap created during battery-cell manufacturing to include lithium-ion battery recycling. The agreement will involve the construction of Li-Cycle's sixth and largest lithium-ion battery recycling facility, which is to be located at the Ultium Cells plant in Warren, Ohio (United States). Ultium Cells will construct a new building and Li-Cycle will install and operate its proprietary technology and equipment. Li-Cycle says this will provide on-site conversion of battery manufacturing scrap to intermediate products and operations are due to begin in early 2023. The facility's design is to be optimized for the particular types of battery manufactured at the Ultium Cells plant. Li-Cycle says that eventually the facility will have the capacity to process up to 15,000 tons of battery manufacturing scrap and battery materials per year. The company says this will mean its global capacity will reach 55,000 tons of lithium-ion battery input per year. Li-Cycle says the Ohio facility, which it calls a Spoke, will produce 'black mass', which it says is a powder-like substance consisting of a number of highly valuable materials, including lithium, cobalt, and nickel. This black mass will be converted into battery grade materials at Li-Cycle's Hub facility in Rochester, New York, also due to be operational in 2023. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
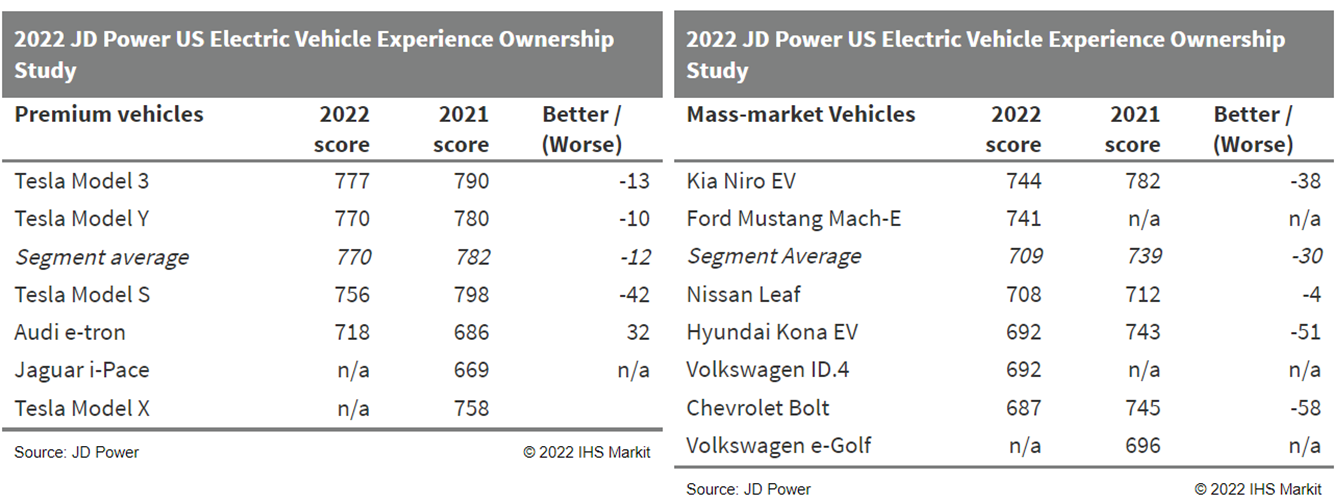
- JD Power has released its second annual Electric Vehicle
Experience (EVX) Ownership Study, which shows satisfaction with
their vehicles is high among first-time owners of EVs, including
BEVs and PHEVs. The study provides rankings of 11 EVs in premium
and mass-market segments. The EVX ownership survey measures
consumer satisfaction and is based on customer feedback. JD Power
carries out a number of annual surveys of owners' responses to
their products, which may be used to assess the direction of change
of product scores. The EV market is expanding and understanding
consumer satisfaction and problem issues may help product
development in the industry. JD Power says that first-time EV
owners are reporting a positive experience with their vehicles,
although the segment average satisfaction scores in this year's
study declined compared with the 2021 study. (IHS Markit
AutoIntelligence's Stephanie
Brinley)
- Tesla CEO Elon Musk has stated that the company has stopped working on a new-entry level model which would have been the firm's cheapest car with a price point of around USD25,000, according to an Automotive News Europe (ANE) report. The car would have been produced at the company's new German factory. However, at the fourth-quarter earnings call last week Musk announced that work on the model had stopped. He said, "We are not currently working on a USD25,000 car. At some point we will. But we have enough on our plate right now -- too much on our plate frankly," Musk's comments show that Tesla is currently having to make big strategic decisions about managing its expansion and allocating resources in the most efficient way to underpin the company's growth. Tesla is struggling to meet demand for its current entry-level cars, the Model 3 and the Model Y, and it appears that the management team has decided it makes no sense at this time to work on and introduce an even cheaper car. Musk explained to analysts and journalists the earnings call that instead of introducing any new models this year that the company would its efforts this year on increasing production at its plant in existing plants in California and China and beginning production at its new factories in Austin (Texas, US) and Grünheide (Germany). The car, which was going to be called the Model 2, was to be Tesla's cheapest car with a price point equivalent to USD25,000. However, the company has decided it is not the most efficient use of capital at this point. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- BYD has announced its Type A zero-emission school bus for the US market, including vehicle-to-grid charging capability. According to a BYD press statement, the vehicle can serve as a power source when not transporting students. It can seat up to 30 people and be equipped with an Americans with Disabilities Act liftgate capable of lifting 800 pounds, and range of up to 140 miles on a single charge. Stella Li, president of BYD North America, is quoted as saying, "This is a timely solution: BYD's Type A battery electric school bus is designed to be there for school districts 24 hours a day, both as a vehicle and power storage resource. The BYD combination of top-notch safety features, innovative design and reliable performance makes this a practical and highly affordable zero-emission solution." The bus has a high-strength steel construction body, electronic stability control, and electronic braking. It has a lithium phosphate battery, available with either a 150kW DC or a 19.2 kw single-phase AC charging solution. The bus will be available in lengths of 26.7 feet, 24.5 feet or 22.9 feet, and BYD says it is perfect for routes with fewer students or transporting those with disabilities. For the driver, there are comfort seats, a 16.5-inch power steering wheel and telescopic steering column, high level of visibility, and easy to reach control switches. The Type A is a smaller counterpart to the Type D that BYD offers in the US; the Type D is available as a 36-, 38.5- or 40.5-foot-long school bus, with range of 155 miles; it can seat up to 185 passengers plus the driver. BYD operates an assembly facility in Lancaster (California, US) and has been making slow and steady progress globally with electric buses. IHS Markit forecasts that BYD's US sales will reach 700 units in 2024 largely through the addition of new school buses, expected to make up about 75% of its US sales. Although BYD is a Chinese company, it is one of the few companies producing electric school buses in the US at a time when federal, state and local governments are looking to explore a transition to electric vehicles (EVs), including bus solutions. BYD is also working with Nuro to produce an autonomous delivery vehicle for that company. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- The US processor John San Filippo & Sons reported that its
Q2 FY2022 (25 June 2021-24 June 2022) sales rose by 8% y/y $253.2
million. The increase in net sales was attributable to a 6.0%
increase in sales volume. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural
Commodities'
Jose Gutierrez)
- Sales volume in the consumer distribution channel accounted for 75.4% of total sales volume in the current second quarter. Sales volume increased 27.1% in the commercial ingredient distribution channel mainly due to a 42.7% increase in sales volume to foodservice customers.
- Gross profit margin, as a percentage of net sales, decreased by two points y/y to 20.6% in Q2 FY2022.
- The total value of inventories on hand at the end of the second quarter of fiscal 2022 increased by 15% to $178.7 million due to higher commodity acquisition costs for almost all tree nuts, peanuts, dried fruit and other raw materials, which were partially offset by lower on-hand quantities of in-shell pecans and cashews.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- Major European equity markets closed mixed; Germany +1.0%, Italy +0.9%, France +0.5%, and UK/Spain flat.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed lower; Italy +2bps, Spain +3bps, France +5bps, and Germany/UK +6bps.
- iTraxx-Europe closed flat/59bps and iTraxx-Xover +2bps/288bps
- Brent crude closed +0.8%/$89.26 per barrel.
- UK food and beverage merger and acquisitions (M&A) market
activity in 2021 was at its highest since 2010, the latest UK Food
and Beverage Sector M&A report from Oghma Partners shows. The
UK F&B market continued its strong performance into the last
four months of the year (T3 2021) with total deal volume amounting
to 29 transactions. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities'
Julian
Gale)
- Compared with 2020, total deal volume for the year was up 50.8% to 89 transactions. The total deal value for T3 2021 was estimated at £722.1 million ($967.5 million). This boosted the 2021 annual deal value to an estimated £6.6 billion, which is the largest annual deal value recorded by Oghma Partners since 2010.
- The appetite from financial investors remained strong throughout 2021. In volume terms they accounted for 20.7% of total deal activity compared with 20.3% in 2020.
- When comparing deal activity from financial buyers in value terms there was a significant increase in both absolute value (2021: c. £2.6 billion versus 2020: c. £380.0 million) and the proportion of total deal value (2021: 39.3% vs 2020: 25.5%). "Driving this activity is the relative defensiveness of the sector's cashflows combined with loose monetary policy which has led to an inflow of funds into private equity companies as well as a low cost of debt," Oghma Partners observed.
- In addition, overseas buyers had another active year, accounting for 39.1% of total deal volume. This was the highest percentage of non-UK corporate buyers involved in UK food and beverage deals since 2010.
- In 2021, there was a wave of activity in the plant-based food and beverage M&A space. Notable activity during the period included Portuguese conglomerate, Sonae, acquiring Gosh Food, the UK producer of vegan sausages, burgers and falafels (EV: £67.0 million; EV/EBITDA: 16.1x).
- In addition, Canadian dairy giant, Saputo, acquired the dairy alternative cheese producer, Bute Island Foods for an undisclosed amount, "although market rumors suggest this was for yet another punchy valuation for a plant-based company," Oghma Partners noted.
- The firm suggested that whilst buyer demand for plant-based food and beverage companies remains high and so do valuations, the 2021 sell off in Oatly shares (IPO in May 2021 ) and Beyond Meat (IPO May 2019) following disappointing revenue numbers could impact valuations in the sector moving forward.
- Another subsector within the UK food and beverage industry that was particularly active was Direct-to-Consumer (D2C). Big food companies were keen to expand into this area as was seen with Nestle's acquisition of SimplyCook (advised by Oghma Partners - financial terms of the deal undisclosed). This deal followed on from its acquisition of the healthy meal kit provider, Mindful Chef at the end of 2020. Further activity in the space included Italian pasta giant, Barilla, acquiring a majority stake in D2C meal kit start-up Pasta Evangelists, an acquisition that represents a new step in Barilla's international growth strategy.
- The trading environment in 2022 is expected to be more challenging. "Cost pressures are appearing in most directions whether that be labor, energy, raw material or distribution costs," Oghma Partners observed. "The next 12 months will be a further test of the business models of many companies. Weaker businesses that struggle to get pricing through and/or reduce costs will find the prospect of a business exit more testing under these conditions."
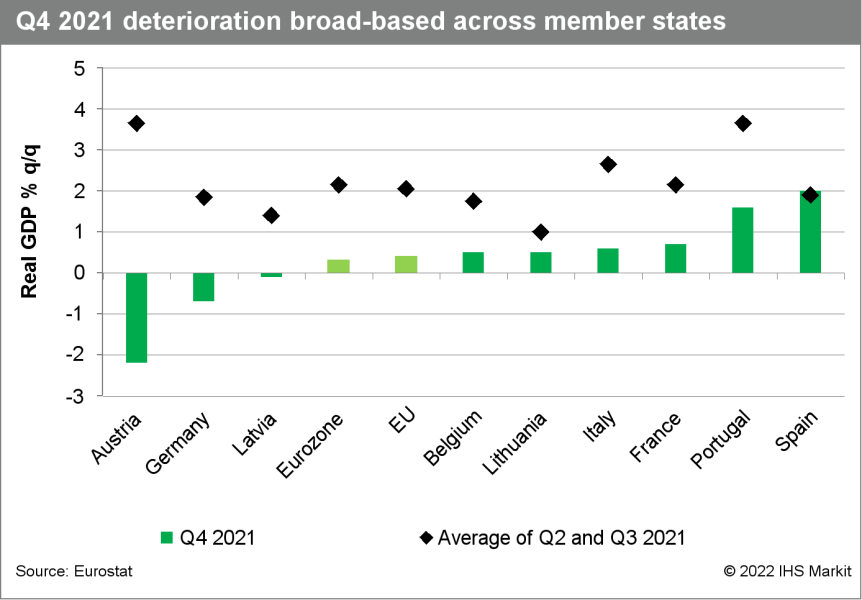
- According to Eurostat's initial preliminary 'flash' estimate,
eurozone real GDP rose by 0.3% quarter on quarter (q/q) in the
fourth quarter of 2021, below the initial market consensus
expectation of 0.6% q/q (according to Reuters's initial survey) and
IHS Markit's January baseline forecast of 0.5% q/q. Following the
release of national data at the end of last week, the market
consensus expectation for eurozone real GDP growth was revised down
from 0.6% to 0.3%. (IHS Markit Economist Ken
Wattret)
- Eurozone real GDP has now returned to its pre-pandemic level of the fourth quarter of 2019. By way of comparison, in the United States there was a net increase of just over 3% over the equivalent period.
- The fourth-quarter-2021 modest increase in eurozone GDP follows back-to-back 2%-plus q/q increases in the second and third quarters of 2021, fueled primarily by surging private consumption as COVID-19 containment measures were eased and demand rebounded strongly. In addition to the fading of that effect, the combination of supply chain problems, deteriorating COVID-19 trends, and soaring energy prices weighed heavily on eurozone economic activity in late 2021.
- Across the eurozone member states that have published data for the fourth quarter of 2021 to date, there were marked variations in performance, although virtually across the board there were marked deteriorations compared with the prior two quarters.
- Austria (-2.2%) and Germany (-0.7%) suffered large but likely
short-term contractions, related to COVID-19 developments. In
contrast, France (0.7%) and Spain (2.0%) experienced sizeable
upward surprises on their q/q growth rates, although both are
likely to deteriorate in the first quarter of 2022, again partly
for COVID-19-related reasons.
- Germany's Federal Statistical Office (FSO) has reported, based
on data from various regional states, that the country's national
(CPI) increased by 0.4% month on month (m/m) in January. This means
that the annual inflation rate has declined only moderately from
the December 2021 5.3% year on year (y/y) rate to 4.9% y/y. Most of
the dampening effects related to the unwinding of the VAT factor (a
temporary cut in second-half 2020) and the introduction of the CO2
tax in January 2021 are being offset by January's additional spike
of energy prices - driven by electricity and gas - that has boosted
total CPI inflation by about a percentage point on its own. (IHS
Markit Economist Timo
Klein)
- Contrary to initial expectations, the annual rate of the EU-harmonised CPI measure softened only modestly more than its national counterpart, as the weighting scheme based on last year's consumer spending pattern mostly remained similar to that of 2020 instead of moving much closer to pre-pandemic conditions. January's monthly increase at 0.9% m/m thus was much higher than that of the national measure, and only the even larger base effect provided for a more pronounced softening of the annual rate from 5.7% in December 2021 to 5.1% in January.
- The detailed breakdown of the German national data will only be published with the final numbers on 11 February, but components are available, for instance, from the largest and most populous state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW). CPI in this state posted 0.7% m/m, allowing its y/y rate to slip only marginally from the December 2021 5.2% to 5.1%. Note that there are huge divergences between states this time, ranging from 0.1% m/m to 0.8% m/m.
- In NRW, energy prices increased massively by 9.7% m/m, which has little to do with fuel (2.7%) but much more with electricity (17.1%) and natural gas (15.5%). The annual comparison for overall energy prices has increased from the December 2021 16.7% to 21.5%. The only other components exerting upward pressure were package tours (from 11.8% to 17.1% y/y) and alcohol/tobacco (from 4.1% to 4.5%). Elsewhere, the dampening VAT effect was particularly visible for clothing/shoes (from 5.4% to -2.1% y/y), furniture/household goods (from 4.3% to 3.3%), healthcare (from 1.6% to 0.9%), food (from 6.3% to 5.4%), and "miscellaneous goods and services (from 3.5% to 2.1%).
- Bosch and Marelli have both announced job cuts relating to cuts in diesel engine production at their Italian operations, according to a Bloomberg report. Bosch announced last week that it would cut 700 jobs at its plant in Bari over the next five years, which equates to 40% of the total headcount, according to a statement by the FIM-CISL union. Marelli announced that it would make 550 voluntary redundancies from its management tiers. Marelli said that this plan would be carried out by June, with its private equity fund owner KKR & Co looking to cut costs "in light of the car industry's particularly adverse conditions." It cited the need to cut costs "in light of the car industry's particularly adverse conditions." (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- Ride-hailing firm Bolt is planning to add more cities to its existing markets of operation across Africa, although it has not named them. To achieve this, the company will hire an additional 200,000 drivers in Africa this year. Paddy Partridge, Bolt's Africa regional director, said, "One of the challenges we have with our growth at the moment is that on the ride-hailing side, the demand for our services is growing faster than we're able to onboard drivers, particularly in West and Southern Africa. We're just not able to continue keeping up with that growth because drivers are not able to access vehicles at an affordable rate", reports TechCrunch. Currently, Bolt has more than 700,000 drivers serving about 40 million riders across its existing seven markets in Africa. The company is also planning to enter at least two new markets within the north and west Africa regions by the end of this year. Last year, MAX partnered with Bolt in a lease-to-own plan that will enable 10,000 drivers under the platform in Nigeria to acquire energy-efficient vehicles. Bolt, which has 75 million customers in 45 countries, sees Africa as one of its main targets for expansion. Recently, Bolt has raised EUR628 million (USD709 million) in a new round of funding co-led by Sequoia Capital and Fidelity Management and Research Company. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Mozambique's upstream oil and gas regulator, the National Petroleum Institute (Instituto Nacional de Petróleo, INP), has unveiled the country's sixth upstream licensing round, its first since the protracted fifth round that extended from 2014 to 2018. The sixth round opened for pre-qualification in November 2021, with roadshows scheduled from February 2022 and pre-qualified companies to be announced by the end of March. The deadline for bids is end-August 2022, with awards to be announced end-November. The round is offering 16 offshore blocks covering more than 92,000 sq km across the Rovuma, Angoche, and Save Basins and the Zambezi Delta. Minimum state participation via national oil company (NOC) Empresa Nacional de Hidrocarbonetos (ENH) is 20%, except for the high-potential Angoche Basin block A6-C, where it is 40%. The launch of the sixth round has been delayed since 2019, initially because of setbacks in preparing the related data packages, and then from early 2020 by disruption and market turmoil caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. Preparations for the sixth round were probably also set back by the protracted finalization of awards from the fifth round; contract awards were announced in 2015 but were only finalized in the second half of 2018 following numerous legislative and fiscal changes intended to address foreign investor concerns about tax rates, foreign exchange rules, and mandatory listing on the local stock exchange. As a result, an updated model exploration and production concession contract (EPCC) was issued in 2016 to underpin the awards (see Mozambique: 3 August 2018: Investor pressure drives further Mozambican E&P contract changes as licenses near finalization). The delays resulted in Equinor and Delonex withdrawing from the awards process, with Equinor citing the unfavorable business environment. Ultimately, contracts were finalized with Eni, ExxonMobil, and Sasol. First drilling by ExxonMobil and Eni is expected later this year in their frontier Angoche Basin blocks, seven years after the initial awards. (IHS Markit E&P Terms and Above-Ground Risk's Roderick Bruce)
Asia-Pacific
- Most major APAC equity indices closed higher; India +1.4%, Hong Kong +1.1%, Japan +1.1%, and Australia -0.2%.
- AutoX has expanded its robotaxis' operational area to over 1,000 square km in Shenzhen, which it claims to be the largest in China. The area includes narrow and congested streets and highways as well as a fully driverless area of 168 square km, reports Gasgoo. Last year, AutoX launched a fully autonomous robotaxi pilot program for the public in Shenzhen. In 2020, California's Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) issued a permit to the company to allow it to test its autonomous vehicles (AVs) without a human back-up driver. AutoX claims that its AV platform, AutoX Driver, can handle the densest and most dynamic traffic conditions in cities around the world. It has reportedly launched its robotaxi production facility, representing China's first Level 4 robotaxi production line. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
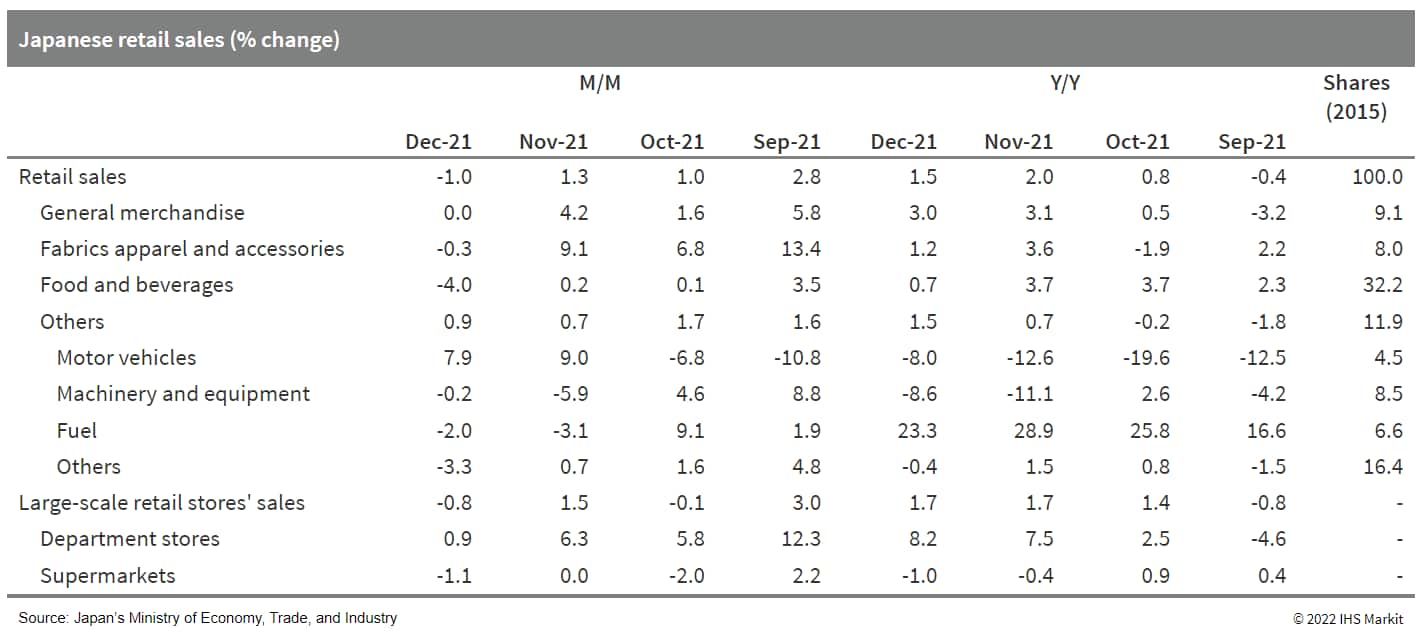
- Japan's retail sales fell by 1.0% month on month (m/m) on a
seasonally adjusted basis in December 2021 following three
consecutive months of increase. Despite the month-on-month
weakness, annual growth for 2021 turned positive, moving up by 1.9%
following a 3.2% drop in 2020. The month-on-month decline largely
reflected a 4.0% m/m decrease in sales of food and beverages and
continued declines in sales of machinery and equipment and fuel.
The weakness was partially offset by a 7.9 m/m increase in sales of
motor vehicles, reflecting improved auto production. (IHS Markit
Economist Harumi
Taguchi)
- The CCI fell by 2.4 points to 36.7 in January. While all component indices declined, the 4.8-point drop (to 36.7) in the employment index probably reflects concerns about the rapid spread of the Omicron variant and negative impacts from the expansion of the quasi-state of emergency in the country. Households' outlooks for higher prices a year ahead also weighed on the overall livelihood index, which moved down by 1.8 points to 36.8.
- The continued uptrend for department store and convenience
store sales reflects the resumption of operations, in line with low
daily infection cases. However, the weaker-than-expected December
results on retail sales were due, in part, to higher prices of food
and energy. Retail sales are likely to weaken over the near term
under the quasi-state of emergency, which covers about 80% of
prefectures.
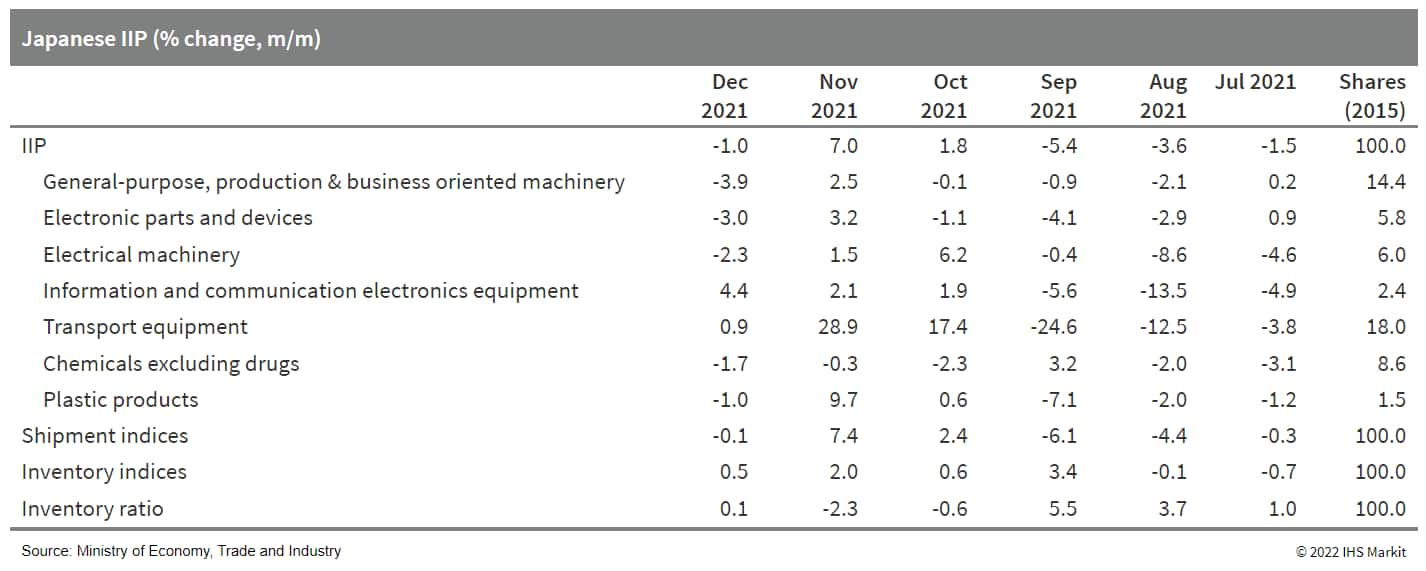
- Japan's industrial production (IIP) fell by 1.0% month on month
(m/m) in December 2021 but annual growth for 2021 moved up by 5.8%
for the first increase in three years. Manufacturers' shipments
also decreased marginally (by 0.1% m/m) and inventories continued
to rise (0.5% m/m), which led the uptrend for the index of
inventory ratio to continue with a 0.1% m/m rise. (IHS Markit
Economist Harumi
Taguchi)
- The weakness of industrial production reflected declines in production of general-purpose, production, and business-oriented machinery, transport equipment (excluding autos), electronic parts and devices, and other industry groupings. Those declines were due partially to softening after solid rises in a broad range of industry groupings in the previous month. However, the first m/m drop in three months also reflected shortages of parts and container supply-chain congestion.
- Although broader industry groupings recorded declines in
manufacturers' shipments than for industrial production, the
weakness was largely offset by increases in shipments of autos,
electronic parts and devices, and information and communication
electronics equipment.
- New vehicle sales in Thailand declined by 12.6% year on year (y/y) during December 2021 to 91,010 units, compared with 104,089 units in December 2020, according to data released by Toyota Motor Thailand, the official compiler of automotive data in the country. Passenger vehicle sales declined by 16.3% y/y during the month to 31,917 units, while commercial vehicle (CV) sales decreased by 10.4% y/y to 59,093 units. It is important to note that the monthly data do not include passenger vehicles sold by BMW and Mercedes-Benz, or CVs sold by some Chinese and European manufacturers. IHS Markit expects light-vehicle sales in Thailand to grow by 4.7% y/y in 2022 to around 768,600 units, while light-vehicle production is expected to grow by 1.1% y/y this year to about 1.66 million units. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- Indonesia's one-month coal-export ban, which had been gradually
relaxed following objections by the governments of Indonesia's
major coal importer countries including Japan, South Korea, and the
Philippines, is ending on 31 January. However, Indonesia on 27
January introduced for the first time a new policy on palm oil,
requiring producers to set aside a proportion of their production
for the domestic market. (IHS Markit Country Risk's Anton
Alifandi)
- Indonesia's competing policy goals on coal and palm oil increase the likelihood of export restrictions at times of high international prices. Coal and palm oil are major foreign-exchange earners for Indonesia; the country is the world's largest exporter of both commodities. However, the government also aims to ensure low domestic prices for energy and cooking oil. Since 2009, the government has imposed a domestic market obligation (DMO) policy that requires coal exporters to set aside a proportion of the production, currently 20%, to the Indonesian market at prices capped by the government. An increase in international prices in 2021 led to the government suspending 34 companies from exporting their coal in August 2021 for not meeting their DMOs.
- More broadly, the government's prioritization of higher added value industrial policy is likely to lead to further restrictions in the export of nickel products. President Joko "Jokowi" Widodo has continued the policy of his predecessor, Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono (2004-14). In 2009, Indonesia passed a mining law that banned the export of raw minerals within five years of its approval. The policy has had its biggest impact on nickel, a mineral Indonesia holds the world's largest reserve deposit of. The nickel-ore export ban was first implemented in January 2014 and led to mostly Chinese companies' investment towards processing nickel ore into ferronickel and nickel pig iron, which are key inputs for stainless steel production, as part of their stainless steel plants in Indonesia.
- The government's aims of positioning Indonesia in the global electric vehicle (EV) supply chain means that it is likely to limit the construction of new nickel processing for stainless steel, in favor of higher value EV battery production in a three-year outlook. A nickel processing plant, whose output can be used to produce battery cathodes for EV batteries, began production in October 2021, with two more under construction. Furthermore, two South Korean companies, LG and Hyundai, began construction of their EV battery plants in West Java in September 2021, while Hyundai's electric car plant on the outskirts of Jakarta is scheduled to begin production later in 2022.
- Indonesia is likely to continue to use its mining commodities to support its industrial policy after President Jokowi's term ends in 2024. The policy to seek greater control of Indonesia's natural resources enjoys broad support among political parties and voters. It is also rooted in the country's Constitution. Jokowi in his speeches over the past two months has stated his intention to ban the export of bauxite, tin, and copper from 2022. The 2020 Mining Law, which updates the 2009 Mining Law, stipulates that the export of raw minerals will be prohibited three years after its passage, by June 2023.
- Philippines' real GDP jumped 7.7% year on year (y/y) in the
fourth quarter of 2021, accelerating from a revised 6.9% y/y
increase in the third quarter. It also represented the third
consecutive quarter of expansion after resuming growth in the
second quarter. For 2021 as a whole, the economy gained 5.6%,
reversing a sharp 9.6% contraction posted in 2020. (IHS Markit
Economist Ling-Wei
Chung)
- In seasonally adjusted quarter on quarter (q/q) terms, the economy expanded 3.1% from the previous quarter during the fourth quarter, similar to the rate recorded in the third quarter.
- The recovery in domestic demand continued to provide the main impetus to the economy during the final quarter. Domestic demand contributed 9.2 percentage points to fourth quarter growth as household consumption contributed 5.7 percentage points and gross investment (including fixed investment and inventory) added 2.6 percentage points. In addition, government spending contributed 1 percentage point, after adding 2 percentage points in the third quarter.
- On the other hand, the contribution from net exports remained negative for the third consecutive quarter. Supported by recovering domestic demand, imports continued to expand at a double-digit pace, outpacing export growth amid slower overseas demand. Net exports subtracted 2.5 percentage points from the fourth-quarter expansion, following the subtraction of 2.1 percentage points in the third quarter.
- Gross investment spending climbed 12.6% y/y in the fourth quarter, albeit slowing from a 20.8% y/y surge in the third quarter. Within that, fixed investment expanded 9.5% y/y in the fourth quarter, decelerating from a 15.5% y/y jump in the third quarter.
- It was led by a 15% y/y expansion in construction investment during the fourth quarter, as the government sped up the implementation of the Build, Build, Build infrastructure program. Public construction spending jumped 25.6% y/y during the fourth quarter, although it decelerated from a 55.3% y/y surge in the third quarter.
- Concurrently, construction investment by private sectors
increased 9.3% y/y in the fourth quarter, decelerating from a 12.7%
y/y expansion in the third quarter. Investment on durable equipment
also moderated in the fourth quarter, rising just 2.7% y/y, after
increasing 6.6% y/y in the third quarter.

S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-31-january-2022.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-31-january-2022.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+31+January+2022+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-31-january-2022.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 31 January 2022 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-31-january-2022.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+31+January+2022+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-31-january-2022.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




