Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Jul 14, 2020
Daily Global Market Summary - 14 July 2020
US equity markets closed higher today, while most European and APAC indices were lower. iTraxx IG and high yield indices closed slighter wider, while CDX-NAIG was flat and CDX-NAHY slightly tighter. Q2 earnings season kicked-off today with the three largest US banks increasing loss provisions another $28 billion and signaling expectations that the pandemic will have a more severe economic impact than originally anticipated.
Americas
- US equity markets closed higher on the day and near the highs of the trading session; DJIA +2.1%, Russell 2000 +1.8%, S&P 500 +1.3%, and Nasdaq +0.9%.
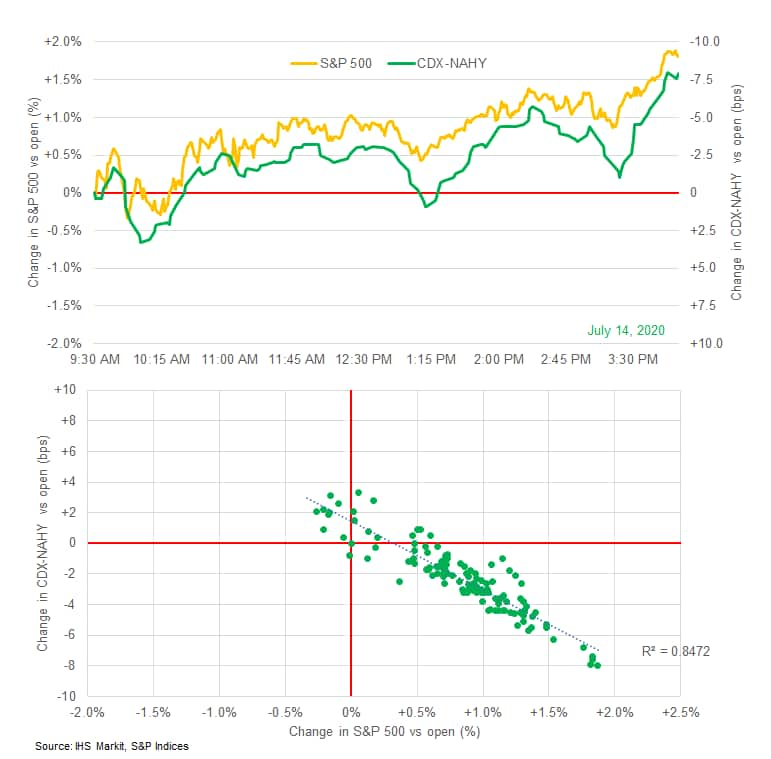
- The charts below compare today's S&P 500 and CDX-NAHY
intraday changes versus the open (note the change in CDX-NAHY axis
is in reverse order). The top chart shows the intraday trends and
indicates that CDX-NAHY widened at a faster rate during the three
main bouts of selling in the S&P. The bottom chart is a scatter
plot of the change in S&P versus the change in CDX-NAHY spread
and indicates that today's R2 was 0.8472.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +1bp/0.63% yield.
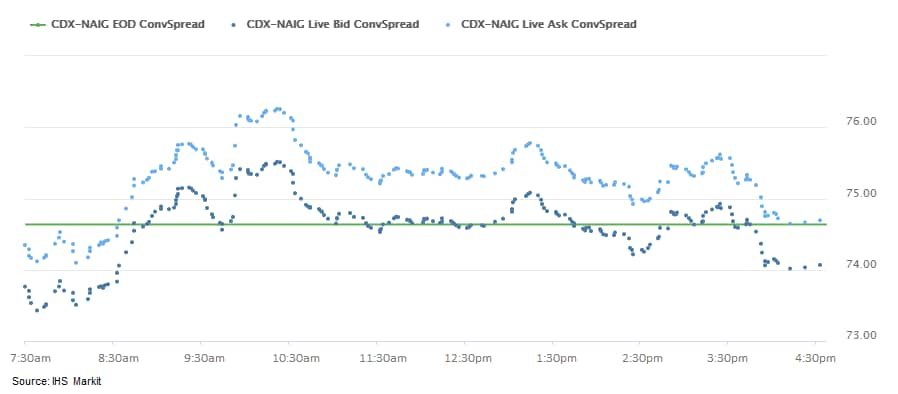
- CDX-NAIG closed flat/74bps and CDX-NAHY -2bps/505bps. CDX-NAIG
was wider for most of the day, but tightened in on the rally in
equities that began at 3:20pm EST.
- Crude oil closed +0.5%/$40.29 per barrel.
- Three of America's biggest banks have set aside a combined $28 billion for current and future loan losses, pushing Wells Fargo to a quarterly loss and hitting profits at JPMorgan Chase and Citigroup as lenders count the cost of the coronavirus crisis. Executives at the three banks stressed that while consumers had largely continued to pay their loans as normal, the outlook was hard to forecast because of uncertainty around the pandemic and the impact of propping up US wages and debt markets. (FT)
- The US consumer price index (CPI) rose 0.6% in June, largely
reflecting a 5.1% increase in energy prices. The food CPI rose
0.6%. The core CPI rose 0.2%, after three consecutive monthly
declines. (IHS Markit Economists Ken Matheny and Juan Turcios)
- The 12-month change in the core CPI remained at 1.2%, matching the lowest reading since March 2011. The 12-month change was 2.4% as recently as February. Despite prices generally firming in June, inflation pressures remain muted.
- Prices in sectors where COVID-19-related disruptions had greatly reduced demand moderately firmed in June (following declines in prior months), as economic activity resumed. The CPI for apparel (1.7%), motor vehicle insurance (5.1%), and airline fares (2.6%) all contributed to the rise in the core CPI. The recent rise in infections could renew downward inflation pressures in these sectors.
- The CPI for gasoline rose 12.3% in June, after declining since the beginning of the year. Gasoline prices are down 23.4% from a year earlier.
- General Motors (GM) has cut a shift temporarily at its Wentzville plant in Missouri, United States, over COVID-19 pandemic-related absenteeism, media reports state. According to the reports, the cutting of the shift is in reaction to absenteeism by employees concerned about coming to work. The company has not reported the presence of the virus at the facility. The shift cut will reportedly affect about 1,270 employees. A GM spokesperson reportedly said, "We believe in the short term, a two-shift operating plan will allow us to operate as efficiently as possible and accommodate team members who are not reporting to work due to concerns about COVID-19 in the local community... People on our team should not be concerned about coming to work. GM Wentzville is following multi-layered safety protocols that are working very well to keep people safe by reducing the possibility that COVID-19 can enter the plant and preventing any spread within the plant." Reportedly, GM is still assessing the specific number of employees to be cut and seniority will be a factor when making its decision. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Tests commissioned by the Environmental Working Group (EWG) detected trace amounts of glyphosate in more than 80% of non-organic hummus and chickpea samples, a finding the organization says supports its call for EPA to rein in use of the herbicide and tighten food tolerances. EWG tested a wide range of hummus and chickpeas purchased online or from major retailers in the Washington, D.C., New York City and San Francisco metropolitan areas. Only one sample exceeded - or even came close - to EPA's tolerance level of 5 parts per million (ppm) for glyphosate in chickpeas, but the EWG contends the agency's safety level is inadequate and has set its own health-based benchmark of 0.16 ppm. EWG tested 27 conventional hummus samples and found nearly one-third exceeded its benchmark based on a 60-gram serving, which equals about four tablespoons. The levels found ranged from 0.008 - 2.38 ppm. Overall 10 hummus samples exceeded EWG's standard, including products made by Sabra, Cava, Harris Teeter and Whole Foods. EWG stressed that Americans should not stop eating hummus, chickpeas or beans because of its findings, but contends the sampling regime backs its call for a ban on all pre-harvest uses of glyphosate - the herbicide is often sprayed on beans and grains as a drying agent before the crops are harvested. EWG is also lobbying for stricter EPA tolerances and increased testing by FDA of foods for glyphosate residues. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Policy's JR Pegg)
- PTTGC (Bangkok) says it is moving forward with its much-delayed Ohio petrochemical project without its partner, Daelim Chemical USA (DCA). Toasaporn Boonyapipat, PTTGC America (PTTGCA) president and CEO, says, "The Ohio petrochemical facility continues to be a top priority for PTTGC America. We are in the process of seeking a new partner whilst working toward a final investment decision [FID]. We look forward to making an announcement by the end of this year or early next year on this transformative project for the Ohio Valley Region." The project would be based on an ethane cracker designed to produce 1.5 million metric tons/year of ethylene using ethane from the Marcellus and Utica shale deposits. The downstream configuration is yet to be decided, especially in view of DAC's withdrawal. Original plans revolved around different configurations, including for the entire ethylene output being used to make the equivalent volume of high-density and linear low-density polyethylene, or some of the ethylene used to make ethylene glycol. Most of the output would be sold on the US market.
- PTTGC has spent about $200 million on site preparation and engineering studies. Bechtel was selected last year as the engineering, procurement, and construction contractor on the project, for which initial costs were estimated at $5-6 billion. The complex would be located on the 500-acre site of a former coal-fired power plant. The site is owned by PTTGC.
- Ecuador announced on 6 July that it has reached a preliminary
debt-restructuring agreement with its largest group of bondholders
involving high-profile investors including Ashmore, BlackRock,
BlueBay, and Wellington. (IHS Markit Economists Claudia Wehbe,
Carlos Caicedo, and Ailsa Bryce)
- The preliminary agreement would restructure Ecuador's debt, lowering its average cost and extending its duration, easing the country's short-term payment obligations significantly. If completed - the initial deadline for acceptance is 15 August - Ecuador's debt profile would be extended from an average life of 6.1 to 12.7 years with 10 issues maturing between 2022 and 2030 being restructured into three new issues maturing in 2030, 2035, and 2040.
- Despite the positive start, several investors have rejected the initial proposals, making further negotiations necessary. Less positively, on 10 July, an investor group of 25 institutional investors including funds such as Amundi, Grantham, and T Rowe Price, together with an ad-hoc group of holders of 2024 bonds, called on Ecuador to improve the terms of the offer.
- Economic recession, strong public resistance to austerity, and the upcoming election (2021) will make it very difficult for Ecuador to achieve fiscal sustainability after 2021.
- Stimulus packages and the Reactívate Ecuador program seek to support small and medium-sized businesses, but a second COVID-19-virus wave could threaten these efforts.
Europe/Middle East/ Africa
- Most European equity markets closed lower except for UK +0.1%, France/Spain -1.0%, Germany -0.8%, and Italy -0.6%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed higher across the region; UK/Spain -4bps and Germany/Italy/France -3bps.
- iTraxx-Europe closed +1bp/62bps and iTraxx-Xover +6bps/374bps.
- Brent crude +0.4%/$42.90 per barrel.
- In line with the indications from member states' data already
released, eurozone industrial production rebounded markedly in May,
rising by 12.4% m/m. As this followed back-to-back double-digit
declines, however, the rebound came from a very low base and
production is still 18.9% below its February pre-pandemic level.
(IHS Markit Economist Ken Wattret)
- Measured on a three-month on three-month basis, industrial production fell by 19.1% in May, by far the biggest contraction on record. To put this fall into perspective, at the height of the global financial crisis, the biggest decline was only around half the size (-9.3% in March 2009).
- May's rebound was broad-based across types of production, although in all the main sectors, levels of production remain well below where they were in February (see first chart below).
- Production of consumer durables, for example, which includes autos, jumped by more than 54% m/m in May. However, given the huge magnitude of the prior declines in March and April, production remained almost 25% below February's level.
- Production of capital goods showed a similar pattern, rebounding by over 25% m/m in May but again with the level of production still around 24% below where it was in February. Non-durable consumer goods, including food, continued its outperformance, falling by a net 12% between February and May.
- The European Central Bank's (ECB)'s quarterly bank lending
survey (BLS) for the second quarter was compiled between 5 and 23
June, with 144 banks polled across the member states. As in the
first quarter, the standout feature of the second quarter's survey
is the divergence of credit standards and loan demand between
enterprises and households. (IHS Markit Economist Ken Wattret)
- Credit standards for loans to enterprises again tightened only marginally in the second quarter (the net percentage of banks tightened at +1% versus +4% in the first quarter). This remains very different from the experience during the global financial crisis (GFC) and subsequent eurozone crisis, when the net percentages peaked at around 60% and 30%, respectively (see first chart below).
- Loan demand from enterprises surged again in the second quarter's survey. The net percentage of banks reporting an increase had already jumped to +26% in the first quarter and soared to +62 in the second quarter, a record high for the survey (data go back to 2003). The surge reflects firms' emergency liquidity needs following the lockdowns of large parts of the economy.
- Demand was again much higher for short-term loans (net percentage +60%) than long-term loans (+11%) in the second quarter. Financing needs for inventories and working capital rocketed, whereas financing needs for fixed investment declined.
- The second quarter's BLS data for household loans paints a very different picture. Demand for housing loans plunged (net percentage -61% versus +12% in the first quarter), as did demand for consumer credit and other lending (net percentage -76% versus -4% in the first quarter).
- The collapse in housing loan demand was mainly caused by lower consumer confidence in the context of the COVID-19 virus pandemic and, to a lesser extent, worsened housing market prospects.
- For consumer credit, a range of factors contributed to the decline in demand, especially lower consumer confidence and decreased spending on durable goods, in line with precautionary savings and low spending possibilities during the strict lockdown period, as well as uncertainty over employment prospects.
- Credit standards for households too diverged from the data for enterprises. For loans to households for house purchase, there was another marked tightening in the second quarter (net percentage +22% versus +9% in the first quarter), as well as for consumer credit and other lending (+26% versus +10% in the first quarter). The deterioration of the economic outlook, a worsening of households' creditworthiness, and lower risk tolerance were the key drivers.
- Across the larger eurozone member states, loan demand from enterprises was exceptionally strong in the second quarter, particularly in France (+97) and Italy (+90). The opposite was evident regarding demand for housing loans, with weakness across the board. Data for Spain (-100) and France (-91) were exceptionally weak.
- Significant changes are expected in the third quarter's data compared with the prior two surveys. The second quarter's expectations data suggest that net demand for loans to firms will fall back markedly in the third quarter of 2020 (net percentage at +11%).
- The UK's Office for National Statistics (ONS) reports that the
economy grew by 1.9% month on month (m/m) in May but was preceded
by m/m falls of 6.9% in March and 20.4% in April. (IHS Markit
Economist Raj Badiani)
- The ONS reports that "manufacturing and house building showed signs of recovery in May as some businesses saw staff return to work" but "most of the economy was in the doldrums".
- In annual terms, the economy in May was 24.1% smaller compared with a year earlier.
- Therefore, the economy contracted by 19.1% in the three months to May compared with the previous three months.
- The service sector, which accounts for 80% of the UK's GDP, shrunk by 18.1% over the same three-month period. The weakest sectors were wholesale, retail, and motor trades; accommodation and food services; and education
- Industrial production tumbled in the three months to May, falling by 15.5%, with declines occurring across 12 out of 13 manufacturing sub-sectors. The weakest sector was the manufacture of transport equipment, which fell by 47.5%. The only sector to post output growth was the manufacture of basic pharmaceuticals.
- Construction output was hit by the imposition of the anti-contagion measures, resulting in a very sharp drop in the three months to May (down by 29.8%).
- Retail sales (including fuel sales) in volume terms increased by 12.0% m/m in May, but sales were still 13.1% below the February level prior to the COVID-19 virus-related lockdown.
- New car registrations fell by 34.9% y/y in June after falls of around 90% y/y in both April and May.
- London Electric Vehicle Company (LEVC) has announced full details of the production VN5 light commercial vehicle (LCV). According to a statement, the vehicle, based on the automaker's TX taxi, features the same underpinnings, frontal appearance and driver cockpit. However, it gains a 5.5-cubic-metre load capacity that can accommodate two Euro sized pallets and can carry 830kg. Access is achieved through a 60:40 split door in the rear, or a large sliding door in the side through which a pallet can also be loaded. It also uses the same plug-in range extender powertrain technology as the TX, which enables a zero-emission range of 58 miles, and over 300 miles of range mixed with the gasoline (petrol) engine under WLTP. Charging can be undertaken via 50kW DC rapid charging or 11kW AC fast charging. Three VN5 variants will be available from launch - Business, City and Ultima - all of which will feature autonomous emergency braking, front and side driver and passenger airbags, cruise control, nine-inch touchscreen and dual zone climate control as standard. Six option packs will be offered including a Comfort pack featuring luxury driver and passenger seats, satellite navigation, under-seat storage and a heated windscreen, while the Safety pack comes with road sign information system, speed limit intelligent function, lane departure warning, and curtain airbags. First deliveries of right-hand drive variants will begin in the fourth quarter of 2020, and left-hand drive models will be available from March 2021. Despite the COVID-19 virus pandemic halting production at its Antsy (UK) facility for around two months, LEVC is continuing with plans to broaden its line-up before the end of the year. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- The Italian government is said to be planning to allocate EUR1 billion to support measures for the Italian passenger car market. Sources have told Reuters that it would come as part of a stimulus package worth EUR20 billion. One person, who asked not to be named because of the sensitivity of the matter, said, "Slightly less than EUR1 billion would be used to strengthen current incentives to encourage sales of state-of-the-art combustion engine cars as well as electric and hybrid vehicles." (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- According to all measures, the Swedish headline consumer price
inflation rebounded strongly in June. The consumer price index
(CPI), which is the national definition, came in at 0.7% year on
year (y/y), up from -0.4% in April and 0.0% in May. According to
the EU-harmonized measure (HICP), inflation was 0.9% y/y, up from
-0.2% in April and 0.1% in May. (IHS Markit Economist Daniel Kral)
- CPI at fixed interest rates (CPIF), which is the most closely watched indicator by the central bank, also jumped to 0.7% y/y in June, which is almost 0.3 pp above the Riksbank's latest forecast from 1 July. CPIF excluding energy came in at 1.3% y/y, slightly higher than in May and 0.2 pp above the Riksbank's latest forecast (see Chart 2).
- On a monthly basis, CPIF rose by 0.6%. The main contribution to the monthly rate came from the price increases in transport, which added 0.4 pp to the rate, and higher prices for the operation of personal transport equipment and car hire, which added 0.2 pp. Higher prices for electricity contributed 0.2 pp.
- In June, 2.7% of the prices in the basket were estimated owing to the absence of transactions data. This is down from 2.9% in May.
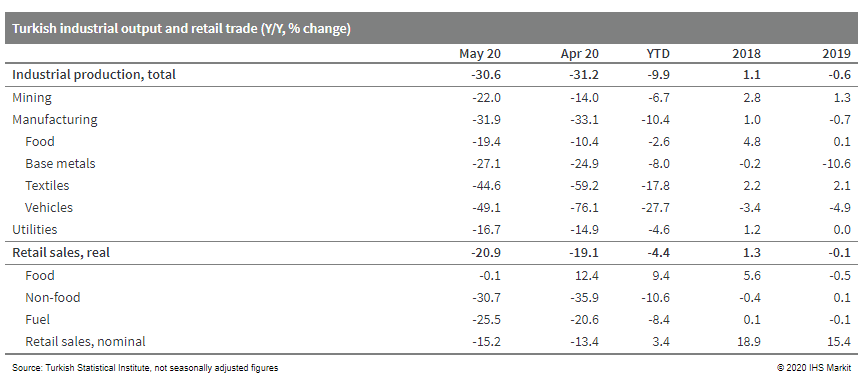
- After plunging in March and April, Turkish industrial
production and retail trade activity rebounded in May. For both
sets of indicators, however, the May recovery was insufficient to
correct for the huge losses in previous months, leaving total
activity well below pre-pandemic levels. (IHS Markit Economist
Andrew Birch)
- In seasonally and calendar-adjusted data, industrial output jumped by 17.4% month-on-month (m/m) in May. However, total production that month remained 24.6% below the production registered in February.
- Similarly, retail trade volume picked up by 3.8% m/m in May, as social distancing rules were relaxed. Nevertheless, the total volume of retail trade activity was still 23.4% below what it had been in February.
- The pandemic continued to decimate Turkish labor markets as of
April, with total employment plunging by 9.2% year-on-year. The
official jobless rate continued to ebb downward to 12.8% as of
April 2020, due to plunging labor participation. In April, the
labor participation rate was 47.2%, 5.7 percentage points lower
than it had been a year earlier.
- Turkey's brief experience with current-account surpluses in
2019 is now firmly over, with the country registering the sixth
consecutive month of a substantial current-account deficit in May
2020. In all, the country's current-account gap ballooned to more
than USD16.7 billion in January-May 2020. (IHS Markit Economist
Andrew Birch)
- To date, most of the year-on-year (y/y) deterioration of the current-account deficit is a result of a more than USD11.5-billion y/y widening of the merchandise trade deficit.
- As the summer tourism season dawns, a dramatic drop-off in the service surplus is increasingly contributing to the worsening of the headline current-account balance. Tourism service exports are a crucial contributor to the country's external financial balance. In the face of the COVID-19 pandemic, these service exports will remain depressed throughout the third quarter, when the bulk of these earnings traditionally occur.
- For the third consecutive month, Turkey registered a huge net outflow of portfolio investment in May. Increasingly active administrative controls over the banking sector and in the conducting of the foreign exchange trade are driving foreign portfolio investors away from Turkey. Negative real interest rates further discourage the inflow of foreign capital.
- Additionally, the net inflow of foreign direct investment (FDI) has fallen to negligible levels in recent months. Although a drop-off is expected given the pandemic, the increased government activity in the economy is further discouraging FDI inflows. The 12-month cumulative total of net FDI inflows - for years extremely steady even in the face of domestic uncertainty - ebbed from nearly USD10 billion as of May 2019 to just over USD5 billion as of May 2020.
- In order to support the lira in the face of significant capital outflows, the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey (TCMB) has drawn down its foreign currency reserves. To rebuild those reserves, the TCMB has engaged in forward swaps with state-owned commercial banks.
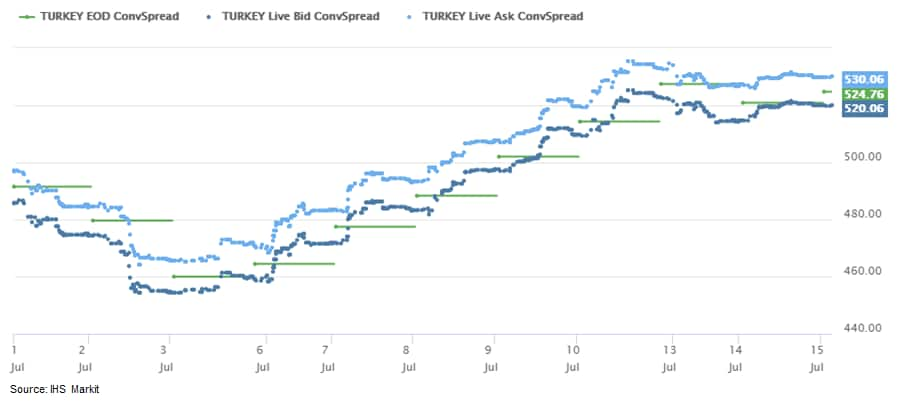
- Turkey's 5yr CDS spreads closed at +4bps/525bps today and are
+34bps month-to-date:
- Kazakhstan's current account started the year on a strong note,
achieving a surplus of USD2.0 billion in the first quarter,
according to preliminary data from the National Bank of Kazakhstan
(NBK). This result marks significant strengthening compared to the
year-ago deficit of USD125 million and the shortfall of USD1.9
billion registered in the fourth quarter of 2019. (IHS Markit
Economist Venla Sipilä)
- The goods trade surplus, in particular, widened by some 13% year on year (y/y), with exports rising by 4.2% y/y and imports contracting by 3.2% y/y. Meanwhile, the services trade deficit somewhat narrowed as both exports and imports contracted.
- The deficit on the primary income account dwindled by 25% y/y. This was mainly the result of falling outflows of FDI-related investment outflows.
- Net inflows of FDI more than halved y/y, totaling USD1.1 billion. However, supported by negative outflows, the overall net FDI position proved somewhat stronger, at USD1.4 billion.
- Gross external debt at the end of the first quarter stood at USD152.7 billion, having eased by 2.6% during the first three months of the year. General government debt accounted for 7.5% of the total, after retreating by some 8% from the beginning of the year.
- The Kazakh current account in early 2020 is holding up well, but deterioration is likely in the coming quarters. The oil price dramatically fell in March, and the price of Brent crude oil in the second quarter averaged USD28.83 per barrel (pb) after averaging USD50.02 pb in the first quarter.
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed lower across the region; India -1.8%, Hong Kong -1.1%, Japan -0.9%, China -0.8%, Australia -0.6%, and South Korea -0.1%.
- The June total social financing rise was largely due to a
continuous increase in medium- and long-term loans; growth is
likely to moderate in the second half as the economy recovers and
the central bank tries to control financial risk. (IHS Markit
Economist Yating Xu)
- China's new aggregate financing, the widest measure of net new financing to the real economy, increased by CNY3.43 trillion in June 2020, up by CNY240 billion from the previous month, according to a release by the People's Bank of China.
- Stock total social financing (TSF) increased by 12.8% year on year (y/y), 0.3 percentage point up from May.
- Bank loans increased by CNY1.81 trillion in June and loans injected to the real economy increased by CNY1.9 trillion.
- Household loans registered the largest monthly increase since the beginning of this year as new short-term loans rose, with recovery in private consumption and a booming real-estate market continuing to boost medium- and long-term term loans.
- Acceleration in infrastructure investment led new corporate medium- and long-term loans to rise by 95.8% y/y, following 96.5% y/y and a 110.2% y/y expansion in April and May, respectively, while receipt financing declined further.
- Off-balance-sheet financing, including entrusted loans, trust loans, and undiscounted bankers' acceptance, increased by CNY85.3 billion in June, compared with a CNY212.3-billion decline a year ago.
- Government bond financing rose as CNY210 billion worth of special national bonds were issued in June.
- Broad money supply (M2) growth remained at 11.1% y/y for a third consecutive month with the expansion in credit and financing, while M1 growth fell because of a high-base effect.
- Fiscal deposit declined by more than CNY110 billion compared with the same period last year, reflecting the acceleration of fiscal stimulus. Meanwhile, household deposits continued to rise.
- TSF increased by CNY20.8 trillion in the first half of the year, with new bank loans reaching a historic record of CNY12.1 trillion.
- Fast expansion of corporate loans and bond issuance is likely to moderate in the second half, while overall liquidity and credit will remain relatively able to support economic recovery.
- Consumption recovery in Hainan is expected to continue
benefiting from the favorable policy, especially as pandemic
disruptions have been driving more tourists to substitute outbound
travels with domestic options. This could also spur more investment
especially in Hainan's retail sector. (IHS Markit Economist Lei Yi)
- Effective 1 July, annual duty-free shopping quota in Hainan has been tripled from CNY30,000 to CNY100,000, as the nation steps up support for local tourism sector as part of the Hainan free-trade port development plan.
- Up to 65,000 shoppers made duty-free purchases of CNY450 million (USD64 million) in Hainan during the first week (1-7 July) after the duty-free shopping quota expansion came into effect, according to the General Administration of Customs. Daily tax exemption averaged CNY9.39 million during this period, up by 58.2% from that of the first half.
- By product, cosmetics, jewelry, and watches ranked top three in terms of duty-free sales revenue and together accounted for 77.2% of the total. In particular, cosmetics took up 51.3% of overall sales thanks to its price advantage. By region, shoppers from Zhejiang, Shanghai, and Jiangsu spent most on duty-free products, with spending per visitor ranging from CNY9,002 to CNY10,130.
- South Korean OEMs - Hyundai, Kia, General Motors (GM) Korea,
Renault Samsung, and SsangYong - have reported a 10.8% year-on-year
(y/y) fall in their combined domestic output to 297,019 units
during June, reports Yonhap News Agency, citing data released by
the South Korean Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy. (IHS
Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- Vehicle exports from the country also declined during the month by around 37.4% y/y to 132,514 units.
- The report highlights that shipments to North America declined by 25.3% y/y in June, while vehicle exports to the European Union fell by 13.3% y/y and to Asian countries by 42.0% y/y.
- Hyundai, South Korea's biggest automaker, experienced a 40.0% y/y decline in exports last month, while its affiliate Kia's overseas shipments shrank by 22.6% y/y.
- Exports by Renault Samsung and SsangYong nosedived 94.7% y/y and 77.6% y/y, respectively.
- Outbound shipments by GM Korea also plunged by 43.2% y/y during the month. During the first half of 2020, South Korean OEMs have reported a 19.8% y/y drop in their combined domestic output to 1.63 million units.
- Vehicle exports from the country during the period fell by around 33.4% y/y to 826,710 units, and the total value of overseas shipments fell by 27.3% y/y to USD15.76 billion.
- Sales of new vehicles in Pakistan fell by nearly 50% year on
year (y/y) in June because of challenges created by the
COVID-19-virus outbreak, according to data released by the Pakistan
Automotive Manufacturers Association (PAMA). (IHS Markit
AutoIntelligence's Isha Sharma)
- Volumes totaled 9,020 units last month, down from 17,973 units in June 2019.
- Passenger car volumes slumped to 7,325 units, down by 50.4% y/y.
- Sales of trucks and buses were down by 35.2% y/y to 267 units, while sales of jeeps and pick-ups were down by 62.5% y/y to 242 units and by 44.8% y/y to 1,186 units, respectively.
- The Suzuki Alto led the passenger car market with sales of 1,656 units last month, closely followed by the Toyota Yaris with sales of 1,160 units.
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-14-july-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-14-july-2020.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+14+July+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-14-july-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 14 July 2020 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-14-july-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+14+July+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-14-july-2020.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




