Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Aug 07, 2020
Daily Global Market Summary - 7 August 2020
Equity markets closed mixed across each region, while gold had its worst day since early-June only one day after hitting its all-time high. iTraxx and CDX indices were flat-to-slightly tighter on the day, with both indices noticeably tighter on the week across IG and high yield. The US added 1.8 million jobs in July, but the data indicates that the pace of rehiring slowed substantially in the wake of the increases in COVID-19 infections that began in early-June across the US.
Americas
- US nonfarm payroll employment rose 1.8 million in July, a sharp
slowing from a 4.8-million increase in June. The unemployment rate
declined 0.9 percentage point to 10.2%. This report is consistent
with our view that, broadly speaking, the economic recovery lost
momentum in July. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Michael
Konidaris)
- The slowing in employment was evident in many sectors. Private service-sector employment rose 1.4 million in July following a 4.2-million increase in June. Employment in goods-producing industries (manufacturing, construction, mining, and logging) rose only 39,000 in July following a 515,000 increase in June.
- This pattern is consistent with our estimate that monthly GDP barely rose in July following a sharp increase in June. Several high-frequency indicators point to a stall in the broad economic recovery. The most relevant for today's report was a plateau and then reversal of the trend in revenues earned at small business in July (from the Opportunity Insights Economic Tracker). The momentum for this indicator heading into August is bad (negative).
- Employment is slowing and remains far short of the pre-pandemic level. Increases in payroll employment since the April trough have reversed only 42% of the two-month decline from February to April. It will take a reacceleration in aggregate output to pull employment back to pre-pandemic levels, which we do not see happening in the near term.
- In other details in today's report, the average workweek declined 0.1 hour to 34.5 hours and the index of aggregate weekly hours rose 1.0%. The latter is on track to grow at roughly a 25% annual rate in the third quarter.
- Stimulus talks between the White House and congressional Democrats broke down on Friday, leading Donald Trump to vow that he would use his "authority as president to get Americans the relief they need". Democrats have rallied around a far larger stimulus plan than Republicans and the two sides remain deeply divided over Democratic calls for $1tn in support for state and local authorities facing declining tax revenues and soaring healthcare costs during the coronavirus pandemic. (FT)
- Most US equity markets closed higher except for Nasdaq -0.9%; Russell 2000 +1.6%, DJIA +0.2%, and S&P 500 +0.1%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +3bps/0.57% yield and 30yr bonds +4bps/1.23% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed flat/65bps and CDX-NAHY -2bps/387bps, which is
-4bps and -46bps (chart below), respectively, week-over-week.

- Crude oil closed -1.7%/$41.22 per barrel.
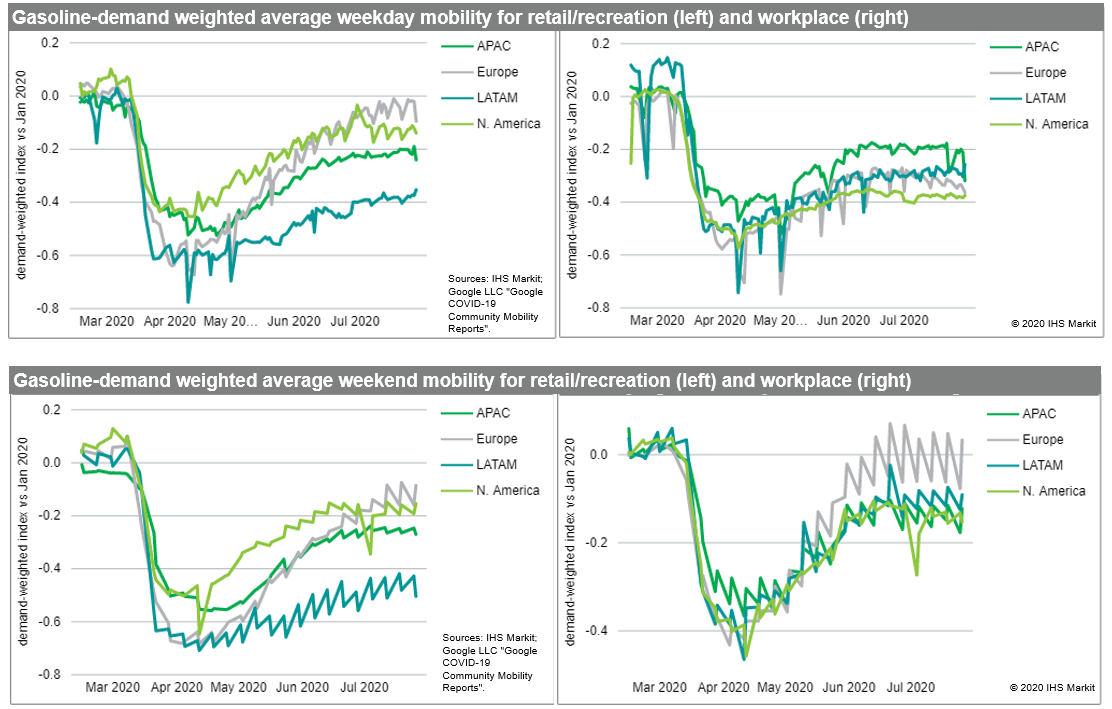
- As of 5 August, IHS Markit estimates that the share of global
gasoline demand in countries under major restrictions worsened
again last week, rising by 1% to 54%. Government restrictions grew
more severe in countries representing 5% of global demand,
including large restriction increases in Vietnam, Spain, Peru,
Indiana, and Washington. Even countries that have somewhat reduced
restrictions from their April peak maintain some containment
measures in place and on a demand-weighted basis, restrictions in
most regions have stayed stable or trended upward over the last
month. Mobility too continues to stagnate in most major demand
countries, with none of the largest consumers except South Korea
having returned to Jan 2020 travel levels in terms of workplace and
retail travel. In a handful of US states and advanced economies,
retail travel has surpassed workplace travel, and returned closer
to Jan 2020 levels. However, it's worth noting that in the US,
trends in the Google travel data appear to have increasingly
diverged from OPIS' estimated gasoline sales, which have continued
to recover albeit at a decreasing rate. The prospect of this
underestimate being replicated globally might represent a minor
cause for optimism about gasoline demand surpassing estimates based
on mobility. (IHS Markit Energy Advisory's Roger Diwan, Karim
Fawaz, Justin Jacobs, Edward Moe, and Sean Karst)
- Gold closed -2.0%/$2,028 per ounce, which was its biggest daily decline since 5 June, ending the week +2.1% week-over-week.
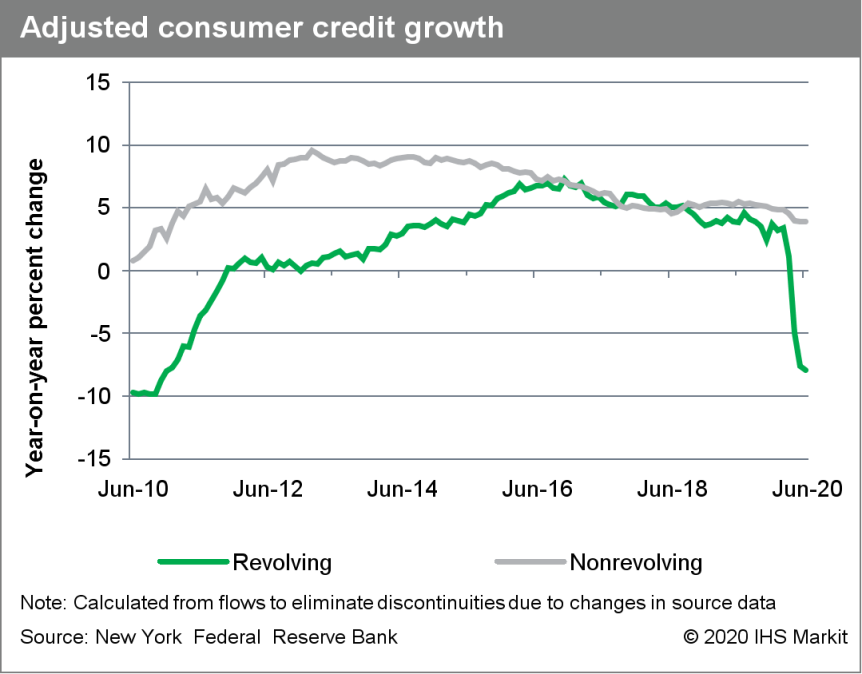
- Outstanding US nonmortgage consumer credit increased by $9
billion to $4.12 trillion in June after declining a cumulative $96
billion over the prior three months. (IHS Markit Economist David
Deull)
- The 12-month change in outstanding consumer credit edged down 0.1 percentage point to 0.9%, the lowest since November 2010, as spending has fallen and incomes have been supplemented by federal stimulus.
- Revolving (mostly credit-card) consumer credit fell $2 billion (seasonally adjusted) in its fourth consecutive decline. The 12-month growth rate of this category was -7.5%.
- Nonrevolving credit increased $11 billion, and its 12-month growth rate was unchanged at 3.9% for the third consecutive month. This category includes student and auto loans.
- The ratio of nonmortgage consumer credit to disposable personal income was 23.3% in June, up 0.4 percentage point from last month, as extraordinary fiscal stimulus, which has bolstered aggregate personal income, took a step back from April and May.
- As consumers have pulled back on spending because of COVID-19,
they have taken the opportunity to pay down credit card debts but
have not made much of a dent in auto and student loans, which
continue to grow at a brisk pace.
- Ride-hailing giant Uber reported a net loss of USD1.78 billion
in the second quarter of 2020. This loss is attributable to
stock-based compensation expenses for employees and restructuring
related charges. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- The company's revenues shrunk to USD2.24 billion in the second quarter, a decrease of 29% year on year (y/y).
- The fall in revenues was the result of a decline in the number of monthly active users across rides, bike shares, and food deliveries, reaching 55 million, down from 99 million a year earlier.
- Gross bookings, a number used to track customer demand, reduced 35% y/y to USD10.22 billion.
- Uber's demand for its core business, ride hailing, was battered by COVID-19 virus pandemic, which resulted in a decline in its revenues by 67% y/y to USD750 million in the second quarter.
- Meanwhile, revenues of its food delivery business, Uber Eats, rose 103% y/y to USD1.21 billion.
- Freight revenue was USD211 million, up 27% y/y in the quarter.
- Canada's total employment expanded 2.4% month on month (m/m),
raising employment to 93% of pre-pandemic levels while total hours
worked is lower at 88.8%. The overall gain can be attributed to the
hefty gain in Ontario (up 150,700, or 2.2% m/m), but employment
expanded the fastest in Alberta, at 3.2% m/m. (IHS Markit Economist
Arlene Kish)
- Net employment increased 418,500 positions in July, a softer gain than expected.
- The increase was concentrated in part-time positions (up 345,300) and in services-producing industry employment (up 347,900).
- The labor force participation rate ticked only 0.5 percentage point higher to 64.3% while the unemployment rate edged down 1.4 percentage points to 10.9%.
- Since bottoming in April, Canada has regained nearly 1.7 million jobs, or just over half of the jobs lost, during this recovery stage.
- Canada's Ivey Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) rose 10.3 points
to 68.5 in July, which is the highest reading since April 2018.
(IHS Markit Economist Alexander Minelli)
- Purchasing managers' spending activity showed moderate improvement in July and the employment index improved by the most, adding 4.8 points to reach 57.6 as Ontario caught up with most other provinces, lifting restrictions.
- The prices index tacked on 4.1 points to 60.5, indicating mild inflation pressure. The inventories index, which was the highest in overall value, was relatively unchanged, falling 0.1 point to 61.7 as purchasing managers accommodate for customer demand.
- The supplier deliveries index saw the largest drop, 3.3 points, to a reading of 50.1, indicating delivery times remained comparable with June.
- At its 5 August monetary policy committee, the Central Bank of
Brazil (Banco Central do Brasil: BCB) decided to cut the policy
rate (SELIC) from 2.25% to 2.00% and hinted that further cuts are
unlikely as the real rate is approaching zero, i.e., the (nominal)
policy rate is almost the same as the inflation rate. (IHS Markit
Economist Rafael Amiel)
- As of the end of June, inflation amounted to 2.1% while core inflation, which excludes items with volatile prices such as energy and agricultural products, was 1.4%. At the current levels, the policy rate is at its historic low. The BCB targets inflation to be at 4.0% +/- 1.5 percentage points.
- The bank assesses that the core inflation measure in Brazil is below the bank's targets in the policy horizon (next 2 years).
- The BCB assesses that the current policy rate is below its structural value; this value is relatively high as it is pushed up by a sizable fiscal deficit and high debt that needs to be financed and rolled over, offering higher rates.
- The very weak state of the Brazilian economy justifies a strongly stimulative monetary policy. IHS Markit assesses that it is only relatively stimulative as the rates that commercial banks charge for their loans to corporations and consumers are still sizable.
- The BCB highlights a number of risks regarding future action: favoring lower inflation, the output gap - the difference between the potential output and actual output - remains wide, which means that additional demand can be easily met by increases in production without the need to increase prices.
- This downside risks may intensify if the COVID-19-virus outbreak's negative impact on demand extends further than anticipated and if precautionary savings because of the pandemic increase.
Europe/Middle East/ Africa
- Most European equity markets closed higher except for Spain -0.1%; Germany +0.7%, Italy +0.2%, and UK/France +0.1%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; Italy/Spain flat, France +1bp, Germany +2bps, and UK +3bps.
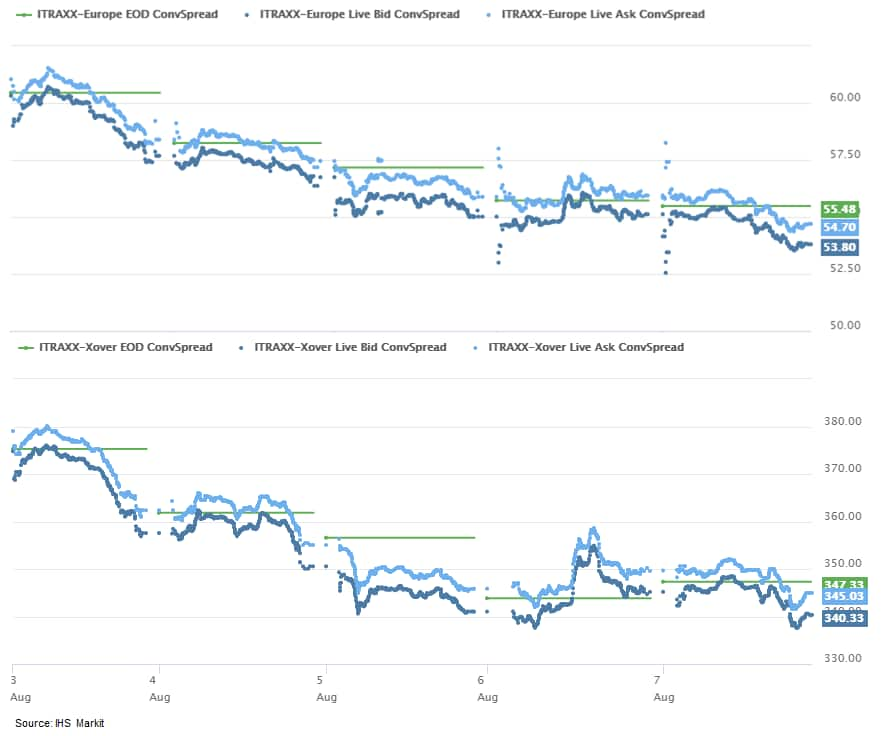
- iTraxx-Europe closed -1bp/54bps and iTraxx-Xover -5bps/343bps,
ending the week -6bps and -33bps, respectively, week-over-week.
- Brent crude closed -1.5%/$44.40 per barrel.
- Seasonally and calendar-adjusted German industrial production
excluding construction grew by 10.8% month on month (m/m) in June,
compared with a 9.2% month-on-month (m/m) gain in May. (IHS Markit
Economist Raj Badiani)
- The production level in June was still 13.8% below its pre-COVID-19 lockdown level in February.
- In annual terms, production stood 13.8% below the level in June 2019.
- At the peak of the COVID-19 virus lockdown, industrial output shrunk by 28.8% during March-April, compared with a decline of 22.7% during the 2008-09 global financial crisis, which spanned eight months.
- Total production including construction rose notably for the second straight month, up by 8.9% m/m in June after a 7.4% m/m rise in May. However, this stands against a cumulative fall of 24.9% during March-April.
- The breakdown of manufacturing output reveals that strengthening investment goods output was the main engine of growth in June, rising by 18.3% m/m after a 27.3% m/m rebound in May. Both intermediate and consumer goods production posted stronger improvements in June after a lacklustre performance in May.
- Production in the automotive industry continued to revive in June, increasing by 54.7% m/m. However, it remained around one-fifth lower compared with February's level, the month before the national lockdown.
- Mercedes-Benz Trucks has started a second testing phase of its eActros electric heavy truck in the Netherlands, according to a company statement. The truck has already been successfully operated in real world environments by freight and logistics companies in Switzerland and Germany, and now testing is branching out to the Netherlands too. Following the 10 units on trial in Germany and Switzerland, eight units are going to new customers in the Netherlands, Germany, and Belgium; Dutch freight provider Simon Loos is the first recipient of the second batch of eActros to be put on real-world trial operations. The initial trials in Switzerland and Germany have fed back some very interesting and tangible data to Mercedes Trucks engineers, with the most pertinent being that the truck's range is extremely consistent at 200km. This has proved consistent irrespective of load, route, or the type of territory the truck drives through. This is extremely important as future commercial operators will have to be very sure of the daily range capability of the truck; 200km is perfect for the kind of delivery duties the fixed chassis eActros is designed for. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
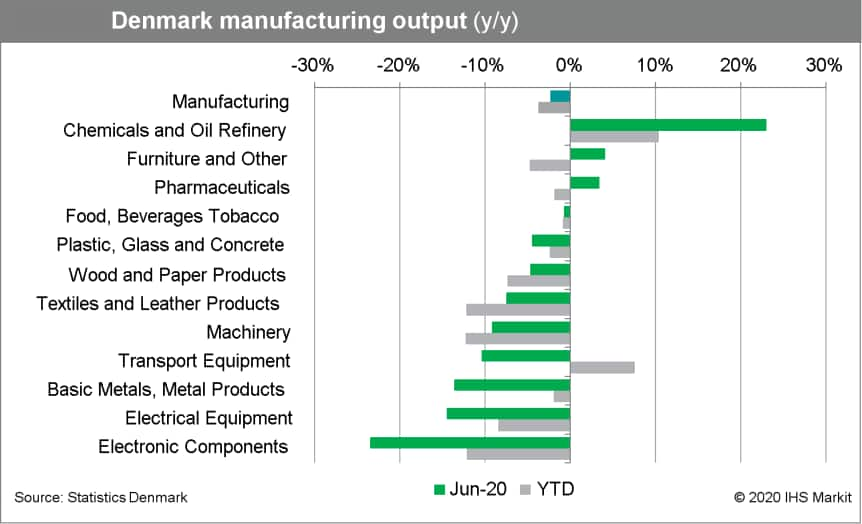
- After several months of declines, in June Danish industrial and
manufacturing output grew by 2.9% and 4.0% month on month (m/m),
respectively. On a three-month rolling basis, industrial output is
down by 10.1% year on year (y/y) and manufacturing output by 7.4%
y/y. (IHS Markit Economist Daniel Kral)
- Among the main sub-components, chemicals grew by 23% y/y, although this is driven by a base effect, as June 2019 was extremely weak.
- Manufacture of furniture was up by 4.1% y/y and pharmaceuticals up by 3.5% y/y.
- The largest drops were in manufacture of electronic components, down by 23.4% y/y, electrical equipment, down by 14.5% y/y, and metals, down by 13.6% y/y.
- In 2019, Danish manufacturing output grew by 4.4%, almost exclusively driven by pharmaceuticals subcomponent, which grew by 15.3% and has the largest weight in the index (20.1%). The high base effects are a contributing factor to the relative underperformance in 2020 (Chart 3).
- Despite the strong growth in June, industrial and manufacturing output remains 5.0% and 4.4% below February levels, prior to the impact of COVID-19 pandemic.
- Danish manufacturing PMI rebounded strongly in July, to 57.4, a
remarkable turnaround from the April low of 38.2. The output
sub-component was up to 64.9 in July, from 31.9 in April,
indicating a continued strong rebound in production in the coming
months.
- Danish passenger car registrations have recorded growth during
July. According to the latest data published by the Danish Car
Importers' Association (De Danske Bilimportører), passenger car
demand increased by 13.4% year on year (y/y) to 18,952 units, with
most of the growth being centered on subcompact crossovers and
sport utility vehicles (SUVs). (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian
Fletcher)
- Registrations in the year to date (YTD) are still down by 22.7% y/y to 107,367 units on the back of earlier COVID-19 virus-related declines.
- The trade association also revealed that light commercial vehicle (LCV) registrations grew by 7.4% y/y to 1,995 units in July, although its YTD remained down by 16.2% y/y at 15,982 units.
- Furthermore, Danish registrations of medium and heavy commercial vehicles (MHCVs) remained weak with a fall of 15.1% y/y to 163 units in July and are now down by 33.3% y/y at 2,143 units in the YTD.
- In June, on a seasonally and working-day-adjusted basis, Dutch
manufacturing output was up by 2.1% month on month (m/m) but down
by 8.8% year on year (y/y) and by 9.2% compared to February, prior
to the impact of the COVID-19 virus pandemic. Even before the
pandemic, manufacturing output has been on a declining trend,
peaking in early 2018. (IHS Markit Economist Daniel Kral)
- On a seasonally unadjusted basis, average daily output of the Dutch manufacturing sector was down by 9.7% y/y. On a three-month moving average basis, output was down by 10.9% y/y, down from 8.2% in May and 4.6% in April.
- In June, all major sub-components were a drag. The biggest drops were recorded in repair and installation of machinery, which fell by 28.0% y/y, transport industry, declining by 17.9% y/y, and metals, down by 16.4% y/y.
- At 47.9 in July 2020, the Dutch manufacturing purchasing managers' index has improved significantly since the May low of 40.5. The output sub-index jumped to 49.2 in July, close to the critical 50-level indicating expansion in annual terms.
- Yandex has begun testing a fleet of autonomous cars in Ann Arbor, Michigan (United States), reports VentureBeat. The fleet includes the company's fourth-generation autonomous Hyundai Sonatas created in partnership with Hyundai Mobis, as well as Toyota Priuses. Yandex said it had planned to provide rides in its autonomous taxis in Detroit, Michigan, in June during the North American International Auto Show (NAIAS), but that event was cancelled as a result of the COVID-19 virus pandemic. Dmitry Polishchuk, head of Yandex's autonomous vehicle division, said, "Ann Arbor, with its bigger size and more progressive regulatory environment, will enable us to take this experience a step further." Yandex has chosen Ann Arbor as it is one of the few cities that allows autonomous vehicles to operate without a human behind the wheel. Currently, Yandex is only allowed to transport passengers in its driverless vehicles in the western Russian town of Innopolis. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed mixed; Hong Kong -1.6%, China -1.0%, Australia -0.6%, India flat, and South Korea +0.4%.
- Business reopenings and cash benefits helped boost Japan's
household expenditures in June, but continued declines in cash
earnings could weigh on the recovery of consumer spending. (IHS
Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
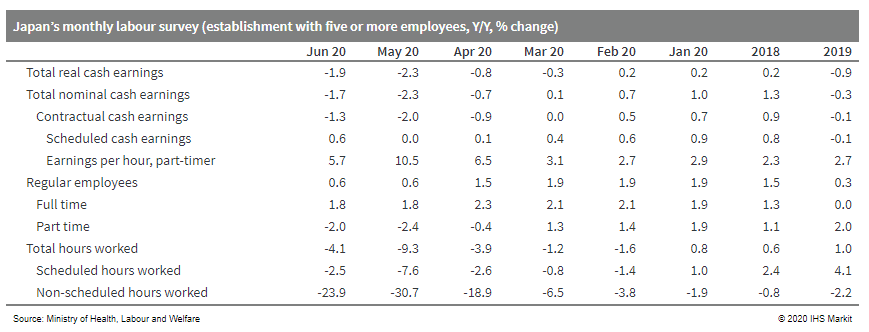
- Japan's monthly cash earnings fell by 1.9% year on year (y/y) in June.
- The continued contraction was due largely to a 24.6% y/y drop in non-scheduled cash earnings, reflecting a 23.9% y/y decline in non-scheduled hours worked in response to continued containment measures for COVID-19.
- Special earnings (mainly seasonal bonuses) also continued to decline with a 2.4% y/y slide. Although the number of full-time employees continued to increase, offsetting a sustained decrease in the number of part-timers, scheduled earnings for full-time employees fell by 0.1% y/y, the first contraction since April 2014.
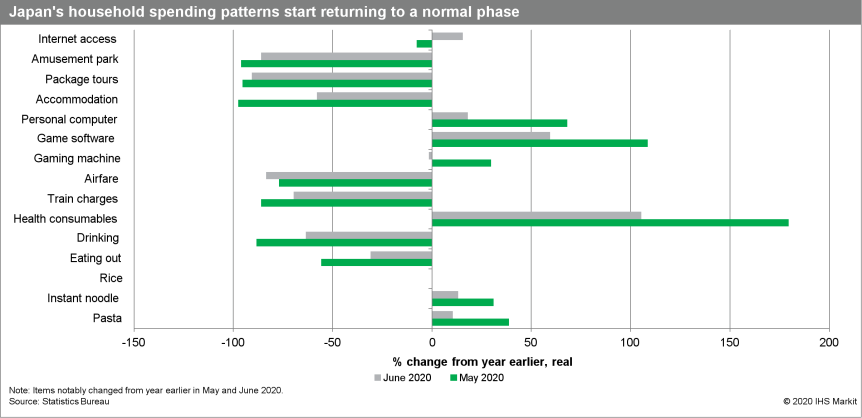
- Japan's real household expenditures rose by 13.2% month on month (m/m) in June following three consecutive months of decline, although the figure was down 1.1% from a year earlier.
- The solid rebound reflected surges in spending in clothing and
footwear, culture and recreation, transportation, and miscellaneous
items because of the reopening of non-necessary stores and
businesses following the lifting of a state of emergency in late
May. Despite the decline in cash earnings, cash benefits helped
boost spending for household durables while spending on
stay-home/work-from-home lifestyle areas eased.
- Honda's earnings took a steep hit during the first quarter of
the fiscal year (FY) ending 31 March 2021 owing to the COVID-19
virus pandemic. During the three months ended 30 June, the
automaker reported a consolidated net loss of JPY80.8 billion
(USD765.6 million), compared with a JPY172.3-billion net profit in
the corresponding period of last FY. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's
Isha Sharma)
- Loss before income tax amounted to JPY73.4 billion, including JPY440 billion from the impact of the pandemic.
- The company's operating income plunged to a loss of JPY113.6 billion during the period from a profit of JPY252.4 billion a year ago.
- This was mainly due to a decrease in profit from lower sales revenue and model mix amounting to JPY467.8 billion and unfavorable currency exchange rate of JPY10.8 billion, which were partially offset by decreased selling, general, and administrative (SG&A) expenses of JPY91.4 billion, a cost reduction worth JPY15.6 billion, and a reduction in research and development (R&D) costs worth JPY5.5 billion.
- Sales revenues dropped by 46.9% year on year (y/y) to JPY2.1 trillion mainly on account of a decrease in vehicle sales.
- By volume, Honda's group-wide unit sales during the three-month period declined by 40% y/y to 792,000 units.
- Sales in the automaker's two largest markets - Asia and North America - reached 473,000 units (down by 14.6% y/y) and 159,000 units (down by 67.8% y/y), respectively. Its Japanese sales declined by 28.7% y/y to 129,000 units.
- Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) has launched a mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) project in Shiojiri City, Nagano Prefecture. The 'Shiojiri Project' includes partners such as Mitsubishi Corporation, Next Mobility Company, and the municipal government of Shiojiri City. The project will include trials of an artificial intelligence (AI)-based on-demand bus service called KnowRoute for specified, inter-regional routes, and autonomous vehicles for intra-regional routes. The project is expected to deploy these services officially from the beginning of fiscal year (FY) 2021. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Toray Industries reports a 62.8% drop in net income for its
fiscal first quarter ended 30 June, to ¥9.5 billion ($90 million),
compared with ¥25.6 billion a year earlier. Operating income
plummeted 63.7% year on year (YOY) to ¥12.5 billion. Revenue was
¥397.6 billion, a decrease of 22.5% YOY.
- Sales by Toray's fibers and textiles segment were ¥145 billion, a decline of 25.9%. Operating income plunged 50.3% YOY to ¥7.2 billion.
- Sales by Toray's performance chemicals business decreased 21.2% YOY to ¥155.6 billion and operating income plunged 52% YOY to ¥8.1 billion.
- Toray says that in the resins business, demand from automotive and industrial applications declined in Japan and overseas. The chemicals business was pressured by a decline in the basic chemicals market.
- In the films business, sales of packaging materials were strong, reflecting the growing demand for home meals.
- Demand for battery separator films for lithium-ion secondary batteries and polyester films remained low. The company says that COVID-19 drove down the performance of this business.
- In the carbon fiber composite materials unit, wind turbine blade and casing applications remained strong in industrial applications. Aircraft applications were hurt by a decline in the production rate of large-sized passenger aircraft. Operating income fell 73.4% YOY to ¥1.7 billion on sales of ¥45.4 billion, down by 26.2% YOY.
- Sales by Toray's environment and engineering segment were ¥37.2 billion, a decline of 11.2% YOY. Operating income plunged 40% YOY to ¥800 million. The company says that demand for reverse osmosis membranes and other products grew strongly and that shipments to some regions were curtailed by the pandemic.
- Australia's federal government has provided a grant of AUD838,000 (USD604,510) to support the nationwide rollout of 150 smart electric vehicle (EV) chargers in an effort to encourage the adoption of EVs in the country while mitigating their impact on the nation's electricity grid. According to caradvice, the government has partnered with electricity provider Origin Energy to begin a two-year trial that will provide chargers to both private owners and fleets. The AC chargers will be fully subsidised for trial participants and will offer 7 kW of charging power to residential customers and 22 kW for fleet operators. EV sales make up only a small percentage of Australia's vehicle sales, but consumer interest in EVs is growing rapidly thanks to the arrival of an array of new models, especially the Tesla Model 3. According to data from the Federal Automotive Chamber of Industries, a total of 283 EVs were sold to private buyers in Australia in the first five months of 2020, compared with 181 units in the same period last year. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- Geely Auto has announced its sales results for July. The
combined sales volumes of Geely- and Lynk & Co-branded vehicles
in July totaled 105,218 units, up 15% year on year (y/y). The data
include sales in the Chinese market and exports. (IHS Markit
AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- Sales volumes in China were 100,695 units in July, up 15% y/y. In the year to date (YTD), Geely's total sales volumes were 635,664 units, down 14% y/y, which represents 45% of the company's target of 1.41 million units in 2020.
- A breakdown of Geely Auto sales by vehicle type shows sport utility vehicles (SUVs) are still in high demand, along with sedans. SUVs and sedan sales stood at 66,387 units and 35,581 units respectively in July.
- Geely Auto's sales of multi-purpose vehicles (MPVs) totalled 3,250 units in July.
- The sales volumes of Lynk & Co brand surged 78% y/y in July to 15,331 units.
- The strong results in July also marked an all-time high in sales for the Lynk & Co brand since its sales began in late 2017.
- The automaker's exports volumes rose by 13% y/y during July to 4,523 units.
- Geely's July sales were underpinned by the strong performance of the Lynk & Co brand. The brand jointly introduced by Geely Auto and Volvo Cars, has been aggressively expanding its product line-up in the Chinese market to five models covering the B to D segments.
- Leading Chinese probiotic materials supplier, Scitop, filed an IPO on the Science and Technology Innovation Board (the equivalent of NASDAQ at Shenzhen on July 27,) and became the first domestic publicly listed company which specializes in probiotics supplies. It is mainly engaged in the research and development, production and sales of compound food additives, edible probiotic products, animal and plant microecological preparations. Its products are widely used in the food industry, healthcare, animal husbandry, agricultural planting and more. It is exploring the build of a complete supply chain for the probiotic lactic acid bacteria industry. The IPO is aimed at raising CNY489 million (USD69.9 million) for ramping up the production capacity. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Hope Lee)
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-7-august-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-7-august-2020.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+7+August+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-7-august-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 7 August 2020 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-7-august-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+7+August+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-7-august-2020.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




