Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Nov 01, 2021
Daily Global Market Summary - 1 November 2021
All major US and European equity indices closed higher, while APAC was mixed. US government bonds closed mixed with the curve steeper on the day, and benchmark European bonds also close mixed. CDX-NA closed slightly wider on the day across IG and high yield and European iTraxx was flat on the day. Oil, gold, silver, and copper closed higher, while the US dollar and natural gas closed lower on the day. All eyes will be focused on the outcome of this week's FOMC meeting, as the market awaits additional details on the plans to unwind some quantitative easing programs.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
- All major US equity indices closed higher; Russell 2000 +2.7%, Nasdaq +0.6%, DJIA +0.3%, and S&P 500 +0.2%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed flat/1.56% yield and 30yr bonds +3bps/1.96% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed +1bp/53bps and CDX-NAHY +1bp/306bps.
- DXY US dollar index closed -0.3%/93.88.
- Gold closed +0.7%/$1,796 per troy oz, silver +0.5%/$24.07 per troy oz, and copper +0.6%/$4.39 per pound.
- Crude oil closed +0.6%/$84.05 per barrel and natural gas closed -4.1%/$5.31 per mmbtu.
- The seasonally adjusted IHS Markit U.S. Manufacturing
Purchasing Managers' Index™ (PMI™) posted 58.4 in October, down
from 60.7 in September and below the earlier released 'flash'
estimate of 59.2. The latest improvement in the health of the U.S.
manufacturing sector was sharp, despite being the weakest for ten
months. (IHS Markit Economist Chris
Williamson)
- Contributing to the overall upturn was a steep rise in new business at manufacturing firms in October. Companies continued to highlight strong demand conditions, but some noted that raw material shortages were hampering demand from clients as stocks of inputs had already been built or delivery times were too extensive.
- The pace of new order growth was the slowest for ten months. New export sales rose only fractionally as foreign demand was also weighed down by the knock-on effects of uncertain supply.
- Despite marked increases in costs, firms expanded their input buying sharply again in October. Although at the slowest pace for seven months, companies attributed higher purchasing activity to efforts to build stocks amid greater new order inflows. Meanwhile, stocks of purchases rose only modestly as firms utilized current input holdings to supplement production.
- Similarly, stocks of finished goods fell solidly as companies sought to meet new order deadlines. Backlogs of work rose markedly, and at one of the sharpest paces on record as firms grappled with pressure on capacity. The rate of growth eased to a four-month low, however, as employment increased at a solid pace.
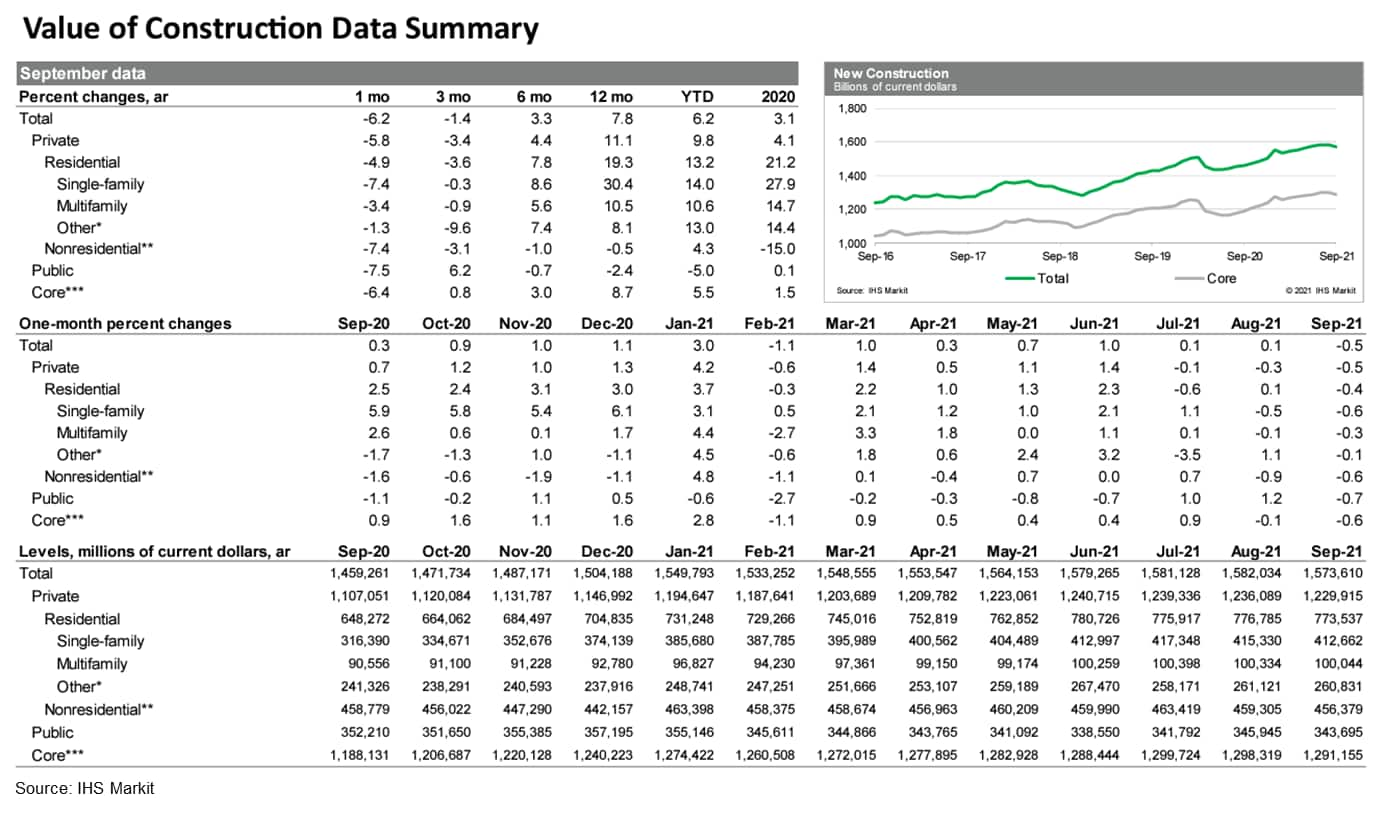
- Total US construction spending declined 0.5% in September.
Revisions to prior months were mixed. The September decline was not
expected. Core construction spending declined 0.6% in September;
prior months were revised higher. The data through September were
stronger than was implicit in the advance estimate of the National
Accounts, implying an upward revision to third-quarter GDP growth
of 0.2 percentage point to 2.2%. (IHS Markit Economists Ben
Herzon and Lawrence Nelson)
- Following a recent downturn in single-family housing permits, the value of new single-family construction put-in-place has peaked and has declined now for two months. Multifamily construction spending has flattened out.
- The residential sector, then, is no longer propelling total construction spending higher, as it was beginning in the summer months of last year.
- Private nonresidential construction spending declined 0.6% in September and remains substantially below a peak reached in January 2020, just prior to the onset of the pandemic.
- State-and-local construction spending declined 0.4% in
September following healthy increases over the prior two months.
Still, state-and-local construction spending remains in line with
what has been a broadly softening trend since early 2020.
- Lear Corporation has announced that it has entered into a "definitive agreement to acquire substantially all of Kongsberg Automotive's Interior Comfort Systems (ICS) business unit". According to a statement, Lear is to acquire the unit for EUR175 million (USD202 million), on a cash and debt-free basis. Lear is expected to fund this purchase through debt financing. The transaction is to include the ICS unit's operational leadership personnel and more than 3,800 employees globally at production, engineering, and sales facilities in Asia, Europe, and North America. The unit is expected to generate approximately USD300 million in revenue during 2021. The transaction is expected to be closed in the first quarter of 2022, subject to regulatory approvals and other customary closing conditions and adjustments. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- The top fix to get the current food industry back on track is
easing the labor burden, but there's no shortage of other issues
pushing up food prices, said FMI-The Food Industry Association's
Andrew Harig, vice president of tax, trade, sustainability and
policy development. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Policy's Joan
Murphy)
- Last year, 80% of FMI members increased wages, provided bonuses, boosted benefits to attract labor but food companies are competing with other sectors in a retracted labor pool to attract new employees, explained Harig during last week's Chamber of Commerce-sponsored webinar on food prices.
- Long-time experts are "scratching their heads" on what's causing the current shortage of workers, he said. Companies holding job fairs for full-time workers expect hundreds or thousands of prospective employees but only a handful of people show up.
- Another speaker at the October 28 webinar, Jayson Lusk, head of the Agricultural Economics Department at Purdue University, called the labor shortage perplexing, acknowledging that the cushion from the stimulus programs may allow them to be more choosy but the cushion has to run out at some point.
- While speakers suggested lingering child care issues, workers taking early retirement, and other complicating factors are continuing to keep people away from the workforce, they still questioned where are all the workers.
- Lusk said animal protein prices are surging in part because of the spikes in labor costs, particularly the double-digit increases for workers at animal slaughter plants.
- On October 29, AEUG Union Solar LLC, the Ohio Farm Bureau
Federation and the staff of the Ohio Power Siting Board filed with
the Board a joint stipulation and recommendation for approval of a
325-MW project. (IHS Markit PointLogic's Barry Cassell)
- The Union Solar Project would be located in Washington and York townships in Union County, Ohio. The Project will occupy just over 2,000 acres within approximately 3,355 acres of land near the intersection of Treaty Line Road and State Route 31. The project will consist of arrays of photovoltaic (PV) modules, ground-mounted on a tracking rack system.
- The facility will deliver power via a short generation interconnection (gen-tie) line from its substation to a single point of interconnection (POI) on an existing 345-kV transmission line owned by American Electric Power, through an adjacent switchyard. The gen-tie line is included in the application, but the switchyard and POI will be certificated through a separate application to the Board.
- Austin Energy, a municipal utility in Texas, on November 1
announced an update to its generation portfolio, including a
non-change for a coal-fired power plant. After multi-year
negotiations with the Lower Colorado River Authority (LCRA), Austin
Energy said it has been unable to reach a deal that would allow the
utility to affordably retire its share of the Fayette Power Project
(FPP) coal plant as originally envisioned. Austin Energy co-owns
FPP with LCRA and will continue to run its portion while still
meeting its carbon reduction goals. However, Austin Energy said it
will shut down its 44-year-old Decker 2 steam unit in March 2022,
in line with previously announced plans, and make its Nacogdoches
biomass-fired plant available to run year-round. Austin Energy
added that it continues to evaluate the timeframe and approach to
replace current fossil fuel resources with carbon-free energy while
maintaining grid reliability and customer affordability. Austin
Energy's Generation Resource Plan (called the "2030 Plan") outlined
a plan to retire the city's share of FPP (570 MW) by the end of
2022 to reduce carbon emissions. Austin Energy said it will
continue to maintain a diverse generation portfolio (currently 66%
carbon free) consisting of (IHS Markit PointLogic's Barry Cassell):
- Contracts with six solar farms (645 MW)
- Contracts with eight wind farms (1,425 MW)
- Four quick-start gas turbines at Decker (200 MW)
- The Sandhill Energy Center (570 MW), which consists of a combined -cycle natural gas unit and six quick-start natural gas peaking turbines
- The South Texas Nuclear Project (430 MW)
- Its share of the Fayette coal plant (570 MW)
- The Nacogdoches biomass plant (100 MW)
- Chile's Mining Minister Juan Carlos Jobet stated at the Lower Chamber's Mining Commission on 28 October that the announced lithium tender was aimed at recovering Chile's world leadership in lithium development. In mid-October, the government launched a tender to explore and produce 400,000 tons of lithium via Special Lithium Operating Contracts (Contrato Especial de Operación de Litio: CEOL). Chilean law classes lithium as a strategic mineral and does not allow concessions. Therefore, only the state, state-owned companies, or private companies in partnership with the Chilean Production Development Corporation (CORFO) can develop the mineral. CEOLs would allow companies to explore and exploit a set quota of lithium; a total of 400,000 tons would be divided into five quotas of 80,000 tons each. Companies would have a period of seven years for exploration, which can be extended for an additional two, and 20 for production, following a royalty payment upon allocation of the quota. (IHS Markit Country Risk's Carla Selman)
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- All major European equity indices closed higher; Spain +1.4%, Italy +1.2%, France +0.9%, Germany +0.8%, and UK +0.7%.
- Most 10yr European govt bonds closed lower except for France -1bp; Germany +1bp, Spain/UK +3bps, and Italy +4bps.
- iTraxx-Europe closed flat/51bps and iTraxx-Xover flat/262bps.
- Brent crude closed +1.2%/$84.71 per barrel.
- Member companies of the Chemical Industries Association (CIA) have stated their collective ambition to halve CO₂ emissions by 2034 and further reduce them 90% by 2050. The CIA, the UK's chemical industry association, made the announcement on Sunday, the opening day of the COP26 climate conference in Glasgow, UK. The CIA notes that a recent analysis by the UK government's Climate Change Committee shows that about 80% of the UK chemical industry's direct emission reductions will require sufficient access to hydrogen, carbon capture and storage, and clean electricity. Complementary actions such as building on the sector's energy-efficiency progress, enabling circularity, and embracing all other possible adaptation measures, will continue to play their significant parts in the collective effort needed in mitigating climate change, the CIA says. (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory)
- The G20 nations vowed to end public financing for overseas coal
power plants and showed ambition about limiting global warming to
1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, but critics said
the pledges lack new, clear objectives that can inject momentum
into the COP26 talks. (IHS Markit Net-Zero Business Daily's Max
Lin)
- The EU and 19 of the world's largest economies, responsible for over three-quarters of GHG emissions globally, concluded their latest summit in Rome 31 October as the UN climate talks began in Glasgow.
- Of the G20 nations, Australia, Canada, China, France, Germany, Japan, Italy, South Korea, Turkey, the UK, and the US had made similar pledges earlier.
- Many researchers believe that coal, as the most carbon-intensive fossil fuel, needs to be phased out in the power sector by 2040 to avert climate disaster.
- Since the Paris Agreement was sealed at 2015's COP21, the global pipeline of proposed coal-fired power plants has collapsed by 76%, or 1,175 GW, an analysis by think-tank E3G showed.
- The G20 refrained from committing to a phaseout date for domestic coal power generation. Among its members, China and India accounts for nearly two-thirds of the world's coal demand.
- The European Commission has opened four-week feedback periods
on four proposals to set up new approval criteria specifically for
microbial active substances under the EU agrochemical registration
Regulation (1107/2009). Comments are invited by November 23rd on
the criteria and on amendments to ensure consistency in other parts
of the legislation relating to data requirements for active
ingredients and products, and the uniform principles underlying
evaluation and authorization procedures. (IHS Markit Crop Science's
Jackie Bird)
- Regulation 1107/2009 was designed for chemical ais and there have long been calls for specific rules for biopesticides. The Commission outlined plans in early 2020 to set new criteria for pesticides based on micro-organisms. Calls for faster action in this area have intensified since the Commission set use-reduction targets for chemical pesticides in its Farm to Fork strategy. Many parties, including the European Parliament in a recent resolution, stress that the targets cannot be achieved unless farmers have access to alternatives. The biopesticide industry also recently criticized the continued absence of specific approval requirements and procedures.
- Amendments proposed for the Regulation reflect different requirements between microbial and chemical pesticides for: the assessment of residues in food and feed; the composition of ais; analysis methods for manufacturing batches; and assessments of risks to human health. Other new data requirements would cover assessments of the risk of transferring genes for antimicrobial resistance.
- Current criteria for approving ais as "low-risk" would be amended specifically for different types of microbial ais. Those based on bacteria and fungi would be subject to a stricter assessment of the risk of developing antimicrobial resistance, and would require information on the number of antimicrobial agents against which the micro-organism is demonstrated to be susceptible. Low-risk criteria are already set for baculoviruses, but the amendments would add criteria for other species of viruses, such as non-virulent variants of plant pathogens.
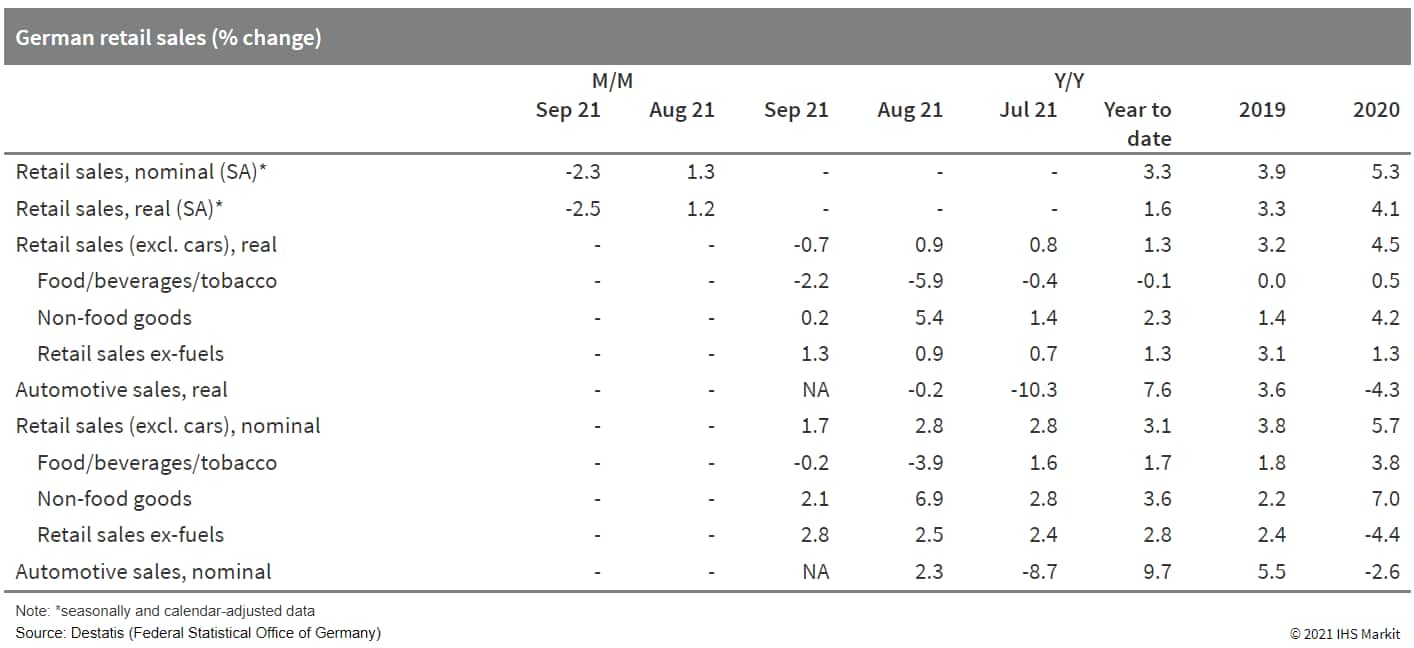
- According to German Federal Statistical Office (FSO) data, real
retail sales excluding cars declined by 2.5% month on month (m/m;
seasonally and calendar adjusted) in September. Combined with net
declines during July-August, the level of real retail sales is now
broadly where it was in September 2020 ahead of the second wave of
the pandemic that eventually triggered another lockdown in
December. (IHS Markit Economist Timo
Klein)
- On the bright side, price- and calendar-adjusted retail sales still were around 4% higher in September 2021 than in February 2020, the last pre-pandemic month.
- September's breakdown by goods category, based on
price-adjusted year-on-year (y/y) data (total -0.7% without
shopping-day adjustment; details see table below), reveals another
underperformance of food versus non-food sales, as in August. Food
sales were 2.2% below year-ago levels whereas non-food sales
increased by 0.2% y/y. Among the latter, 'internet and mail orders'
re-established their traditional lead at 18.8% y/y, followed by
pharmaceutical/cosmetic goods at 6.9% y/y. All other major
categories experienced a decline in sales, foremost clothing/shoes
at -14.2% y/y - this corrects for an unusual spike of 8.3% in
August. Sales at general department stores (-9.7%) and of
'furniture/household goods/DIY' (-9.0%) also did badly, while sales
at specialized shops lost only moderately (-1.9%).
- Valeo has announced that its sales during the third quarter of 2021 fell by 9.7% year on year (y/y) after being "particularly impacted by the shortage of electronic components." For the three months ending 30 September, sales retreated to EUR3,964 million from EUR4,389 million in the third quarter of 2020. While Aftermarket sales increased by 16.1% y/y to EUR520 million boosted by price increases and service rate, sales of Original Equipment components contracted by 15.1% y/y to EUR3,183 million. The decline in sales by Original Equipment components hit all Valeo's business areas. Comfort & Driving Assistance Systems retreated 9% y/y to EUR794 million as Visibility Systems declined 14.8% y/y to EUR1,126 million. In addition, Thermal Systems recorded a drop of 8.8% y/y to EUR928 million and Powertrain Systems slipped by 6.1% y/y to EUR1,080 million. Despite the decline in sales suffered during the third quarter, sales in the year to date (YTD) have grown by 13.2% y/y to EUR12,958 million, of which Original Equipment sales made up EUR10,695 million, a gain of 11.2% y/y. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- Vestas has completed the construction of all the blades
nacelles and most of the tower sections for Akita Offshore Wind
Corporation's Akita Noshiro offshore wind farm in Japan. Vestas
prepares to deliver the components in December of this year. The
wind farm includes Vestas installing all 33 V117-4.2MW wind
turbines. Kajima Corporation is the project's EPCI contractor. The
two wind farms are scheduled to be operational in 2022. (IHS Markit
Upstream Costs and Technology's Monish Thakkar)
- At the project sites, located offshore Akita and Noshiro ports, the Seajacks Zaratan vessel, which installed the final monopile foundation last month, will also install the 33 Vestas units, starting in April 2022. The site off Noshiro Port will comprise 20 turbines and the remaining 13 will be installed off Akita Port.
- According to Vestas, the construction team would have to apply a "plug and play" approach to the installation of the wind turbines. This will begin at the pre-assembly area of Akita Port where full assembly, including internals of the towers, preparation of the blades, and a final power test of the nacelles, will be performed. Due to the requirement of precision and efficiency at this stage of pre-assembly, Vestas said it will allow for five streamlined crane lifts during the offshore installation for each turbine. This will involve all turbine components, including the blades. Mobilization of the pre-assembly area at Akita Port will commence in November.
- The Akita Noshiro project is being developed by a consortium led by Marubeni which also includes Obayashi Corporation, Tohoku Sustainable & Renewable Energy, Cosmo Eco Power, The Kansai Electric Power, Chubu Electric Power, The Akita Bank, Ohmori, Sawakigumi Corporation, Kyowa Oil, Katokensetsu, Kanpu, and Sankyo.
- Czechia's seasonally adjusted GDP rose a preliminary 2.8% year
on year (y/y) and 1.4% quarter on quarter (q/q), well below our
latest forecast. According to the Czech Statistical Office,
third-quarter results were driven by domestic demand, particularly
household consumption and gross capital formation. (IHS Markit
Economist Sharon
Fisher)
- Net exports were reportedly the main factor pulling down Czechia's GDP growth, with July-August balance-of-payments data indicating that imports rose considerably faster than exports in the third quarter. In August, the goods balance shifted to a deficit for the first time since April 2020.
- Monthly trade data indicate that the slowdown in export growth has been driven mainly by the automotive sector. Meanwhile, strong domestic demand and rising energy prices have boosted imports.
- By sector, trade, transport, and hospitality had a positive impact on third-quarter GDP growth, and most other services also performed well. While construction was reportedly supportive of third-quarter growth, manufacturing recorded a q/q decline.
- On the labor front, total employment grew 0.2% q/q and 0.6% y/y during the third quarter, while the registered jobless rate (at 3.6%) was lower than during the same period of 2020.
Asia-Pacific
- Major APAC equity indices closed mixed; Japan +2.6%, India +1.4%, Australia +0.6%, South Korea +0.3%, Mainland China -0.1%, and Hong Kong -0.9%.
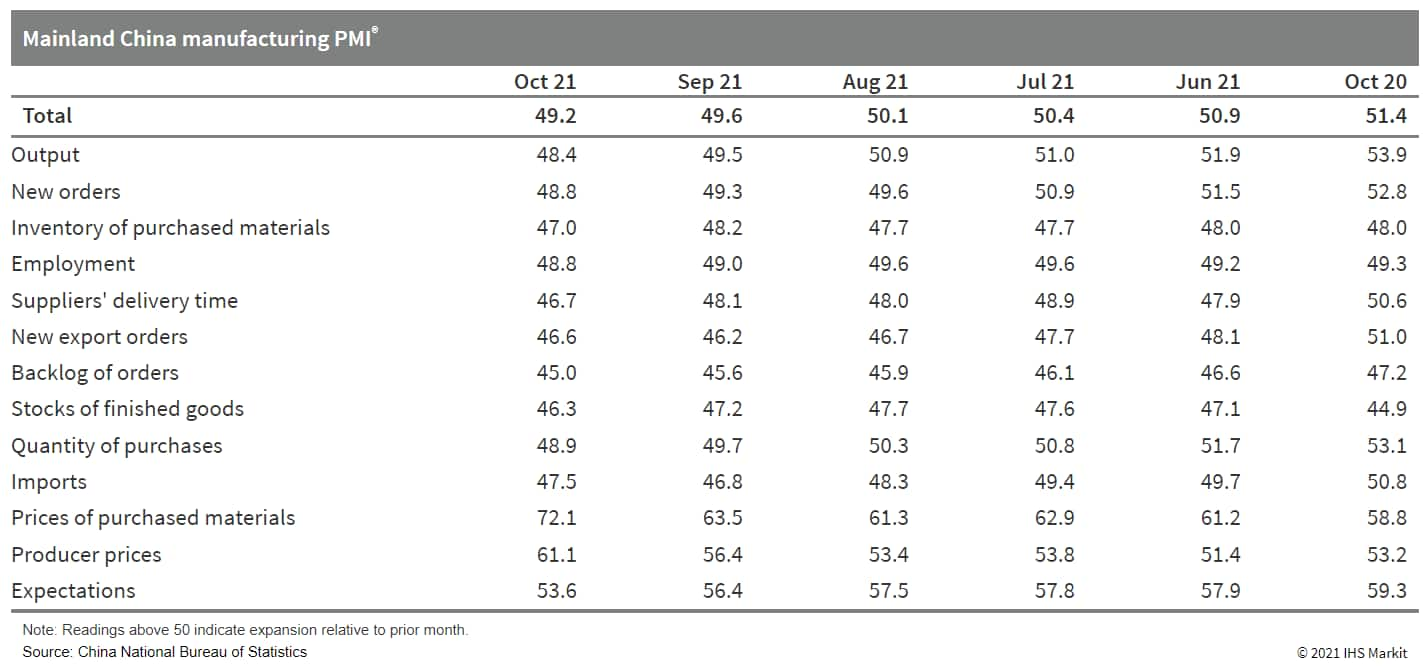
- Mainland China's official composite output purchasing managers'
index (PMI), covering both manufacturing and non-manufacturing
sectors, fell by 0.9 point from the previous month to 50.8 in
October, with an acceleration of contraction in manufacturing and
slower expansion in services and construction. (IHS Markit
Economist Yating
Xu)
- Mainland China's official manufacturing PMI declined by 0.4 point to 49.2, after a 0.5-point drop in the previous month as both demand and supply remained sluggish amid power crunch and raw material shortages. The breakdown of the survey showed that output and new orders both declined at a faster clip than in September. New export orders dropped for the sixth month in a row, while at a slower pace driven by the United States' strong consumption during Halloween and the upcoming Black Friday and Christmas.
- Manufacturers have been facing high inflationary pressure as prices of purchased materials surged at the fastest pace since June. Output prices also registered the fastest rate in recent years. Under the rising cost and weakening demand, inventory of purchased materials and finished goods both declined at faster paces compared with a month ago. Manufacturing growth outlook further weakened as expectations sub-index dropped to the lowest since March 2020.
- By scale of firms, the decline in manufacturing PMI was largely driven by faster contraction in medium-sized firms and continuous weakness in small firms, while the figure for large firms remained in expansion. Specifically, output sub-index for small firms declined to the lowest since the start of the pandemic while large firms' production improved. By sector, energy-intensive industries continued to lead the headline decline while high-tech and equipment manufacturing remained in expansion.
- Mainland China's non-manufacturing business activity index fell
by 0.9 point to 50.8, staying in expansion territory for two
consecutive months. Both service businesses and construction PMI
moderated owing to the escalated pandemic control in response to
the spread of Delta virus and the rising input prices.
Telecommunication maintained robust growth and holiday-related
catering and accommodation showed acceleration from September,
while transportation sub-index declined to low 50 and finance and
real estate remained in contraction territory.
- Qatar's public transport company Mowasalat (Karwa) has announced the beginning of test operation of the Level 4 fully autonomous electric minibuses in co-operation with Chinese commercial vehicle manufacturer Yutong, reports Qatar Tribune. According to the source, the Minister of Transport His Excellency (HE) Jassim Saif Ahmed Al Sulaiti witnessed the test operation and inspected the public transit bus plans. The vehicles will be tested during a months-long test operation to evaluate compatibility with Qatar's climate conditions. The Level 4 autonomous electric minibuses are equipped to carry eight passengers, travel at a speed of 40 km/hour, and come with a range of 100 km on a single charge. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tarun Thakur)
- Hyundai and Kia are partnering with Massachusetts-based electric vehicle (EV) battery startup Factorial Energy to test its novel solid-state battery technology and the battery's integration in Hyundai EVs, according to a press release by Factorial Energy. "Under the Joint Development Agreement, which includes a strategic investment, the companies will integrate Factorial technology at the cell, module, and system levels, perform vehicle-level integration, and co-develop specifications for manufacturing Factorial's batteries," the company said in its official statement. According to the battery startup, Hyundai's investment is its first major strategic investment from a major automotive group. It said that Hyundai's investment in Factorial would further deepen its existing research relationship with the South Korean automaker. Factorial is known to have developed a breakthrough solid-state technology that addresses key issues holding back the wide-scale consumer adoption of EVs, including driving range and safety. According to Factorial, its battery cell advances are based on FEST, which stands for 'Factorial Electrolyte System Technology.' It leverages a proprietary solid electrolyte material that enables safe and reliable cell performance with high-voltage and high-capacity electrodes and has been scaled in 40Ah cells that perform at room temperature. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- South Korean electric vehicle (EV) battery manufacturer SK Innovation will invest USD30 million to acquire an undisclosed stake in Colorado-based solid-state battery startup Solid Power. SK Innovation said that it has signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) and a joint development agreement (JDA) with Solid Power to develop all-solid-state batteries. Notably, leading global automakers such as Ford and BMW have also invested in Solid Power to get access to the startup's all-solid-state cell development and production technology. According to SK Innovation, under the JDA, the two companies are committed to set out to produce all-solid-state batteries employing the nickel, cobalt, and manganese (NCM) cathode materials used in lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries and high-content silicon anode materials. "These materials are expected to realize a target energy density of 930 Wh/L or higher. If achieved, this signifies approximately 33% higher performance than that of current lithium-ion batteries," it said, adding that this means that assuming a battery of the same size, an electric car is capable of running 700 km on a single charge and could travel up to 930 km with the new all-solid-state battery. Interestingly, the two companies also plan to validate that Solid Power's all-solid-state-cells can be manufactured on the existing lithium-ion battery manufacturing equipment, thereby removing the need for expensive and time-consuming re-tooling of the existing battery manufacturing plants. "Under the JDA, Solid Power will leverage the plants owned by SK On, SK Innovation's battery business subsidiary, to produce all-solid-state batteries," said the company. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- India, the world's third-largest GHG emitter, committed 1
November to higher decarbonization goals for the next decade and
achieving net-zero emissions by 2070. During the COP26 climate
summit in Glasgow, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi made some of
the boldest climate pledges from a major emitter in recent weeks.
The country will reduce its total projected CO2 emissions by 1
billion metric tons (mt) between now and 2030, Modi said. India
expects to reduce emissions intensity by 45% relative to 2005
levels by 2030, compared with a prior target of 33-35% set in 2015.
(IHS Markit Net-Zero Business Daily's Max Lin)
- India's CO2 emissions of about 2.2 million metric tons/annum rank behind only those of China (about 9.3 million mt/year) and the US (2.8 million mt/year).
- Moreover, Modi said India's non-fossil fuel energy capacity will reach 500 GW by 2030, compared with an earlier goal of 450 GW. The country also raised the target share for renewables in its power mix from 40% to 50% in the same time span.
- When large hydropower projects were taken into account, official figures showed India's installed renewable energy capacity reached 141 GW as of 16 June, or 37% of the country's total.
- India's new ambition for 2070 failed to impress many, as
scientists believe the world needs to reach net-zero emissions by
2050 to avert a climate disaster. But it could also be a positive
surprise to some as New Delhi had publicly rejected the calls to
set a carbon neutrality target.

S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-1-november-2021.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-1-november-2021.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+1+November+2021+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-1-november-2021.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 1 November 2021 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-1-november-2021.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+1+November+2021+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fssl.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-1-november-2021.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




