Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Aug 17, 2021
Daily Global Market Summary - 17 August 2021
Most APAC and all major US equity indices closed lower, while European markets were mixed. US and benchmark European government bonds closed mixed. CDX-NA closed wider across IG and high yield, while European iTraxx was close to unchanged on the day. The US dollar closed sharply higher, while gold, silver, copper, oil, and natural gas closed lower on the day.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our newly launched Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
- All major US equity indices closed lower; S&P 500 -0.7%, DJIA -0.8%, Nasdaq -0.9%, and Russell 2000 -1.2%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed -2bps/1.26% yield and 30yr bonds flat/1.93% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed +1bp/50bps and CDX-NAHY +7bps/293bps.
- DXY US dollar index closed +0.5%/93.13, which only 0.2% below this year's high close of 93.30 set on 30 March.
- Gold closed -0.1%/$1,788 per troy oz, silver -0.6%/$23.66 per troy oz, and copper -2.8%/$4.21 per pound.
- Crude oil closed -1.0%/$66.59 per barrel and natural gas closed -2.8%/$3.84 per mmbtu.
- US total retail trade and food services sales decreased 1.1% in
July. Core sales were revised higher over May and June and declined
about as expected in July. We raised our estimate for
second-quarter growth of real personal consumption expenditures
(PCE) 0.6 percentage point to 12.4% and our forecast for
third-quarter growth 0.3 percentage point to 2.2%. (IHS Markit
Economist James
Bohnaker and David
Deull)
- Sales at motor vehicle and parts dealers declined 3.9% in July, extending a three-month slide after sales peaked in April. Consumers satisfied much of their demand for autos with the support of early year stimulus, and now semiconductor chip shortages and high retail prices are hampering sales.
- Retail sales at food and beverage stores eased 0.7% in July as more people opted to dine out. Sales at food services and drinking places increased 1.7% to build on the recent expansion; sales rose to 9% above the pre-pandemic level in July. However, July may be the peak of the expansion as the number of seated diners on the OpenTable platform has backtracked in recent weeks amid mounting virus concerns.
- Nonstore retail sales fell 3.1% in July, which was not a big surprise given the expected payback from Amazon's Prime Day that took place in June this year, instead of its traditional timeframe of mid-July. Nonstore sales remain elevated relative to the pre-pandemic trend and may perk up further in the coming months as some shoppers avoid physical stores.
- Retail sales were destined to slow as consumers ease back into services consumption. But rising concerns about the Delta variant could weigh down goods and services spending simultaneously as consumers draw down excess savings amid dwindling stimulus and unemployment benefits.
- US total industrial production (IP) rose 0.9% in July,
reflecting increases in manufacturing (1.4%) and mining (1.2%) that
were partially offset by a decrease in utilities IP (down 2.1%).
Total industrial production remains 0.2% below its pre-pandemic
(February 2020) level. (IHS Markit Economists Ben
Herzon and Akshat Goel)
- Manufacturing industrial production rose 1.4% in July with most market groups posting increases. The gain in output of motor vehicles and parts (11.2%) accounted for about half the increase in factory output as several automakers trimmed or canceled their typical July shutdowns. Manufacturing output excluding motor vehicles and parts was up 0.7% in July.
- The strength in motor vehicle output in July does not mean that supply constraints due to a shortage of semiconductor chips are behind us. Indeed, motor vehicle assemblies, before seasonal adjustment, declined…just not as much as usual. That is why seasonally adjusted output was so strong. We would not be surprised to see a contraction of (seasonally adjusted) motor vehicle output in August, as the normal ramp-up from July shutdowns will be muted.
- While July was hot, the excessive heat was in the Pacific Northwest, where air conditioning is less prevalent. Temperatures in other parts of the country were normal. As a result, the output of utilities fell 2.1% in July from a level in June that was boosted by unusual heat then.
- Mining activity increased 1.2% in July.
- The headline US housing market index dropped 5 points to 75 in
August. A reading above 50 indicates that more builders view
conditions as good rather than poor. A 5-point drop should be
interpreted as a modest drop in confidence. (IHS Markit Economist
Patrick
Newport)
- The current sales conditions index decreased 5 points to 81; the index measuring sales prospects over the next six months was unchanged at 81; the traffic of prospective buyers' index dropped 5 points to 60.
- By region, the Northeast increased 3 points to 76 and the West edged up 2 points to 85; the South and Midwest lost 6 points each to 77 and 64, respectively.
- According to the National Association of Home Builders (NAHB), higher construction costs, supply shortages, and rising home prices pushed the headline index to a 13-month low in August. The NAHB views two of these obstacles as temporary and expects a return to normal conditions as the supply bottlenecks ease.
- The rise in construction costs is stunning. The price deflator for single-family new construction increased at a 15% annual rate in the second quarter, its highest reading in 41 years. Lumber prices have plummeted to pre-pandemic levels, while labor costs, as measured by the employment cost index for the construction industry, are growing about 3%—lower than the national average. But other costs have skyrocketed as evidenced by the producer price index for inputs to single-family residential construction, goods less foods, and energy, which increased 20% from a year earlier in July.
- Pfizer (US) and BioNTech (Germany) have announced that they have submitted data from their Phase I clinical trial of a booster dose of their COVID-19 vaccine Comirnaty to the US FDA, as they seek to obtain approval for booster doses in the general population. The companies declared that on the basis of the data already seen, the booster dose elicited antibody levels considerably higher than those elicited from the two-dose primary schedule. Reportedly, the third dose elicited significantly higher levels of neutralizing antibodies than the two-dose schedule in the case of the initial SARS-CoV-2 virus, as well as against the Beta and Delta variants. The partners are reportedly soon expecting to be able to submit Phase III results to the FDA, European Medicines Agency (EMA), and other regulators. In the US, they are planning to obtain approval of the booster on the basis of a supplemental Biologics License Application (BLA) for people aged 16 and above, pending the approval by the FDA of the BLA submitted for the two-dose regimen in May. Currently, a third booster dose is not approved generally in the US. However, following a recent extension to the vaccine's emergency use authorization (EUA), it was approved for a restricted at-risk group. Separately, it has been widely reported in US media that the administration of President Joe Biden is set to recommend boosters for all age groups, eight months after a second vaccination, in the face of growing infection rates. US newspaper USA Today reported that an official had offered this information on condition of anonymity. (IHS Markit Life Sciences' Brendan Melck)
- The US Department of Interior (DOI), citing concerns about GHG releases from oil and natural gas operations, decided to appeal a court decision that blocked President Joe Biden from pausing new leasing on federally managed lands and waters DOI said it is both "important and necessary" to appeal the preliminary injunction the US District Court for the Western District of Louisiana issued in mid-June against the pause Biden ordered. The pause was imposed to enable the agency to assess GHG contributions from all new oil and gas leases. The court's ruling had the effect of restarting the leasing process, which had been on hold since January. The department said it would resume the leasing process, adhering to court's injunction during the appeal, while it continues to review new oil and gas leases in light of what the agency claims are "the program's shortcomings," which include a failure to account for climate impacts. "Together, federal onshore and offshore oil and gas leasing programs are responsible for significant greenhouse gas emissions and growing climate and community impacts. Yet the current programs fail to adequately incorporate consideration of climate impacts into leasing decisions or reflect the social costs of greenhouse gas emissions including, for example, in royalty rates," the DOI wrote in a 16 August statement. According to DOI, the oil and gas industry currently has leases on more than 26 million acres of federal lands, and more than 12 million acres of public waters. (IHS Markit Net-Zero Business Daily's Amena Saiyid)
- In July, Canada's housing starts decreased 3.2% month over
month (m/m) to 272,176 units (annualized). (IHS Markit Economist Chul-Woo
Hong)
- The increase in urban single starts (up 7.1% m/m) was cancelled out by the decrease in multifamily starts (down 3.1% m/m). Rural starts plunged 24.2% m/m.
- Regionally, the monthly decline was concentrated in British Columbia, followed by Manitoba and Saskatchewan.
- Given the strong housing demand reflected in the existing home market, new home building activities will continue to support overall economic growth in the third quarter.
- Although total housing starts fell to the lowest reading since December 2020, the level remained solidly elevated in July compared with the historical long-term average.
- The Central Bank of México (Banco de Mexico: Banxico) has
published a report detailing the situation of credit to small and
medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The document reveals several
patterns in the segment that have been developing over the last few
years. One of the main highlights is that while this type of credit
has kept the stagnant pattern of the sector, it is one of the
segments with the most severe contractions in lending over the last
year, falling by 12% year on year (y/y) in March 2021. (IHS Markit
Banking Risk's
Alejandro Duran-Carrete)
- Banxico's report reinforces IHS Markit's assessment that SME credit stands at a weaker position than most other segments of credit in the Mexican banking sector. Given their higher risk compared with larger corporations, SME credit is subject to significantly higher interest rates than larger enterprises. Moreover, mandates for business closures in 2020 and a stricter fiscal stance over the last two years have decreased disposable income and increased difficulties affecting the companies' capacity to pay their debts.
- As a result, lending to the SME segment has been contracting since 2018, with the current stock of credit to the segment being 24% lower compared with 2018.
- Despite the deterioration, SME lending represents a very limited proportion of total credit, accounting for 9.6% of the sector's credit outstanding and less than 18% of credit to corporations. Even if the SME non-performing loan (NPL) ratio further increased from the 6.5% reported in June (as we are expecting it to), its effect on the overall sector will be limited. The corporate segment's NPL ratio stood at 2.2% over the same period, while the overall sector's ratio stood at 2.3%, largely unaffected by the deterioration in SME credit.
- The monthly index of Brazil's economic activity (MIEA)
published by the Central Bank of Brazil (Banco Central do Brasil:
BCR) expanded by 1.1% in June compared with May, month on month
(m/m); this follows a decline in May (down by 0.6% m/m). These
comparisons are based on seasonally adjusted data. If sustained,
monthly growth rates above 1% would yield growth above 12% in a
full year. (IHS Markit Economist Rafael
Amiel)
- Using unadjusted data, MIEA grew by 9.1% in June 2021, compared with June 2020, year on year (y/y); this exceptionally high growth rate reflects the low comparative base of a month where the economy was partially closed because of the COVID-19 virus pandemic.
- Growth in June was driven by services. The index of service sales increased by 1.7% m/m, while industrial production was flat and retail sales were down by 1.7% m/m. The Brazilian industry, especially manufacturing, is affected by the shortage of semiconductors. The decline in retail sales only reflect a correction after jumping by 2.5% m/m and 2.7% m/m in April and May, respectively.
- MIEA and GDP are both above pre-pandemic levels, although MIEA is still 5.4% from its all-time peak of December 2013.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- Major European equity indices closed mixed; UK +0.4%, Germany 0%, France -0.3%, Spain -0.7%, and Italy -0.9%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; UK -1bp, Germany/France flat, and Italy/Spain +1bp.
- iTraxx-Europe closed flat/46bps and iTraxx-Xover +2bps/236bps.
- Brent crude closed -0.7%/$69.03 per barrel.
- Mining group Glencore has announced that it has invested in UK battery-making startup Britishvolt. According to a statement, the size of the investment has not been disclosed. Glencore has also revealed that it has signed a strategic partnership for the long-term supply of "responsibly sourced" cobalt with Britishvolt, as well as supporting the battery-makers recycling and recycled content ambitions. On the announcement, David Brocas, Head Cobalt Trader at Glencore said, "We are delighted to be partnering with Britishvolt, a pioneer in UK electric vehicle battery technology and production… Our commitment to support our partners in meeting their requirements for essential battery ingredients is key to underpinning long-term supply agreements. As the mobility and energy transition accelerates, so does future demand for battery metals such as cobalt, copper and nickel. Glencore is already a leading producer and supplier of these metals, helping to underpin our ambition of achieving net zero total emissions by 2050." (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- The UK government has today launched its first national
hydrogen strategy, aimed at meeting its goal of achieving 5
gigawatts (GW) of low-carbon hydrogen production by 2030, including
funding of up to £240 million ($331 million) in total toward the
commercial development of new low-carbon hydrogen production
plants. (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory)
- The strategy includes plans for the development of both green and blue hydrogen, with the government saying the strategy could create a UK hydrogen economy worth £900 million by 2030, along with over 9,000 new jobs. This could increase potentially to a UK hydrogen economy worth £13.0 billion by 2050, it says. The strategy could unlock up to £4.0 billion of investment by 2030, it adds.
- The hydrogen strategy builds on a 10-point plan outlined by the UK prime minister Boris Johnson last year setting the foundation for how the government will work with industry to meet the target of building 5 GW of low-carbon hydrogen production capacity by the end of the decade. By 2030, hydrogen could play "an important role in decarbonizing polluting, energy-intensive industries like chemicals, oil refineries, power, and heavy transport like shipping, HGV lorries and trains, by helping these sectors move away from fossil fuels," according to a statement by UK business and energy secretary Kwasi Kwarteng.
- Government analysis suggests that 20-35% of the UK's energy consumption by 2050 could be hydrogen-based, which would be "critical to meet our targets of net-zero emissions by 2050 and cutting emissions by 78% by 2035," he says.
- Eurozone employment rose by 0.5% quarter on quarter (q/q) in
the second quarter on a seasonally adjusted basis, more than
reversing the prior quarter's 0.2% q/q contraction, and the third
increase in four quarters. (IHS Markit Economist Ken
Wattret)
- The q/q increase matched the market consensus expectation (according to Reuters' survey).
- Employment rose by 1.6% year on year (y/y) in the second quarter on a seasonally adjusted basis, following a contraction of 1.9% y/y in the prior quarter, with COVID-19-related base effects driving the huge swing.
- Employment levels offer a less distorted picture. Eurozone employment in the second quarter was 1.6% below its fourth-quarter-2019 level prior to the pandemic, roughly half the peak contraction of 3.1% back in the second quarter of 2020.
- Net eurozone employment has fallen by around two and a half million in the six quarters since the pandemic started. By way of comparison, over the same number of quarters following the global financial crisis (GFC) in 2008-09, employment in the eurozone fell by over three and a half million.
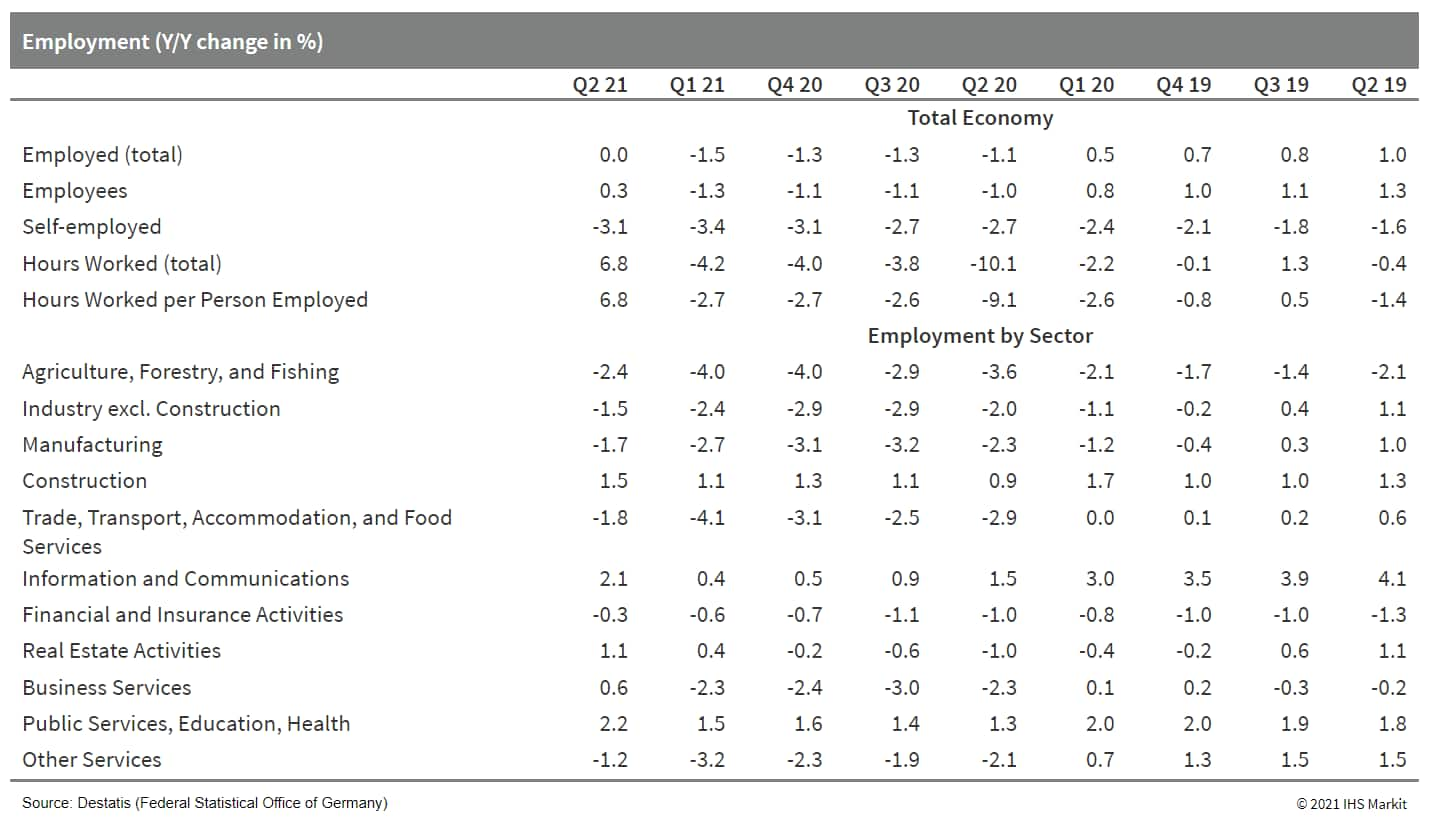
- Federal Statistical Office (FSO) data show that total German
employment increased by almost 0.3 million to 44.716 million in the
second quarter, exceeding the usual seasonal increase. Together
with the base effect of the pandemic outbreak a year ago, the
year-on-year (y/y) change moved up sharply from the previous
quarter's -1.5% y/y to 0.0% y/y. This compares with a 1.0% average
y/y gain during 2010-19. (IHS Markit Economist Timo
Klein)
- In seasonally adjusted terms, employment increased by 75,000 or 0.17% versus the fourth quarter of 2020. This compares with an average quarterly gain of 0.26% q/q during 2020-19. Separate monthly data show that the bulk of this rebound occurred only in June, which is linked to the late start to loosened COVID-19 restrictions only in mid-May.
- The breakdown by sector reveals that about one half employ more people now than they did a year ago. Apart from construction, this pertains solely to services-sector activities, led by the public services/education/health and information and communications sectors. In contrast, the secular employment decline in agriculture persists, and the manufacturing sector only managed to curtail its annual employment losses compared with the four preceding quarters.
- As expected, the economic rebound that developed during the
second quarter first led to a reduction in short-time work numbers,
therefore hours worked recovered more sharply than employment.
Thus, the -4.2% y/y in the first quarter was followed by a 6.8% y/y
increase in the second quarter as short-time work numbers dwindled
from February's interim peak of 3.3 million (having reached an
absolute high of 6.0 million in April 2020) to 2.2 million in May.
They most likely fell below 2 million in June (data not available
yet). Accordingly, hours worked per employee similarly jumped from
-2.7% y/y in the first quarter to equally 6.8% y/y in the second
quarter.
- MingYang Smart Energy has delivered all 10 of its MySE3.0-135 wind turbines for the Taranto project off Italy's Mediterranean Coast. The project is the first for a mainland Chinese turbine manufacturer supplying to the European region. The developer of the 30 MW project, Renexia, ordered the turbines at the beginning of 2021, switching supplier from the now defunct Senvion. The Taranto wind farm, also known as Beleolico, is located in the Apulia Region, off Taranto Harbor, in water depths of 3 to 18 meters. The project obtained its final investment decision in February 2019 and is scheduled for construction in the third quarter of 2021. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Melvin Leong)
- According to the latest monthly production value index (PVI)
published by Statistics Sweden (SCB), Swedish calendar-adjusted
private-sector output in June increased by 10.5% year on year
(y/y). Hardly budging from April's convincing gain of 11.0% y/y,
this brought the second-quarter growth rate to 10.7% y/y.
Seasonally adjusted output increased by 0.8% month on month (m/m).
(IHS Markit Economist Venla
Sipilä)
- A substantial push from the motor vehicle industry lifted industrial-sector production growth to 16.7% y/y in June. Conversely, mining and quarrying activity contracted y/y.
- The construction sector expanded by 2.0% y/y in June, thus returning to growth following an increase of around the same rate in February. Even against a weak base, this sector contracted by 1.7% y/y in the first half of 2021.
- Services supply on the whole increased by an accelerated rate of 20.1% y/y in June and by 15.5% y/y in January-June. Among private service fields, the information and communications industry contributed the most (2.0 percentage points) to private-sector production, growing by 17.6% y/y.
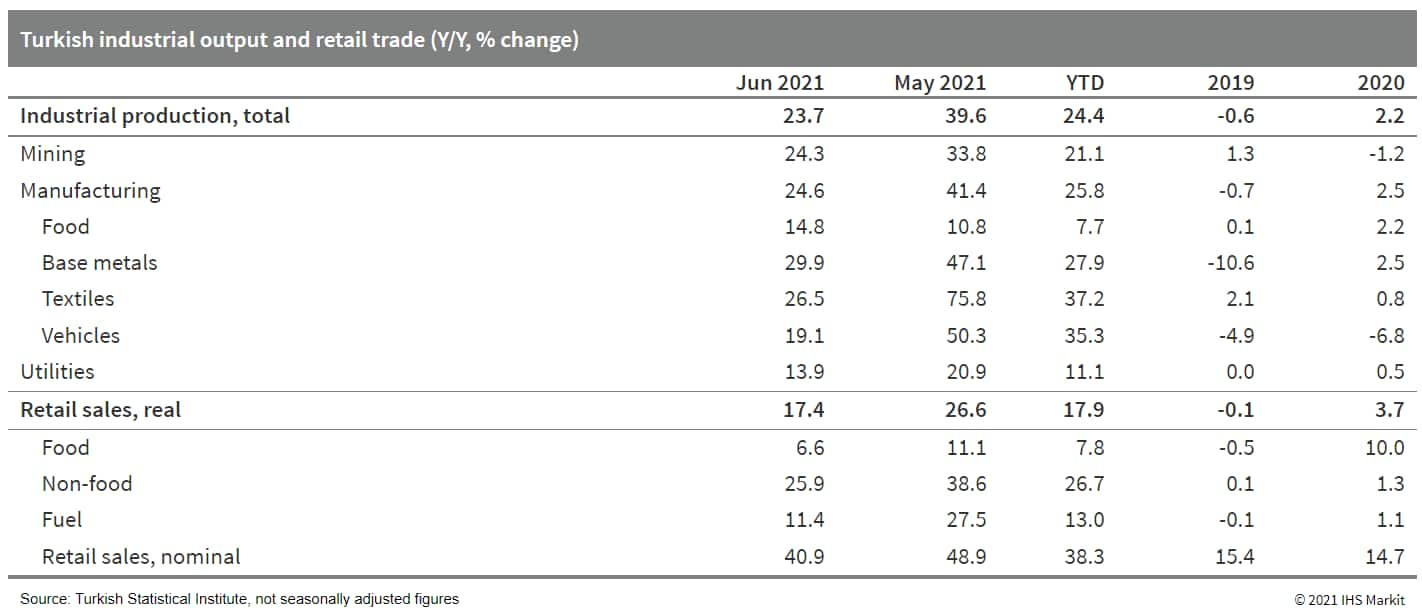
- Turkish retail trade soared by 14.4% month on month (m/m) in
seasonally and calendar adjusted data in June after having
contracted by 5.9% m/m and 5.5% m/m in the two months preceding.
Even with the overall faltering of activity in the first two months
of the second quarter, the total volume of retail trade activity
was up by 17.8% year on year (y/y) in the first half as a whole.
(IHS Markit Economist Andrew
Birch)
- Anti-pandemic lockdown measures did not take as heavy a toll on industrial activity in April-May and thus, the bounce-back in June was not as substantial. Nonetheless, total industrial output did increase by 2.3% m/m in seasonally and calendar adjusted data as the first half came to a close, accelerating over the prior two months.
- Easing of lockdown measures in June also positively affected
the country's labor markets, adding over 600,000 new jobs to the
economy. The resulting unemployment rate dropped to 10.6% at the
end of the first half, the lowest it has been since mid-2018.
- In the first half of 2021, Turkey posted a current-account
deficit of USD13.6 billion, down by over USD7.6 billion from the
same period of 2020. The previously reported - based on customs
data (see Turkey: 3 August 2021: Turkey's merchandise-trade deficit
narrows, tourism earnings increase in H1) - reduction of the
merchandise-trade deficit helped to dramatically narrow the overall
current-account gap. (IHS Markit Economist Andrew
Birch)
- A recovery of service exports also contributed to a sharp reduction of the current-account deficit in the first half. Turkish tourism officials reported a USD1.4-billion year-on-year (y/y) jump in revenues in the first half. Even with the sharp improvement from 2020, however, the services surplus remains well down from pre-pandemic levels.
- In the first half of 2021, Turkey attracted a total net inflow of USD1.9 billion in portfolio investment. The February-March interest rate rise helped to attract gross capital inflows. Continued net inflows in recent months also contributed to the rebuilding of foreign currency reserves and stabilized the lira.
- Although the country's foreign currency reserves have improved, they remain perilous. As of 6 August, the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey (TCMB) reported USD66.3 billion of foreign currency reserves, up from USD48.5 billion at the end of 2020.
- However, once commercial bank required holdings at the central bank (counted as reserves) and short-term TCMB currency swap debts are deducted from that headline figure, the Bank's net foreign currency reserve position is still deeply negative, at USD31.0 billion, equal to 1.6 months of imports. That figure has improved also from end-2020, however, when the deficit was USD40.9 billion, equal to 2.4 months of imports.
Asia-Pacific
- Most major APAC equity markets closed lower except for India +0.4%; Japan -0.4%, South Korea -0.9%, Australia -0.9%, Hong Kong -1.7%, and Mainland China -2.0%.
- China's governments at different levels continue to exercise "zero tolerance of Covid-19" and strict lockdowns once a single case emerges. One worker at Ningbo Meishan Port (MSICT) was tested positive, the whole operation at the port has been suspended ever since (11 August), causing delays and congestions. About 2,000 workers are affected. Meishan is one of Ningbo Zhoushan's 19 ports. Other ports are reportedly to continue operations as usual. Meishan handles over five million standard containers (TEU) in 2020, about 41 million tons, accounting for about 20% of the container cargo by weight of the Ningbo Zhoushan Port. Affected by the typhoon, the Meishan port was shut between 23-26 July, already causing congestions in Shanghai and Ningbo. Some sources are concerned about the spillover congestion effect as nearby ports may not be able to fully digest the goods destined for Meishan. Several major shipping companies have already skipped Ningbo as a temporary measure. Chinese media reported that Meishan is an important port for imported fruits and grains for Eastern China, particularly for the Jiaxing Fruit Market, a major local wholesale market, which relies on Ningbo and Shanghai ports. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Hope Lee)
- Beijing reportedly aims to have over 10,000 fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) on the road and to install 37 hydrogen filling stations by 2025, reports Gasgoo. Beijing Municipal Economic and Information Technology Commission is said to have mapped out the ambitious plan yesterday (16 August). The city has laid out specific plans to develop the local hydrogen energy industry and by 2025, aims to build a hydrogen energy industrial chain worth CNY100 billion (USD15.4 billion). The plans also include building three or four industrial research and development (R&D) innovation platforms and constructing an industrial cluster for the manufacture of hydrogen-related core parts and equipment. There have been similar reports in the past, but a final plan is yet to be announced. The move is in line with Chinese government's plan to have around 100,000 FCVs on its roads by 2025 and to build 1,000 hydrogen refueling stations by 2030 to support the commercialization of FCVs in both the commercial and passenger car sectors. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Isha Sharma)
- Autonomous vehicle (AV) startup Qcraft has closed its Series A plus funding round worth USD100 million, reports China Daily. The funding round was led by YF Capital and Genesis Capital, with participation from DragonBall Capital and existing investor IDG Capital. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Thailand's economic activities rose by 7.5% y/y during the
second quarter, rebounding from a 2.6% y/y contraction in the first
quarter. In seasonally adjusted terms, the economy grew by 0.4%
quarter on quarter (q/q). Real GDP averaged 2.0% in the first half
of 2021. (IHS Markit Economist Jola
Pasku)
- Favorable base effects and robust external demand encourage economic rebound
- On the expenditure front, all the components of GDP recorded positive growth during this period, although the strong y/y growth largely reflects a rebound from the sharp decline in 2020. Private consumption rose by 4.6% y/y in the second quarter of 2021, jumping from a 0.3% y/y contraction in the first quarter with support from government stimulus measures and relaxed containment measures since May. Spending on durable goods and services expanded by 15.1% and 8.1%, respectively.
- Fixed-investment spending picked up the pace to 8.1% y/y as higher private investment was able to offset a drop in public investment. Investment in machinery and equipment improved on the back of recovering exports.
- On the external front, exports of goods surged to 30.7% y/y, up from 3.2% y/y growth recorded in the first quarter. The y/y growth was recorded in most categories and was supported by the low base effect and strong external demand for electronics. Service exports, which include spending by non-residents such as tourists, continued to slide, shrinking 1.9% even with the base effect.
- LG Energy Solution has secured 100% rights to the battery-grade nickel and cobalt materials from Australian Mines Ltd. for six years, starting from the end of 2024, according to a company press release. "LG Energy Solution announced Monday it has entered into a binding long form offtake agreement with Australian Mines Ltd. for nickel and cobalt, which will be supplied in the form of mixed hydroxide precipitate (MPH) from the Sconi Project in North Queensland," it said, adding that the Sconi Project is a nickel and cobalt mine valued at USD1.5 billion. The project is capable of creating quality battery materials and boost battery supply chain. Under its agreement with Australian Mines, it will have access to 71,000 tons of nickel and 7,000 tons of cobalt for six years starting from the end of 2024. The six-year supply deal would translate into production of batteries that can power up to 1.3 million high-performance electric vehicles (EVs), with a driving range surpassing 500 km on a single charge. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-17-august-2021.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-17-august-2021.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+17+August+2021+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-17-august-2021.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 17 August 2021 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-17-august-2021.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+17+August+2021+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-17-august-2021.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}






