Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Apr 23, 2021
Daily Global Market Summary - 23 April 2021
All major US equity indices closed higher, APAC was mixed, and most European markets were lower. US government bonds closed lower and benchmark European government bonds were mixed. European iTraxx was close to unchanged on the day, while CDX-NA was tighter across IG and high yield. The US dollar, gold, silver and natural gas closed lower, while oil and copper were higher.
Americas
1. All major US equity indices closed higher; Russell 2000 +2.0%, Nasdaq +1.4%, S&P 500 +1.1%, and DJIA +0.7%.
2. 10yr US govt bonds closed +2bps/1.56% yield and 30yr bonds +1bp/2.24% yield.
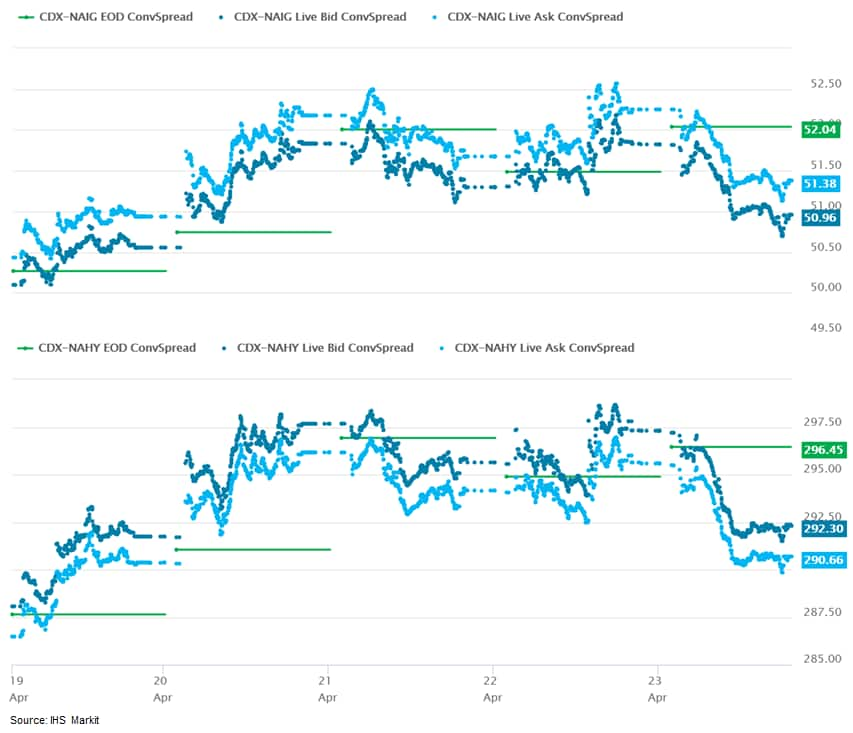
3. CDX-NAIG closed -1bp/51bps and CDX-NAHY -5bps/291bps, which is +1bp and +4bps week-over-week, respectively.
4. DXY US dollar index closed -0.5%/90.86.
5. Gold closed -0.2%/$1,778 per troy oz, silver -0.4%/$26.08 per troy oz, and copper +1.5%/$4.34 per pound.
6. Crude oil closed +1.2%/$62.14 per barrel and natural gas closed -0.7%/$2.73 per mmbtu.
7. Adjusted for seasonal factors, the IHS Markit Flash U.S. Composite PMI Output Index posted 62.2 in April, up from 59.7 in March, to reach the highest since data collection began in October 2009. (IHS Markit Economist Siân Jones)
a. New order growth accelerated again in April, with firms
noting the strongest upturn on record. The reopening of large
portions of the economy following an easing in lockdown measures
led to firmer client demand.
b. Unprecedented supply chain disruptions pushed input costs higher
once again in April. That said, the rate of inflation eased
slightly amid softer increases among service providers.
8. US new home sales rose 20.7% in March (±23.7%) to a seasonally
adjusted annual rate of 1,021,000. This update completes the
preliminary data for the first quarter of 2021. Following a 5.1%
decline in the fourth quarter of last year, new home sales rose
3.8% to a 959,000-unit seasonally adjusted annual rate. Relative to
the prior quarter, sales rose in the Northeast, Midwest, and South,
but fell in the West. (IHS Markit Economists David Deull and
Patrick Newport)
a. Sales figures for December through February were collectively
revised up by a sizable 163,000. (Note: About one-fourth of new
home sales—homes sold before a permit is issued—are
imputed. Imputed sales account for most of the data revisions to
new home sales.)
b. The three-month average—959,000 units—had edged down
since last September, when it peaked at 974,000 units. Even before
the March jump, this figure was elevated compared with pre-pandemic
levels. (Note: The three-month and quarterly estimates are more
reliable than monthly estimates because averaging reduces
statistical noise.)
c. As of the March estimate, the median sales price for new
single-family homes has fallen by more than 4% for two straight
months. At $331,000 in March, it was down from $365,000 in
December. However, the first quarter's median price remained 5.1%
higher than a year earlier, a pace of change also matched by the
average (mean) price.
d. The Census Bureau's monthly construction cost index was up 7.1%
from a year earlier in the first quarter, cutting deep into
builders' profit margins.
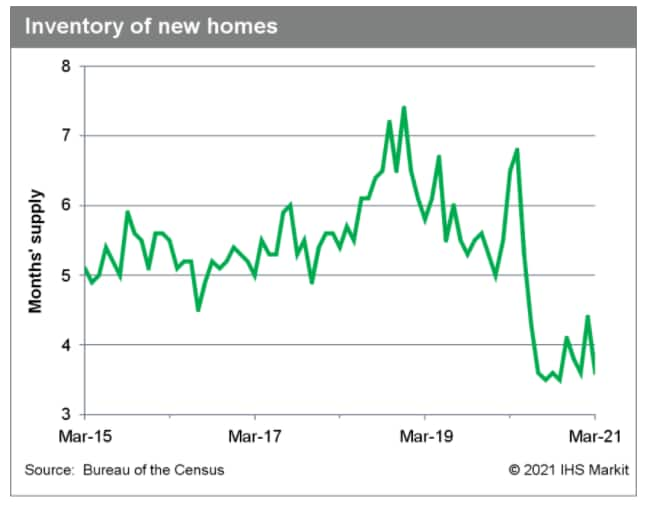
e. Inventory is lean. Some 307,000 new homes were up for sale in
March, matching February but down from 330,000 in March 2020. The
months' supply, at 3.6, was near the lowest ever recorded (3.5)
which was seen twice in the second half of 2020. For the quarter,
the average of 305,000 was a step down from the 327,000 recorded in
the first quarter of 2020.
9. US President Joe Biden, speaking at a global climate summit,
committed the US to significant emissions reduction by 2030, while
his administration outlined plans for USD15 billion in EV charging
infrastructure investment. Separately, US Republicans proposed an
alternative infrastructure investment plan. Overall, the
announcements on 22 April, timed to co-ordinate with Earth Day, did
not provide specific details on expected automakers' activity or
targets for the industry. However, the comments continue the Biden
administration's focus on climate change and supporting the
fledgling demand for EVs. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie
Brinley)
10. The construction of the largest industrial offshore wind facility dedicated to the production of monopiles in the United States is underway at Paulsboro Marine Terminal in Gloucester County, New Jersey. The construction work, partly funded by the state of New Jersey with a USD250 million investment announced in December 2020, will be completed under a Project Labor Agreement with the South Jersey Building Trades Council. Construction works, led by European foundation specialist EEW, include the clearing and grading of the 70-acre site, the construction of two buildings to house circumferential welding, sand-blasting, and painting stations, and the strengthening of the quayside to be able to support 2,500 metric ton monopiles. The establishment of the facility is supported by the Ocean Wind project, and project owners Orsted and PSEG. Once completed, the monopile facility will produce around 92 monopiles to support the 1,100 MW offshore wind farm project, and possibly other upcoming projects too. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Melvin Leong)
11. U S companies Vertex Pharmaceuticals and Obsidian Therapeutics have jointly announced that they have entered into a research and licensing collaboration for the discovery of novel therapies that regulate gene editing for the treatment of serious diseases. The collaboration will use Obsidian's patented cytoDRiVE technology to discover gene-editing medicines whose therapeutic activity can be precisely controlled using small molecules, while Vertex will rely on its scientific and clinical capabilities in small molecule, cell, and genetic therapies to help expedite development. Under the terms of the deal, Vertex will pay Obsidian up to USD75 million in upfront payments and research milestones, including an equity investment in Obsidian. Obsidian is eligible to receive up to USD1.3 billion in potential payments based upon the successful achievement of specified research, development, regulatory, and commercial milestones across up to five potential programs. (IHS Markit Life Sciences' Milena Izmirlieva)
12. The MIEA published by Brazil's central bank, the Banco Central do Brasil (BCB), expanded by 1.7% in February compared with January month on month (m/m); this follows another strong performance in January when the MIEA gained 1.3% m/m. These comparisons are based on seasonally adjusted data. If sustained, monthly growth rates above 1% would yield growth of more than 12% in the full year. (IHS Markit Economist Rafael Amiel)
a. Using unadjusted data, the MIEA grew by 1.0% in February 2021
compared with February 2020, year on year (y/y), and was down by
0.5% y/y. These growth rates reflect more accurately the situation
of the Brazilian economy, i.e., that it is returning to
pre-coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-virus pandemic levels, but
the speed of growth is not significantly high.
b. Growth in February was driven by services. The index of service
sales jumped by 3.7% m/m, while industrial production was down by
0.7% m/m.
c. The resurgence in COVID-19 cases and new containment measures
have suppressed economic activity. The IHS Markit Brazil
Manufacturing PMI plunged by 5.6 points to a nine-month low of 52.8
in March as output, new orders, and employment declined. Severe
supply-chain disruption led to sharp increases in supplier delivery
times and input costs.
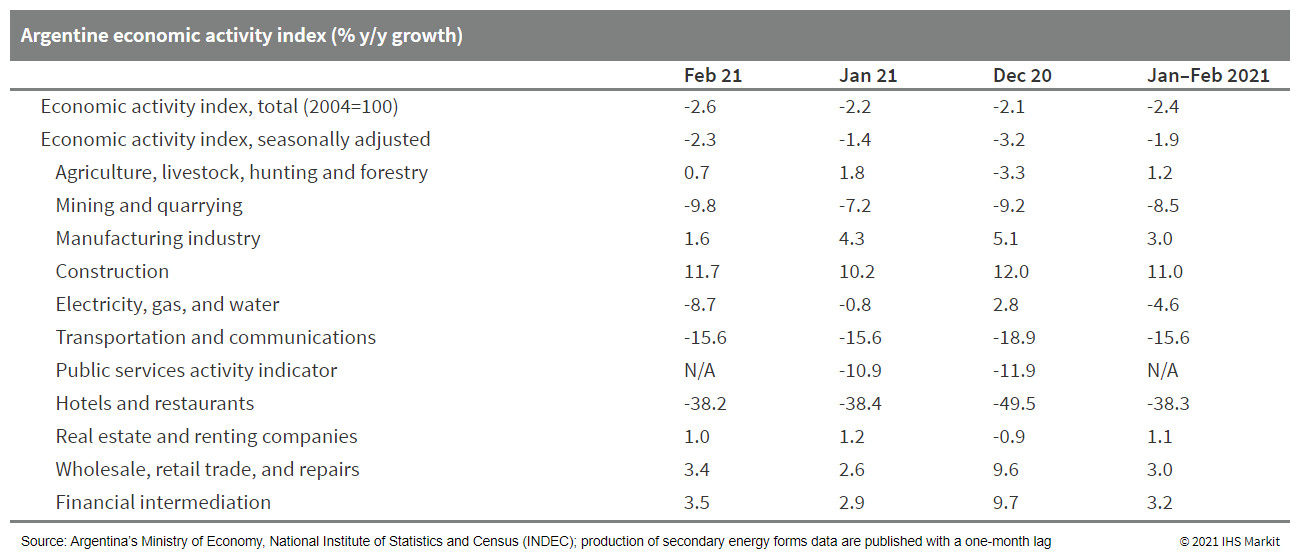
13. Argentina's economic activity index decreased by 2.6% year on year (y/y) in February 2021, while seasonally adjusted data showed a 1% m/m decline during the month. More than half of the categories in the composite index show an annual reduction in February. (IHS Markit Economist Paula Diosquez-Rice)
a. There were steep declines in the hospitality sector, which
was down by 38% y/y; the transport and communication, fishing,
mining, and social and personal service sectors; and the government
services sector, which fell by 5.4% y/y.
b. Customs trade imports jumped in March 2021 compared with March
2020 led by the increase in capital goods, capital goods parts, and
raw material imports. On the export side, a total increase in value
by 30.5% y/y in March was because of a 13.9% y/y increase in prices
and a 3.1% y/y rise in volume. The growth in exports was driven by
the rise in sales abroad of manufactured goods of agricultural
origin.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
1. Most major European equity indices closed lower except for UK
flat; Italy -0.1%, France -0.2%, Germany -0.3%, and Spain
-0.4%.
2. 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; Germany/France flat, UK +1, Spain +2bps, and Italy +3bps.
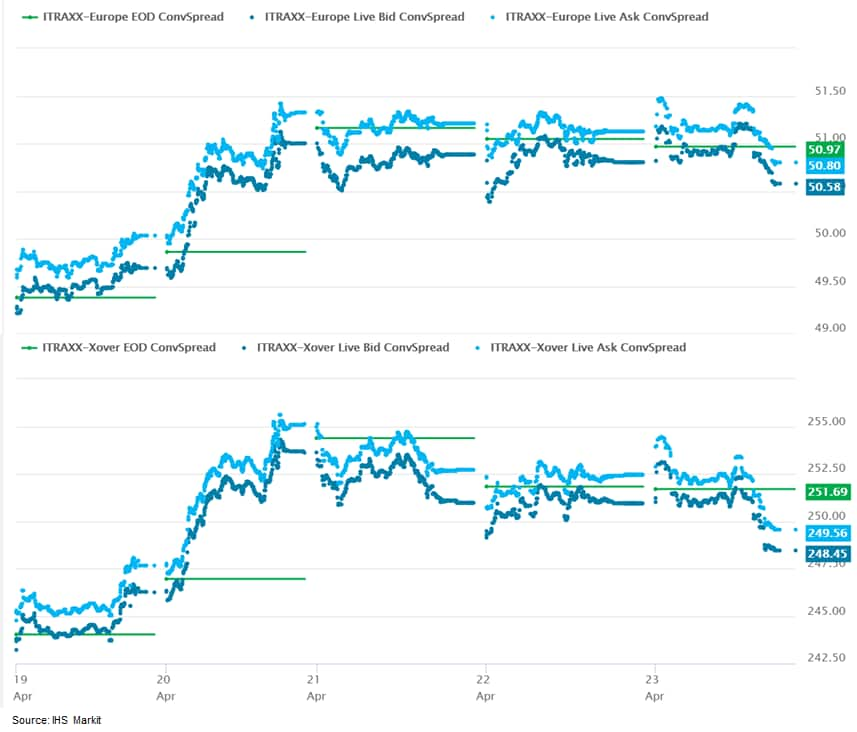
3. iTraxx-Europe closed flat/51bps and iTraxx-Xover -3bps/249bps, which is +1bp and +5bps week-over-week, respectively.
4. Brent crude closed +1.1%/$66.11 per barrel.
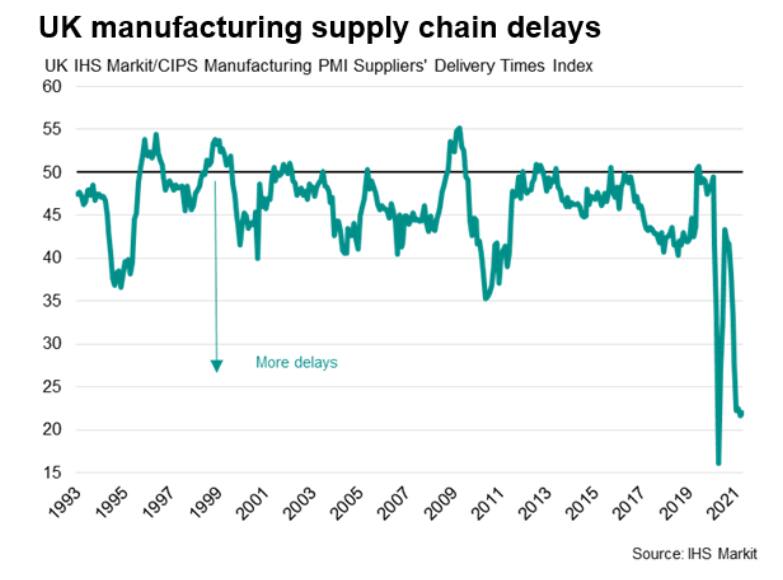
5. The headline UK PMI covering both manufacturing and services rose from 56.4 in March to 60.0 in April, well above expectations of a rise to 58.2. In more than 23 years of PMI history, there has been one spell of faster growth, recorded between August and November 2013. (IHS Markit Economist Chris Williamson)
a. Manufacturing trends varied by sector. Best performing was
the mechanical engineering sector, linked in part to strong
exports, followed by food and drink, despite the latter seeing a
marked fall in exports.
b. Especially robust output growth was also recorded for electrical
& electronic goods, basic metals goods and chemicals &
plastics.
c. Transport (vehicle) producers stood alone in reporting a decline
in both production and employment during the month, also reporting
a sharp drop in exports, while textiles and clothing manufacturers
were notable in reporting only modest growth.
d. Supply delays were broad based across manufacturing, however,
running at near-record levels, but were especially acute in the
vehicle manufacturing, electrical & electronics and basic metal
industries.
6. Vattenfall has suffered yet another setback for its planned
Norfolk coast projects, this time for the Norfolk Boreas. The
United Kingdom (UK) Secretary of State for Business, Energy , and
Industrial Strategy (BEIS) will be postponing the Development
Consent Order (DCO) decision on the project from later this month.
The setback comes after the UK High court, in February 2021,
overturned the decision by BEIS to grant development consent for
the Norfolk Vanguard project in July 2020. The judge presiding
cited concerns around the substantial objections from residents to
the building of the substation and cabling route, and that the BEIS
has breached regulations as a result of a failure to evaluate the
cumulative impacts of both the Norfolk Boreas and Vanguard
projects. Both projects are located more than 40 kilometers from
the Norfolk coast and will each have a capacity of 1.8 GW. The
initial schedule for operations was for mid-2020s. (IHS Markit
Upstream Costs and Technology's Melvin Leong)
7. The headline IHS Markit Eurozone Composite PMI® rose from 53.2 in March to 53.7 in April, according to the preliminary 'flash' reading, which is typically based on approximately 85% of final responses. The consensus, according to Reuters, was for a reading of 52.7. (IHS Markit Economist Chris Williamson)
a. Output has now risen for two months after four months of
decline, with the latest expansion the second-largest recorded
since September 2018.
b. Although the service sector continued to be hard hit by lockdown
measures, it returned to growth as companies (and their customers)
showed further signs of adjusting to life with the virus and
preparing for better times ahead. Service firms reported the first
expansion of activity since last August, albeit growing only very
modestly.
c. Manufacturing output grew for a tenth straight month, expanding
at a rate unsurpassed in over two decades of survey history.
Germany led the factory upturn, its rate of increase easing only
slightly from March's all-time high to remain the second-strongest
on record. France's factory expansion also slowed slightly, though
remained the second best seen over the past three years. Record
manufacturing output growth was meanwhile seen across the rest of
the region as a whole.
d. Backlogs of work grew for a second month in a row, rising to an
extent not seen since January 2018, as firms struggled to cope with
the influx of new business. A survey record increase in
manufacturing backlogs was joined by the first increase in
outstanding business in the service sector since the pandemic
began.
8. Air Liquide reports sales of €5.33 billion ($6.40 billion) for the first quarter of 2021, up 3.8% year on year (YOY) on a comparable basis and slightly higher sequentially than in the fourth quarter of 2020. It also beat analysts' consensus estimate of €5.25 billion, compiled by Vara Research (Frankfurt, Germany). The company does not provide quarterly earnings figures. (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory)
a. Sales growth was "particularly strong" in the healthcare
sector, up 10.1% YOY, and in the industrial sector merchant
activity returned to growth for the first time since the start of
the COVID-19 crisis, up 0.3% YOY, supported by a pickup in volumes,
solid pricing that rose 1.6%, and strong activity in China,
according to Potier.
b. In the gas and services business, revenue in the Americas
declined 1.5% YOY to €2.0 billion in the first quarter. A strong
January in North America was followed by the impact on sales in
February from the winter storm in Texas, most notably in the large
industries business, the company says. Sales in Latin America grew
strongly in all businesses. Healthcare posted sales growth of
13.3%, it adds.
c. In Europe, gas and services revenue rose 4.5% to €1.80 billion,
with industrial activities returning to sales growth. Industrial
merchant activity showed strong improvement, with sales growth of
3.6% YOY, and healthcare activities—which represent more than a
third of gas and services sales in Europe—rising 8.8% compared
with the prior-year period.
d. Sales in APAC rose 6.7% YOY to €1.15 billion, with all business
lines recording growth in China, where revenue increased 12.8%.
Higher volumes in the large industries segment in APAC resulted in
an 8.7% increase in sales. Sales growth of 10.6% YOY in the
industrial merchant segment was supported mainly by the momentum in
China, with sales in the rest of the region "just returning to
growth," the company says.
9. GE Renewable Energy has completed the first 40 of the planned 80
Haliade 150-6MW turbine nacelles for the Saint-Nazaire offshore
wind farm. The first nacelle for the project was produced at its
factory in Montoir-de-Bretagne in September 2020, and transported
to the Port of Saint Nazaire in February 2021. The 480 MW Saint
Nazaire offshore wind farm is scheduled to commence operations in
2022 and will the first commercial wind farm offshore France. (IHS
Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Melvin Leong)
10. The Daimler Group has bounced back in impressive style after the COVID-19 pandemic hit its results last year, posting a very healthy first-quarter net profit of EUR4.4 billion (USD5.3 billion) compared with EUR168 million in the same period of 2020. The Chinese market was hugely affected by the COVID-19 virus outbreak in the first quarter of 2020, and conversely it powered Daimler's very strong first-quarter 2021 result. The company's global group vehicle sales grew by 13% year on year (y/y) to 728,600 units during the period. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
11. Austrian industrial production (including construction) increased by 3.7% month on month (m/m) in seasonally adjusted, EU-harmonised terms in February, extending January's rebound of 2.6% m/m. The manufacturing sector rebound in key export markets is reflected in these numbers, but also another major surge in construction and the loosening of pandemic-related restrictions on 8 February. (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
a. Production excluding construction, i.e. largely
manufacturing, increased at a somewhat more limited pace of 2.4%
m/m in February, while construction output jumped by 7.9% m/m (for
further details, see table below).
b. In year-on-year (y/y) terms, seasonally and calendar-adjusted
production excluding construction returned to positive territory in
February, up 1.3%, which compares favorably with Germany, Austria's
main trading partner, which recorded a decline of 5.9% y/y during
the month - despite the latter country also showing clear signs of
life lately.
12. The Swiss essential oil and flavor house Givaudan reports its Q1 sales reached CHF1.67 billion (USD1.87 billion), 7% more year-on-year. Taste and wellbeing division sales increased by 5.8% to CHF886 million and the fragrance and beauty by 10% to CHF788 million. In addition, Givaudan completed the acquisition of the French artificial intelligence firm Myrissi for an undisclosed sum. Myrissi started in 2014 and has developed a patented technology capable of translating fragrances into color patterns and images. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Jose Gutierrez)
13. Aker, through its subsidiary companies Aker Offshore Wind and Aker Horizons, have teamed up with the University of Strathclyde to develop a novel process for the recovery of glass fiber from used wind turbine blades. The memorandum of understanding (MoU) signed by the parties seek to plan, scale up, and commercialize the proprietary method for thermal recovery and post-treatment of glass fibers from the glass-reinforced polymer composites (GRP) scrap to achieve near-virgin quality glass fibers. This will enable the recycling and reuse of wind turbine blade waste, which the university estimates will be generated at a rate of 400,000 metric tons per annum by 2030. The university expects that the mid- and high-grade fibers produced from the process will cover a broad range of reuse and can serve up to 50% of global glass fiber demand worldwide. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Melvin Leong)
Asia-Pacific
1. APAC equity markets closed mixed; Hong Kong +1.1%, South
Korea/Mainland China +0.3%, Australia +0.1%, India -0.4%, and Japan
-0.6%.
2. As national and regional economies continue to recover from the recessions induced by the COVID-19 pandemic, more than 800 power generation projects, dominated by renewables, are now in the Asian pipeline outside China, representing at least $316 billion in investment opportunities, according to a recent EY report. Of that total, about $306 billion will pour into the renewables sector, with offshore wind and solar photovoltaic facilities accounting for 85% of these projects. The consulting firm identified a total of 811 projects in three north Asian jurisdictions - Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan - as well as Southeast Asian nations Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, the Philippines, and Vietnam. (IHS Markit Climate and Sustainability News' Bernadette Lee)
3. Chinese electric vehicle (EV) startup AIWAYS has partnered with Blue Park Smart Energy, a BAIC BJEV-backed company engaging in battery swapping businesses, to co-operate on development of battery-swappable vehicles and battery swapping technologies, according to Gasgoo. The two partners plan to deploy at least 20,000 vehicles featuring swappable battery packs across 17 cities in the country and will build more than 200 battery-swapping stations. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Nitin Budhiraja)
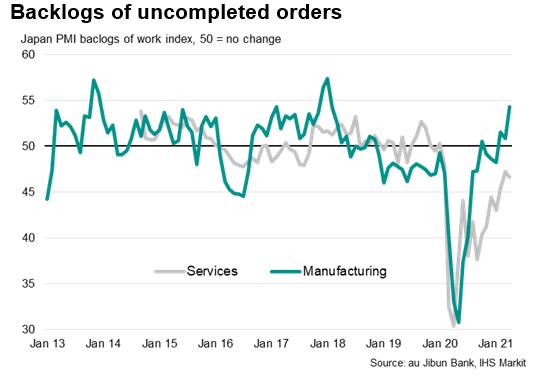
4. The flash au Jibun Bank composite PMI, compiled by IHS Markit and based on around 80% of normal monthly survey replies, rose to 50.2 in April from 49.9 in March. This signals the first expansion since January 2020, when the COVID-19 pandemic first hit the Japanese economy, and bodes well for the recovery at the start of the second quarter. (IHS Markit Economist Chris Williamson)
a. Expansion in the private sector had been underpinned by the
manufacturing sector, where output rose in April at the fastest
rate for three years. Output momentum also improved further, as
emphasized by a rising orders-to-inventory ratio. Factories are
struggling to meet demand, leading to falling inventory and
increasing backlogs in April.
b. In contrast, services saw backlogs and inflows of new business
still dampened by the deteriorating COVID-19 conditions in Japan
and abroad. Exports of services were especially hard-hit,
contrasting with the strongest surge in goods exports for over
three years, reflecting travel restrictions.
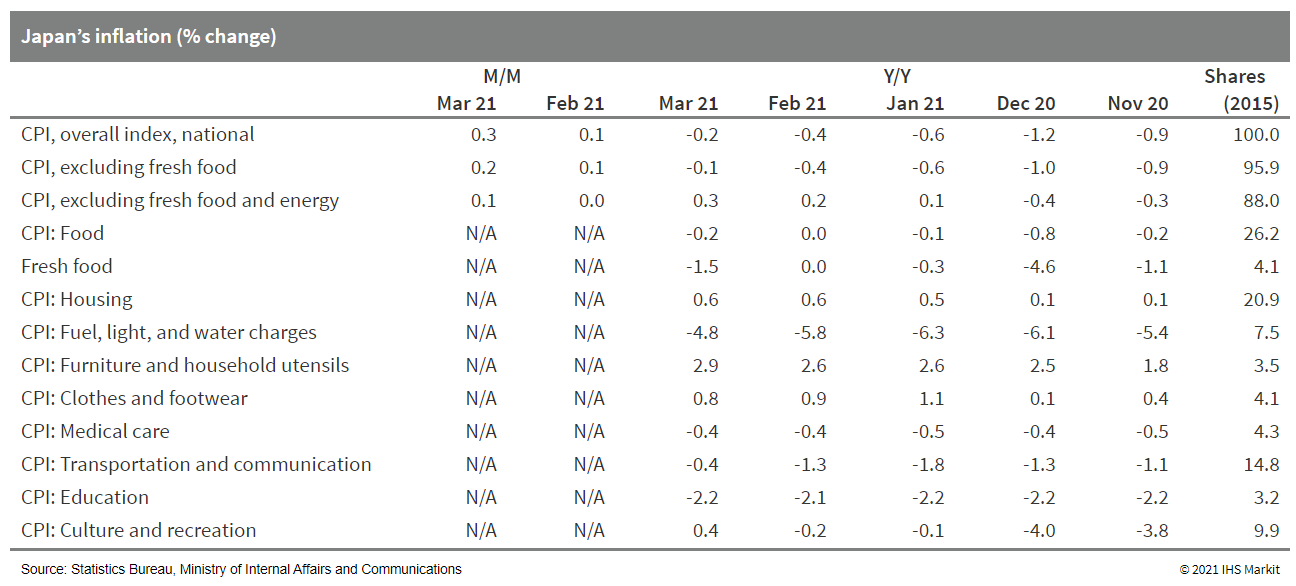
5. Japan's CPI rose by 0.3% month on month (m/m) on a seasonally
adjusted basis in March, and the year-on-year (y/y) contraction
softened to 0.2% from a 0.4% drop in the previous month. The CPI,
excluding fresh food, rose by 0.2% m/m, and the y/y contraction
narrowed to 0.1%. The CPI, excluding food and energy (the core-core
CPI), rose by 0.1% m/m and moved up to 0.3% y/y. (IHS Markit
Economist Harumi Taguchi)
a. While milder declines in energy prices (mainly gasoline) were
the major factor behind the improvement, the rise in the core-core
CPI reflected increases in prices of household durables, clothes
and footwear, and culture and recreation items.
b. This reflected the continuation of work-from-home lifestyles
encouraging demand for value-added household electric appliances.
It was also a reflection of the resumption of economic activity in
line with the lifting of the state of emergency for seven
prefectures by the end of February.
6. Indonesian network service provider Telkomsel is planning to
invest n aadditional USD300 million in ride-hailing firm Gojek,
reports Reuters. This follows USD150-million investment by
Telkomsel in Gojek in November 2020. Setyanto Hantoro, president
director of Telkomsel, said, "Telkomsel has the option to invest up
to USD450 million in Gojek within one year from the first
investment. We are working to examine whether to exercise the
USD300 million option more quickly than that, after seeing positive
results from the collaborations the two firms have carried out
together since early 2021". Gojek is close to finalizing a proposed
merger with Indonesia's e-commerce giant Tokopedia that would
result in a new entity called GoTo. The combined entity will create
a powerhouse dominating the Indonesian market, one of the world's
fastest-growing internet economies. (IHS Markit Automotive
Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
7. The Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) published on 23 April its draft guidelines on Climate Change Financial Risks, seeking financial-sector feedback before issuing definitive guidance later this year. The draft Prudential Practice Guide CPG 229 Climate Change Financial Risks (CPG 229) highlights physical, transition and liability risks as areas for concern, noting that for financial institutions, climate factors can generate credit, market (valuation), operational, underwriting, liquidity, and reputational concerns. The guidelines assess that climate risks need a "strategic approach", with differing risk characteristics from other perils, stemming from the potential for "irreversible changes in climate", the far-reaching nature of climate risks spanning "multiple lines of business at the same time", their extended time horizon and unprecedented nature. The latter hinders modelling using past data (as widely applied elsewhere in modelling financial risks). To address this, the report seeks changes in governance and risk management procedures, while encouraging firms to have climate scenario stress testing capabilities and to move to stronger relevant disclosure. (IHS Markit Country Risk's Hannah Cotillon and Brian Lawson)
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary--23-april-2021.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary--23-april-2021.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+23+April+2021+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary--23-april-2021.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 23 April 2021 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary--23-april-2021.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+23+April+2021+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary--23-april-2021.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




