Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Aug 31, 2021
Daily Global Market Summary - 31 August 2021
All major APAC equity indices closed higher, while the US was mixed and all major European markets were lower on the day. US and benchmark European government bonds closed sharply lower. CDX-NA and European iTraxx closed almost unchanged across IG and high yield. Natural gas, gold, and silver closed higher, the US dollar and copper were flat, and oil was lower on the day. All eyes will be on Friday's US non-farm payroll report, as another better than expected report could reinforce the Fed's initial thoughts on the timing of tapering of QE and unwinding of other accommodative policies.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our newly launched Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
- Major US equity indices closed mixed; Russell 2000 +0.3%, Nasdaq flat, and DJIA/S&P 500 -0.1%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +3bps/1.31% yield and 30yr bonds +3bps/1.93% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed flat/46bps and CDX-NAHY flat/275bps.
- DXY US dollar index closed flat/92.63.
- Gold closed +0.3%/$1,818 per troy oz, silver +0.2%/$24.01 per troy oz, and copper flat/$4.38 per pound.
- Crude oil closed -1.0%/$68.50 per barrel and natural gas closed +1.7%/$4.38 per mmbtu.
- The health and climate benefits of wind generation installed in
the US in 2020 were more than twice the levelized cost of energy
(LCOE) of the facilities, according to data released by the US
Department of Energy (DOE) 30 August. DOE valued the health and
climate benefits of wind energy installed in the US in 2020 at
$76/MWh, while the nationwide LCOE-or the lifetime cost divided by
production-for wind was $33/MWh, it said in a report on onshore
wind energy, one of three on wind the agency issued concurrently.
(IHS Markit Net-Zero Business Daily's Keiron Greenhalgh)
- Such disparity between the cost and benefits supports the Biden administration's plans to ramp up US renewable power generation capacity and cut the country's emissions by 50-52% compared with 2005 levels by 2030 as part of efforts to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius compared with pre-industrial levels.
- In Land-Based Wind Market Report: 2021 Edition, analysts at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory evaluated the benefits by extrapolating the positive climate impact by multiplying the amount of avoided CO2 emissions by the social cost of carbon.
- Health benefits were calculated by estimating the cost of avoided nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide emissions, including cost of premature mortality, increased hospitalization, and workdays missed, the report said.
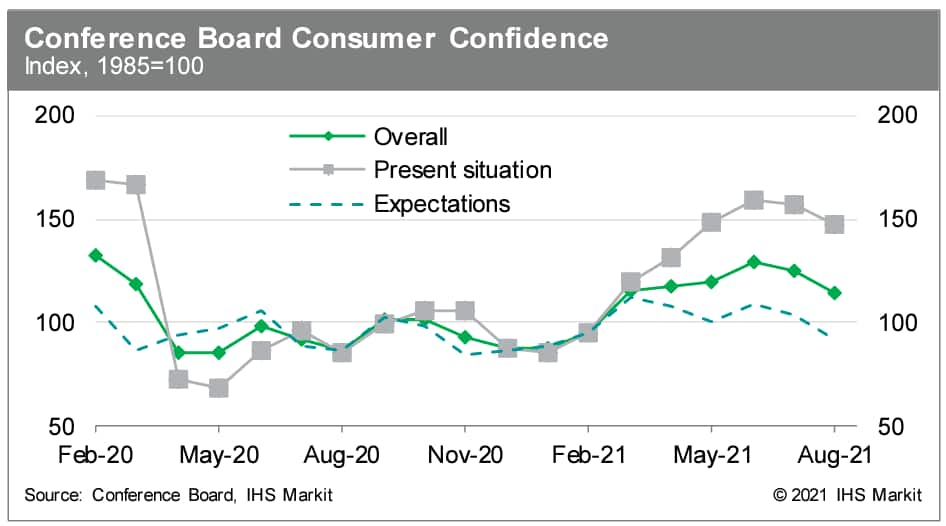
- The US Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index fell sharply
in August by 11.3 points (9.0%) to 113.8, following a (downwardly
revised) 3.8-point decline in July. The index is at its lowest
level since February. (IHS Markit Economists David Deull and James
Bohnaker)
- The index of views on the present situation declined 9.9 points to 147.3. The expectations index plunged 12.4 points to 91.4.
- In August, the labor index (the percentage of respondents viewing jobs as currently plentiful minus the percentage viewing jobs as hard to get) decreased 1.3 percentage points to 42.8%, still higher than at any point before the pandemic dating back to 2000.
- Despite the strong job market, consumers are not as optimistic about income growth. The net percentage of respondents expecting higher incomes in the next six months declined 3.4 points to 7.8%, still well below the 15.0% average recorded during the half-year preceding the pandemic.
- Purchasing plans were modestly lower in August. The share of respondents planning to buy homes in the next six months edged down 0.2 point to 6.2%; the share planning to buy autos fell 1.3 points to 10.8%; and the share planning to buy major appliances declined 3.7 points to 50.2%.
- The percentage of respondents planning a vacation in the next six months rose 3.2 points from June to 41.1%. However, the percentage planning to travel by air edged down 0.8 point to 20.6%, likely in response to the rapid spread in the Delta variant. We have seen the number of domestic air travelers decline modestly in recent weeks.
- Survey respondents reported a 6.8% expected year-ahead
inflation rate in August. Although this was the highest reading
since 2008, it has not moved significantly higher since first
surging during the initial months of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Monthly US home price gains were steady in June according to
the S&P CoreLogic Case-Shiller index. The 10-city composite was
up 1.6% month over month (m/m) while the 20-city index was up 1.8%.
In another record-setting month, home price appreciation in the US
accelerated to new highs in June. Data from S&P CoreLogic
Case-Shiller show that US price growth reached 18.6% y/y in the
three months ending in June. This was by far the fastest yearly
increase in the national index and considerably faster than any
month in the housing boom of the mid-2000s. (IHS Markit Economist
Troy
Walters)
- Monthly home price changes were positive in all 20 cities, ranging from 1.0% m/m in Boston and New York to 3.5% in Phoenix.
- The 10-city and 20-city composite indices both set yet another new record for year-over-year (y/y) price growth in June. The 10-city index was up 18.5% y/y and the 20-city index was up 19.1% y/y.
- All 20 cities covered in the report experienced home price appreciation in the double digits again in June. Increases ranged from 13.3% y/y in Chicago to 29.3% in Phoenix.
- The national index was up 18.6% y/y in June, the fastest pace on record.
- The Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA) House Price Index
(purchase-only) increased a record 4.9% in the second quarter from
the first quarter and 17.4% from a year earlier, also a record.
(IHS Markit Economist Patrick
Newport)
- Home prices grew in all 50 states from a year earlier. They rose fastest in Idaho (37.1%), Utah (28.3%), and Arizona (23.9%) and slowest in Alaska (8.2%), North Dakota (8.7%), and Louisiana (9.6%). Forty-seven states saw double-digit growth. Home prices grew by more than 20% in 13 states.
- Home prices were also up from last year in all of the 100 largest metropolitan areas, with Boise City, Idaho (prices up 41.1%) leading the pack and San Francisco-San-Mateo-Redwood City, California (home prices up 4.5%) in last place. (Are people moving from San Francisco to Boise?) Ninety-seven metro areas had double-digit growth; home prices soared by more than 20% in the top 20 metropolitan areas.
- The monthly purchase-only index, up by more than 1.0% for the 13th straight month, grew a record 18.8% from a year earlier in June, with the Mountain division witnessing the fastest growth (25.5%) and the West North Central states the slowest (15.8%).
- Housing prices over the long term are linked to construction costs, which have risen less than house prices. This indicates a correction is likely—particularly in places where geography and zoning restrictions make it easy to build.
- Low mortgage rates, tight inventories, and the "Great Reshuffling"—workers able to work from home moving to more favorable locations—are behind this unprecedented surge in house price growth.
- Inventory is inching up, home sales appear to have leveled, and homebuilders are ramping up housing starts in all 50 states. Our view is that these will moderate house price gains later this year.
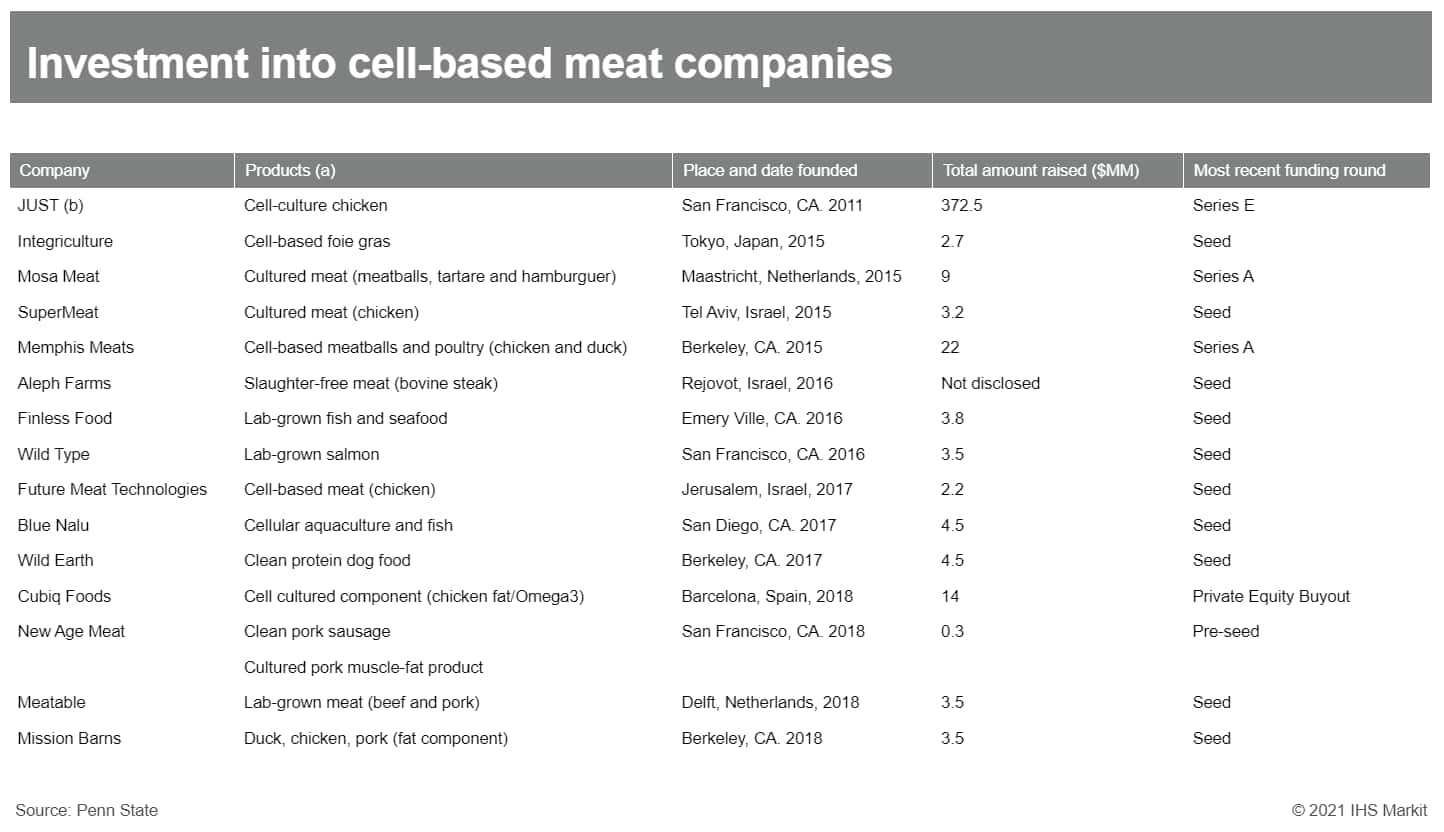
- Lab-grown meat could concentrate ownership and power in the
global food system by displacing livestock producers, according to
a new study. Researchers at Penn State University assessed the
potential trajectories for new tissue engineering technologies and
found these innovations could accelerate concentration of wealth
and diminish participation in agriculture, from ranchers to
fishermen. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Policy's Steve
Gillman)
- The study was published on 24 August and explains that large entities are best positioned to capitalize on lab-grown meat products because of their existing power while the general smaller size of farms means certain producers could be displaced more easily.
- "Many ranchers, for example, are self-employed, employ lower skilled workers, and manage small herds—79% of beef cattle farmers own fewer than 49 animals. Taken together, there is good reason to be skeptical," the researchers wrote.
- "New technologies such as artificial intelligence, smart agriculture, bioengineering, synthetic biology and 3D printers are also being used to decentralize and personalize food manufacturing," said Robert Chiles, one of the lead researchers behind the study. "They have the potential to democratize ownership and mobilize alternative economic organizations devoted to open-source licensing, member-owned cooperatives, social financing and platform business models."
- Chiles and his colleagues collected data from 33 cellular agriculture and alternative economic organization events held around the United States over two years, as well as interviewed key experts asking how they think the industry will develop and should develop.
- Chiles and his colleagues collected data from 33 cellular
agriculture and alternative economic organization events held
around the United States over two years, as well as interviewed key
experts asking how they think the industry will develop and should
develop.
- Arkema says it has signed an agreement to acquire Ashland's
performance adhesives business for an enterprise value of $1.65
billion—15 times (x) the business's estimated 2021 EBITDA after
taking into account the tax benefits linked to the structure of the
transaction. The deal is subject to approval from the antitrust
authorities in the countries concerned and is expected to be
completed in the next 4-6 months, according to Arkema. The relevant
legal information and consultation process involving
employee-representative bodies will be performed before closing,
the company says. (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory)
- The transaction will be financed fully in cash, and the level of Arkema's net debt including hybrid bonds on closing will remain tightly controlled at 1.9 x the company's estimated 2021 EBITDA, integrating the full-year impact of M&A operations already announced in 2021, it says. This is in line with Arkema's objective to maintain the ratio below 2.0, it adds.
- Ashland's performance adhesives business is a key player in pressure-sensitive adhesives in the US with significant growth potential in Europe and Asia, Arkema says. The business has about 330 employees and six production plants, mainly in North America. It operates in high-growth applications in decorative, protection, and signage films for automotive and buildings, it says. The business has estimated 2021 sales of about $360 million and EBITDA of approximately $95 million, according to Arkema.
- Ideanomics has agreed to buy Via Motors, in a deal that values Via at USD450 million, according to a joint statement by the companies. The deal is said to be worth up to USD630 million, based on the potential for Via shareholders to receive USD180 million in an earnout component. Ideanomics is described as an "electric vehicle adoption facilitator and financial services company". Under the agreement, Via shareholders are to receive 162 million shares of Ideanomics common stock, worth USD2.34 each as of 27 August 2021. The statement says that Via shareholders will hold about 25% of the combined company, excluding the potential earnout payment. In addition, Ideanomics is to advance USD50 million of financing to Via through a secured convertible note issued by Via to fund growth. Via shareholders' eligibility for the potential earnout of USD180 million is contingent upon pre-established (and undisclosed) vehicle delivery volumes through 2026; the earnout would be paid in Ideanomics stock. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Aurora has launched the next generation of its Fusion hardware kit to power autonomous trucks and robotaxis. It has more powerful sensors and a new powerhouse computer allowing Aurora's software platform Aurora Driver with advanced field of view, data accuracy, and efficiency; required to manage autonomous vehicle (AV) operations. This year, the hardware kit will debut on Aurora's Class 8 trucks in commercial pilots and on the company's test fleet of Toyota Siennas. Aurora said these pilots will lay the foundation for the launch of its trucking and ride-hailing businesses in 2023 and 2024 respectively. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
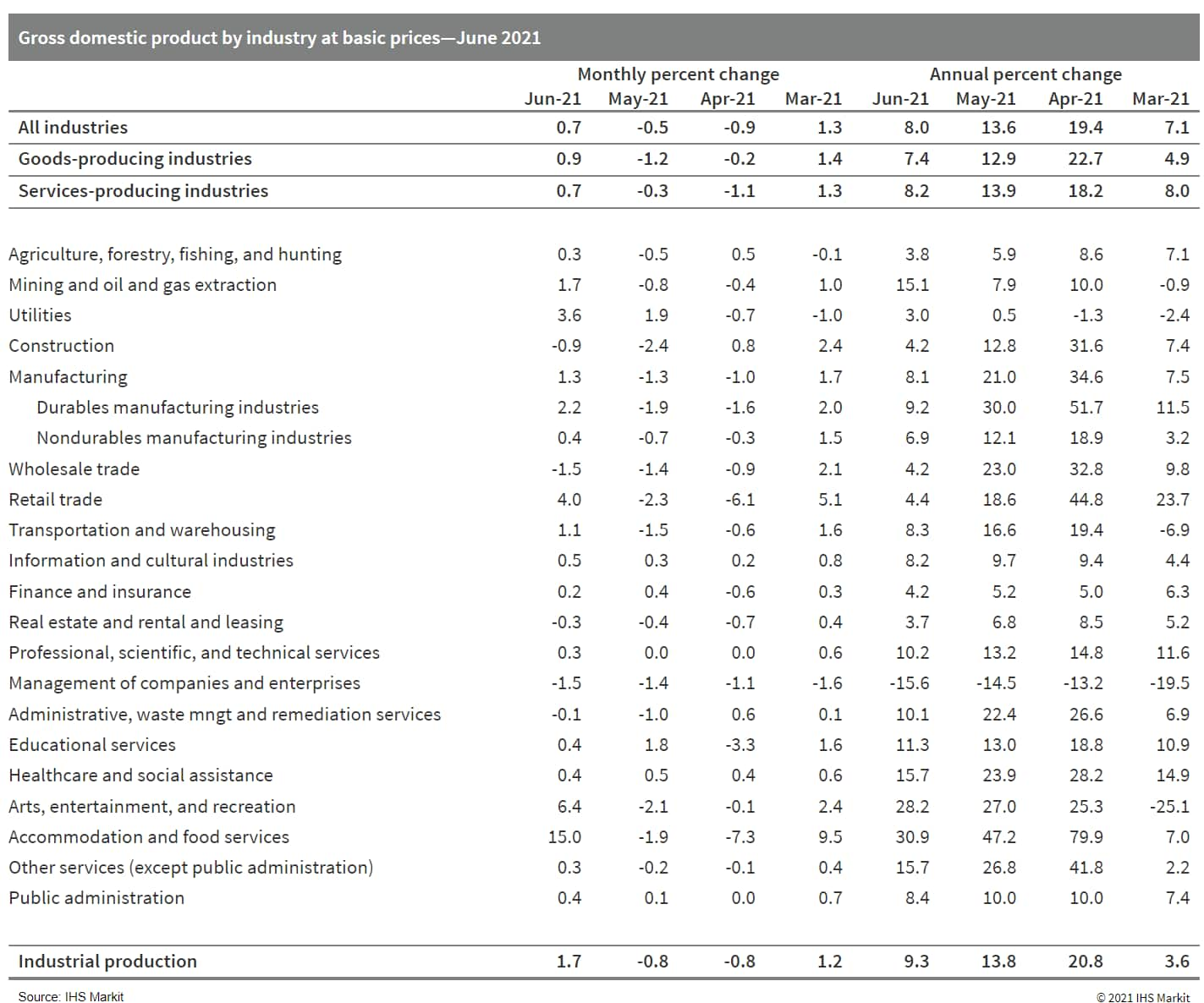
- Matching consensus, Canada's GDP by industry grew 0.7% month on
month (m/m) in June. However, revised April and May data showed
larger losses of 0.9% m/m and 0.5% m/m, respectively. (IHS Markit
Economist Evan Andrade)
- The reopening effect helped push goods-producing industries up 0.9% m/m and service-producing industries up 0.7% m/m. With construction being the only industry holding back growth within goods industries, industrial production advanced 1.7% m/m.
- It is not all smooth sailing moving forward, as Statistics
Canada's initial July estimate calls for a decline of 0.4% m/m.
Manufacturing, construction, and retail trade were the reported
industries responsible for the anticipated decline.
- The Central Bank of Colombia (Banco de la República: Banrep)
and the Ministry of Finance have announced an exchange of Special
Drawing Rights (SDRs) for government treasury notes for the full
amount of the International Monetary Fund (IMF)'s SDR allocation to
Colombia. (IHS Markit Economist Rafael
Amiel)
- The IMF has allocated SDRs worth USD51.5 billion to Latin America.
- Banrep received on 23 August USD 2.78 billion worth of SDRs and on 30 August, it exchanged an equivalent amount of money for government bonds (TES).
- In a press conference, the governor of the central bank, Leonardo Villar, and finance minister José Manuel Restrepo, among other authorities, emphasized that the transaction does not imply an increase in public debt or money supply.
- Banrep gave the government liquidity (USD 2.87 billion) and the government gave the central bank TES, which were purchased in the secondary market or were already in the portfolio of the treasury.
- Restrepo added that the government had recently swapped in the secondary market TES due in 2022 for longer term bonds due in 2029 and 2037, with the latter being the bonds given to Banrep.
- The emphasis given to the secondary market transactions is because by law, the central bank cannot buy directly debt issued by the government in order to avoid monetization of fiscal deficits.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- All major European equity indices closed lower; Italy/France -0.1%, Spain -0.2%, Germany -0.3%, and UK -0.4%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed sharply lower; Italy +7bps and Germany/France/Spain/UK +4bps.
- iTraxx-Europe closed flat/45bps and iTraxx-Xover -2bps/228bps.
- Brent crude closed -0.8%/$71.63 per barrel.
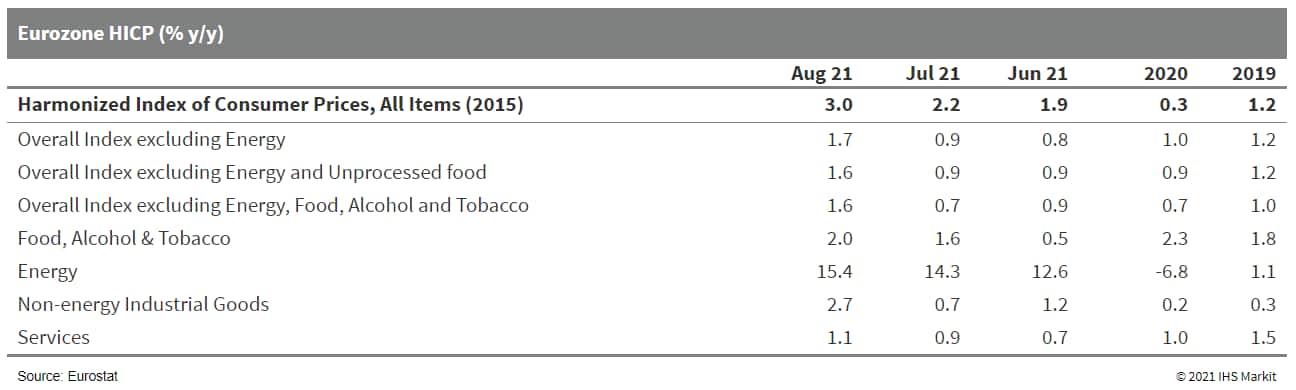
- Eurozone harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) inflation
jumped from 2.2% to 3.0% in August, according to Eurostat's 'flash'
estimate, well above the market consensus expectation (of 2.7%,
based on Reuters' survey). (IHS Markit Economist Ken
Wattret)
- This is the highest rate since November 2011 and, unusually, it is not solely a result of accelerating energy inflation.
- The year-on-year (y/y) rate of change in energy prices did rise again in August, by just over one percentage point to 15.4%, a new cycle high.
- However, the standout aspect of August's data is the jump in core inflation rates. The rate excluding food, energy, alcohol and tobacco prices shot up from 0.7% to 1.6% , slightly above the market consensus expectation (of 1.5%).
- The key driver was non-energy industrial goods (NEIG) inflation, which surged from 0.7% to 2.7%, one of the largest accelerations on record and surpassed only by prior increases during the COVID-19-virus pandemic.
- The NEIG inflation rate has now risen by over three percentage
points since December 2020 (-0.5%) and is over two points up on its
pre-pandemic rate in February 2020 (0.5%).
- Pace of improvement in German labor market conditions loses
some momentum at data edge in August. Seasonally adjusted German
unemployment declined by 53,000 month on month (m/m) in August,
having plunged by 90,000 in July and by a monthly average of 21,000
between July 2020 and June 2021. Thus, almost 60% of the initial,
pandemic-related unemployment surge in the second quarter of 2020
has been unwound now. (IHS Markit Economist Timo
Klein)
- The Labor Agency calculates a cumulative COVID-19 net boosting effect on unemployment of 261,000 by August 2021, down from 316,000 by July and an interim peak of 638,000 in June 2020. This represents a comparison with a hypothetical continuation of the pre-pandemic trend if the pandemic had never occurred.
- Germany's (national) unemployment rate declined from July's 5.6% (revised down from 5.7%) to 5.5% in August. This compares to a peak of 6.4% after the end of the first pandemic wave in mid-2020 and a pre-pandemic 40-year low of 5.0% in March 2020.
- Employment, data for which regularly lags by one month, increased by 100,000 to 44.950 million in July. In addition, the June level was revised up by 20,000, so that the gap with the pre-pandemic high in February 2020 has narrowed to 1.1% after 1.3% the month before.
- In year-on-year (y/y) terms, the subcategory of "regular" jobs - for which employers pay social security contributions, i.e. excluding the self-employed, mini-jobs, or other forms of precarious employment - has improved again from May's 1.2% to 1.4% in June (latest data available).
- Estonian GDP in seasonally and working-day-adjusted terms rose
by 4.3% in the second quarter compared with the previous quarter.
(IHS Markit Economist Vaiva
Seckute)
- Growth in value added was broad based; however, manufacturing, ICT and transportation, and storage contributed the most to annual growth in the second quarter.
- Accommodation and food services, one of the sectors most affected by the COVID-19-virus outbreak, rose by 44.5% y/y, but remained below pre-crisis levels. Value added in arts and entertainment continued contracting on an annual basis.
- Growth in investment, which until now has been mainly driven by investment in intellectual property, did not decelerate as expected and was 60% higher compared with the second quarter of 2020. According to Statistics Estonia, investment growth was broad based, but the most noticeable increases were recorded in transport equipment, machinery and building, and infrastructure.
- Private consumption rose by 12.5% y/y and was also broad based. However, expenditure on transport, clothing and footwear, leisure and entertainment, and hotels and restaurants increased the fastest as consumption of those services and goods rebounded from last year's lows.
- Israel's real GDP surged 3.6% quarter-on-quarter (q/q)
seasonally adjusted according to data released in August by
Israel's Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS). (IHS Markit Economist
Ana
Melica)
- This followed a contraction of 0.4% q/q in the first quarter during the third nationwide lockdown, upwardly revised from -1.5% q/q.
- The second-quarter rebound was driven by private consumption, which surged 8.0% q/q, and to a lesser extent by fixed investment (2.3% q/q) and government consumption (1.0% q/q).
- Exports and imports both grew around 4.0% q/q, although exports continued to exceed imports, leading to a slightly positive contribution to GDP from the net trade surplus.
- The Nation reported on 26 August that Kenya Commercial Bank
(KCB) has completed the acquisition of Banque Populaire du Rwanda
(BPR). Following a statement of intent signed on 26 November 2020
to acquire 62% of the Rwandan bank, KCB secured regulatory
approvals this month, making it the majority shareholder in BPR.
KCB Group Chairman Lawrence Njiru stated that acquisitions proved
"the easiest way to penetrate new markets". He added that KCB
intends to create one banking entity in Rwanda called BPR Bank by
merging the already established KCB Bank Rwanda and the newly
acquired BPR. (IHS Markit Banking Risk's Ronel Oberholzer)
- KCB is Kenya's largest bank by assets, accounting for 14% of total sector assets at the end of 2020, with a presence in seven African countries, including Tanzania and Rwanda. According to KCB's 2020 annual report, subsidiaries outside of KCB bank Kenya's contribution to the overall balance sheet has increased from 9% to 14% over the last two years.
- IHS Markit expects the current COVID-19 virus pandemic and the subsequent slow economic recovery across the region to catalyze similar mergers and acquisitions as larger banks use the opportunity to acquire weaker banks in a challenging economic environment of slow loan growth, depressed margins, and asset-quality deterioration.
Asia-Pacific
- All major APAC equity markets closed higher; South Korea +1.8%, Hong Kong +1.3%, India +1.2%, Japan +1.1%, Mainland China +0.5%, and Australia +0.4%.
- China's official composite output Purchasing Managers' Index®
(PMI®) - covering manufacturing and non-manufacturing sectors -
fell by 3.5 points from the previous month to 48.9 in August,
largely owing to the slowdown in manufacturing and contraction in
the services sector, while construction activity improved. (IHS
Markit Economist Yating
Xu)
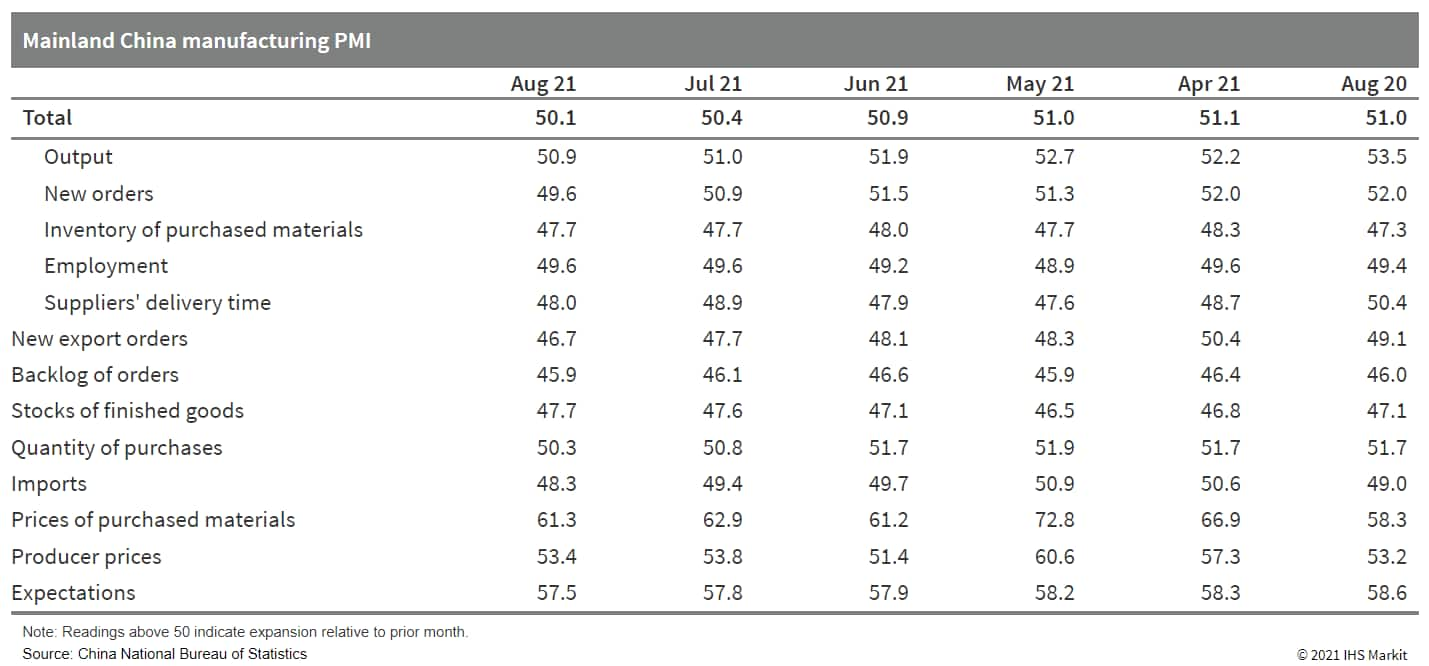
- The official manufacturing PMI declined by 0.3 point to 50.1 in August, the lowest reading since March 2020, and marking the fifth consecutive month of decline. The headline deterioration was broadly across sub-indices owing to the decline in demand and low supply growth.
- The new orders sub-index experienced its first contraction since March 2020, representing the lowest August reading since 2013. The new export orders sub-index declined to 46.7. The production sub-index remained above the neutral 50.0 mark, indicating expansion, but it was the lowest August reading since 2013.
- Owing to the faster demand moderation and relatively stable supply, the input and output price sub-indexes both declined, and the gap between the two narrowed for the third consecutive month.
- The decline in the inventory sub-index came to a halt as the purchased materials inventory remained unchanged compared with the previous month, and the finished goods inventory contracted at a slower pace. Softer demand further weakened the manufacturing outlook as expectations sub-index dropped to its lowest level since the beginning of the year.
- By firm scale, the deterioration in manufacturing PMI was entirely driven by large firms, although the PMI readings remained in expansion territory. The PMIs for medium-sized firms suggested faster growth whereas the PMIs for small firms declined at a slower pace.
- By sector, energy-intensive industries led the headline moderation, with the processing of petroleum and coal, chemical fibers, and plastic segments reporting consecutive declines in new orders and increasing cost pressure. On the other hand, the performance of the food and beverages, medicine, and special-purpose equipment segments improved from the previous month.
- China's non-manufacturing Business Activity Index fell by 5.8
points to 47.5 in August, the first contraction since March 2020.
Slowing services business activity drove the headline decline,
while the construction PMI accelerated to above 60.0.
COVID-19-induced regional lockdowns have notably restrained service
activities as the indexes for the road and air transportation,
hotel, catering, cultural and sports, leasing, and environment
protection segments all fell to contraction territory, while the
reading for the wholesale, postal, telecommunications, and
financial services sectors remained in expansion territory.
- China's Ningbo Meishan port is partially reopened (25 August), following the temporary closure upon a COVID-19 case (11 August). By 1 September, full operation will resume. A shipping industry source estimated the suspension might impact $172 billion worth of global trade. It will take about two weeks to clear the accumulated container ships. The port is expected to regain the usual full capacity by mid-September. In the past week, at least five cargo ships stopped over the port and left, showing signs of movements and creating a positive sentiment. Some China's ports such as Shanghai, Xiamen and Hong Kong have seen their congestion worsen as the spillover effects spread. Overall, the situation caused by Meishan suspension is less serious than Yantian's incident. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Hope Lee)
- Geely-backed ride-hailing platform Caocao Chuxing has reportedly secured investment worth billions of yuan in its latest funding round. Following this capital increase, Geely Technology Group will become the largest shareholder, with about a 77.3% stake in the ride-hailing platform. The newly added Zhejiang Geely Holding Company will hold 15.4% of the company's shares with a subscribed capital contribution of CNY66.7 million (USD10.3 million) making it the second largest shareholder, reports KR Asia. Caocao Chuxing claims to be one of the first companies in China to offer new energy vehicle (NEV) ride-hailing services. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
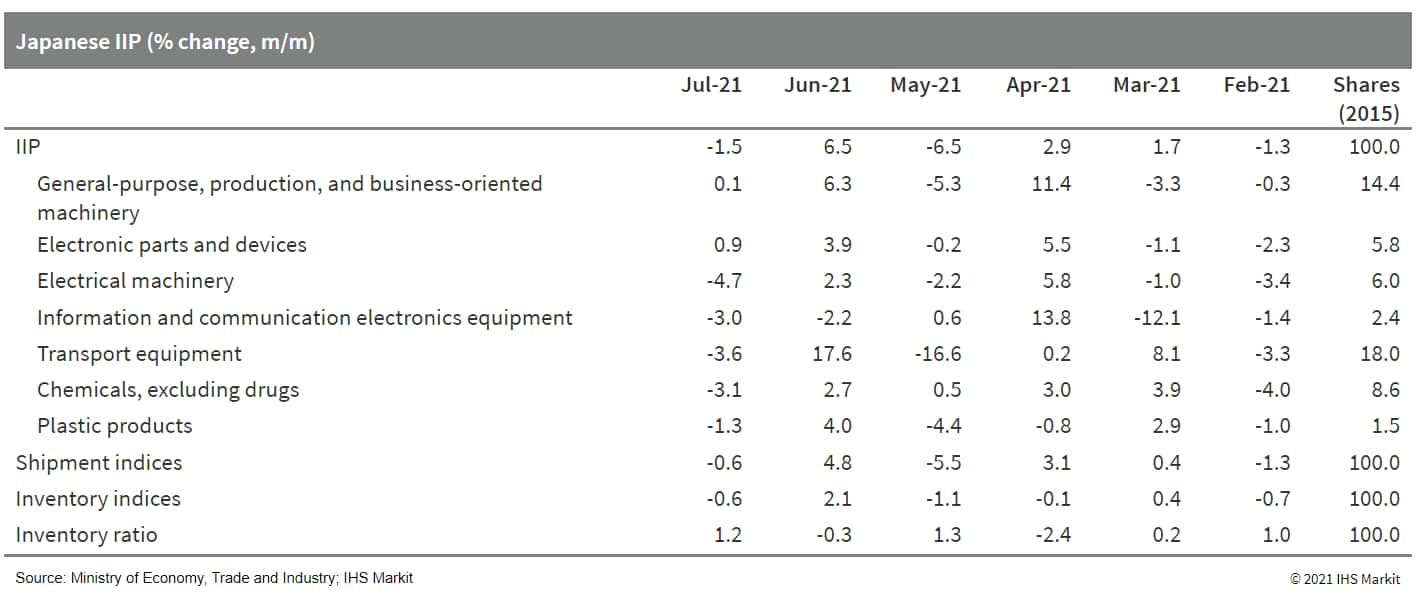
- Japan's index of industrial production (IIP) fell by 1.5% month
on month (m/m) in July following a 6.5% m/m rise in the previous
month. A softer decline in manufacturers' shipments compared with
production, at 0.6% m/m, led to a decline in inventories (0.6%
m/m), but the index of inventory ratio increased by 1.2% m/m. (IHS
Markit Economist Harumi
Taguchi)
- Major factors behind the weakness were production shortfalls after solid increases in the previous month for a broad range of industry groupings, particularly autos and electrical machinery.
- Shortages of semiconductors and other components because of the
infections caused by the Delta variant of the COVID-19 virus and
supply-chain disruption in Asia weighed on auto production;
production of some electrical machinery (such as air conditioners)
was also disrupted by the chip shortages. The weakness was
partially offset by increases in production of production machinery
(including semiconductor production machinery) and electronic parts
and devices.
- Japan's unemployment rate fell to 2.8% in July, thanks to an
increase of 420,000 in the number of employees (largely
self-employed) while the participation rate also rose. (IHS Markit
Economist Harumi
Taguchi)
- The major contributors to the year-on-year (y/y) increase in employees were wholesale and retail sales, research and professional services, and finance and insurance.
- That said, containment measures to curb COVID-19 Delta variant infections continued to weigh on employment conditions, even though the ratio of active job openings to active job applications improved slightly to 1.15 in July. The ratio of new opening to new applications fell to 1.98 for a second consecutive month of decline because of a continued drop in new openings, while the number of people who found employment declined by 6.4% m/m (or 5.3% y/y).
- The consumer confidence index fell by 0.8 point to 36.7 in August following two consecutive months of improvement. While all component indicators declined, the largest slide was for the index of employment, which slid 1.9 points to 33.2. The extension and expansion of states of emergency in response to a surge of Delta variant infections made consumers more concerned about employment.
- Japanese semiconductor manufacturer Rohm has warned that it is unlikely to clear its current order backlog during 2022, while Scania and light-vehicle manufacturers Stellantis and Volkswagen (VW) Group have announced that they will see production further disrupted at plants around the world. The latest reports highlight that the semiconductor shortage appears to be very far from over, with very little in the way of visibility. With the situation continuing to worsen during the third quarter of 2021, IHS Markit expects vehicle production to be affected by the issue in the fourth quarter of 2021 and that the production disruption will spill over into the first quarter of 2022. We currently anticipate that the second quarter of 2022 may be when we look for the stabilization of supply, with lost production recovery efforts starting only from the second half of 2022. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley and Ian Fletcher)
- South Korea-based materials supplier Posco has started production of high-purity nickel required for secondary batteries used in electric vehicles (EVs). According to a company press release, the company stated that a new production facility has been set up in Dongho-bay, Gwangyang, South Korea for this purpose. This new nickel production factory has capacity to produce 20,000 tons per year from 2023 onward to supply cathode materials necessary for the high-capacity batteries installed in EVs. This is to be uprated to produce 100,000 tons of nickel by 2030. The company's plan of producing high purity nickel is to manufacture 99.9% purity nickel materials made from 75% purity nickel mattes through its wet refining process. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- SK Innovation says that its affiliate SK Global Chemical is
changing its name to SK Geo Centric (SKGC), to focus on more
eco-friendly material activities including plastic waste recycling.
"We chose the new company name Geo Centric to transform the company
from Korea's first petrochemical company to the world's best urban
oil company based on recycling of waste plastic and to make an
eco-friendlier world," says CEO Na Kyung-soo. The new name will be
officially used from 1 September. (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory)
- SKGC plans to invest about 5.0 trillion South Korean won ($4.3 billion) by 2025 to establish the capacity to process 900,000 metric tons/year of waste plastic equivalent as part of its domestic plastic production, and produce eco-friendly materials.
- The renamed company intends to expand production capacity for eco-friendly materials from 500,000 metric tons/year to 1.9 million metric tons/year (MMt/y) in 2025. "In addition, it plans to reduce the number of plastics from petroleum by introducing bio-oil and pyrolysis oil as raw materials," the company says.
- SKGC has also announced a plan to recycle 2.5 MMt/y of plastic waste directly and indirectly, equivalent to about 20% of the plastic waste that flows into the world's oceans every year.
- The company projects that growth of the recycled plastics market will be 12% by 2030. It adds that a waste plastic recycling market worth W600 trillion will have developed by 2050. "In 2025, we will create W600 billion worth of EBITDA margin to completely transform into a green company," says Na.
- Indian ride-hailing giant Ola has started hiring banks to advise on its initial public offering (IPO) that could raise about USD1 billion, reports Bloomberg. According to the report, Ola is seeking a valuation of more than USD8 billion in the IPO and could lodge a filing as soon as October. Ola has reportedly selected Citigroup, Kotak Mahindra Bank, and Morgan Stanley to manage its IPO. Details of the IPO, including size and timeline, may change as discussions are ongoing. In a separate statement by TechCrunch, Ola Electric, the electric mobility arm of Ola, is in advanced talks to raise USD250-500 million in a new financing round. Falcon Edge Capital is expected to lead the round, which will value Ola Electric between USD2.75 billion and USD3.5 billion. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Sarawak Shell Berhad (SSB), a subsidiary of Royal Dutch Shell, has, along with its partners Petronas Carigali and Brunei Energy Exploration, sanctioned the Timi gas development project off Malaysia. The project will have a new unmanned wellhead platform (WHP) tied back to the existing Shell-operated F23 hub platform via 80km of new pipeline. The is unmanned platform is SSB's first wellhead platform in Malaysia powered by a solar and wind hybrid system. The platform will weigh around 60 percent lighter than a conventional Tender Assisted Drilling (TAD) wellhead platform. Timi is a sweet gas field discovered in 2018 under the SK318 PSC and is located approximately 200 kilometers off the coast of Sarawak, Malaysia. The project includes the drilling of two wells and is designed to produce up to 50,000 barrels of oil equivalent per day (boe/d). (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Monish Thakkar)
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-31-august-2021.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-31-august-2021.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+31+August+2021+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-31-august-2021.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 31 August 2021 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-31-august-2021.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+31+August+2021+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-31-august-2021.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}






